J Korean Soc Radiol.
2014 Sep;71(3):146-149. 10.3348/jksr.2014.71.3.146.
Multiple Xanthomas in a Patient with Familial Hypercholesterolemia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ikyang@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 1736481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.3.146
Abstract
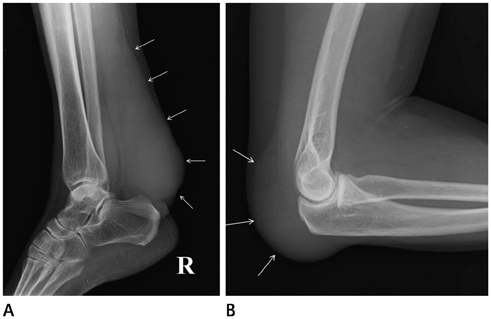
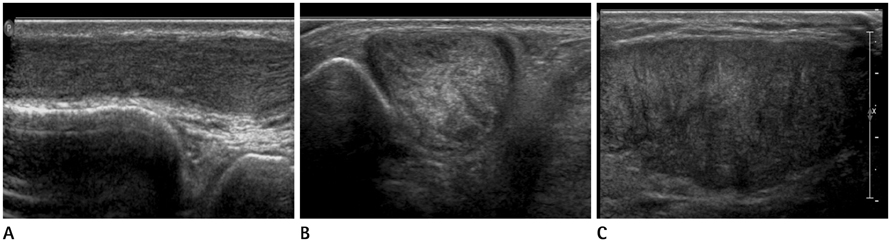
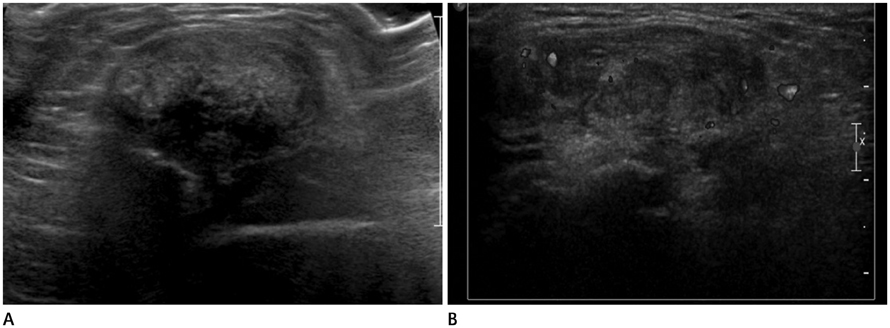
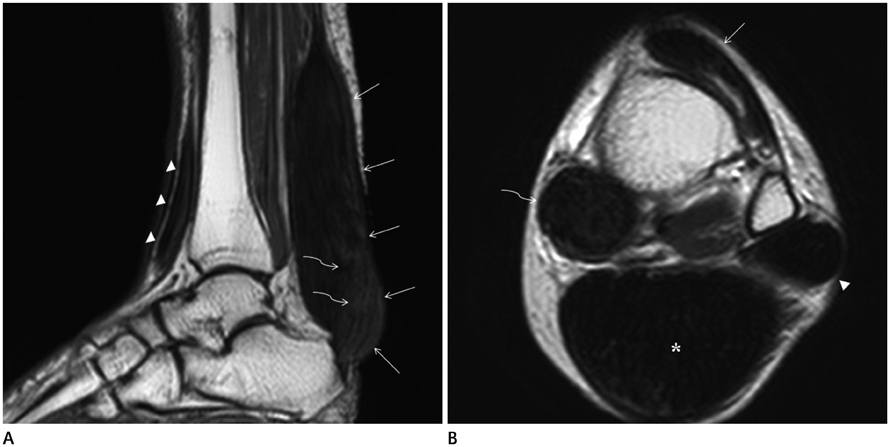
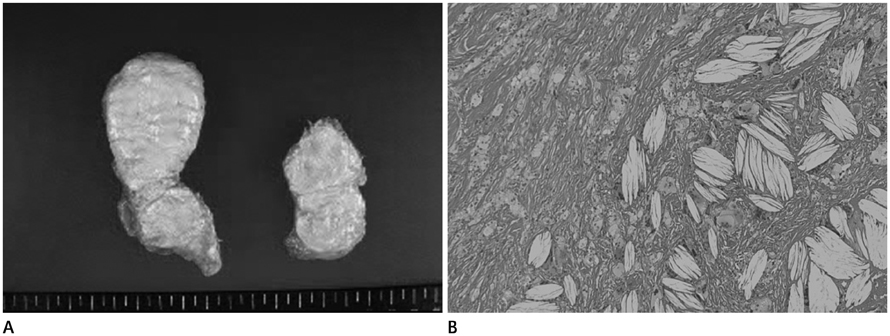
- Tendinous xanthomas are often associated with type 2 hyperlipoproteinemia, in which low-density lipoprotein derived from the circulation accumulates in the tendons. Therefore, the demonstration of tendinous xanthomas is helpful in diagnosing familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). In this study, we describe the sonographic and MR features of the case of bilateral multiple xanthomas of the ankles and elbows in a 52-year-old female patient with FH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kwiterovich PO Jr. Pediatric implications of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Screening and dietary treatment. Arteriosclerosis. 1989; 9:1 Suppl. I111–I120.2. Thompson GR, Seed M, Niththyananthan S, McCarthy S, Thorogood M. Genotypic and phenotypic variation in familial hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosis. 1989; 9:1 Suppl. I75–I80.3. Fahey JJ, Stark HH, Donovan WF, Drennan DB. Xanthoma of the achilles tendon. Seven cases with familial hyperbetalipoproteinemia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973; 55:1197–1121.4. Doyle JR. Tendon xanthoma: a physical manifestation of hyperlipidemia. J Hand Surg Am. 1988; 13:238–241.5. Glueck CJ, Levy RI, Frederickson DS. Acute tendinitis and arthritis. A presenting symptom of familial type II hyperlipoproteinemia. JAMA. 1968; 206:2895–2897.6. Gilbert PD, Kain TM, March HC. Hypercholesteremic xanthomata of the tendons. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1957; 77:109–114.7. Bude RO, Adler RS, Bassett DR. Diagnosis of Achilles tendon xanthoma in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: MR vs sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 162:913–917.8. Descamps OS, Leysen X, Van Leuven F, Heller FR. The use of Achilles tendon ultrasonography for the diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2001; 157:514–518.9. Kelman CG, Disler DG, Kremer JM, Jennings TA. Xanthomatous infiltration of ankle tendons. Skeletal Radiol. 1997; 26:256–259.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intertriginous Xanthoma in an Infant with Familial Hypercholesterolemia
- Multiple Huge Tendinous Xanthomas with Normal Lipid Profiles in All Extremities
- A Case of Familial Hypercholesterolemia with Diabetes Mellitus
- Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer of the Descending Thoracic Aorta in a Patient with Heterozygote Familial Hypercholesterolemia
- Two Cases of Familial Multiple Lipomatosis