Korean J Radiol.
2008 Feb;9(1):80-83. 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.1.80.
Metastatic Thymoma of the Breast
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and the Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. claudel@skku.edu
- 2Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1734279
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2008.9.1.80
Abstract
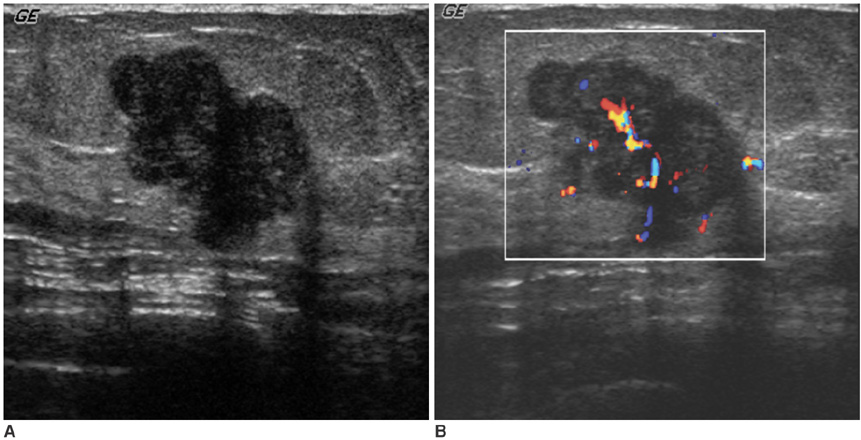
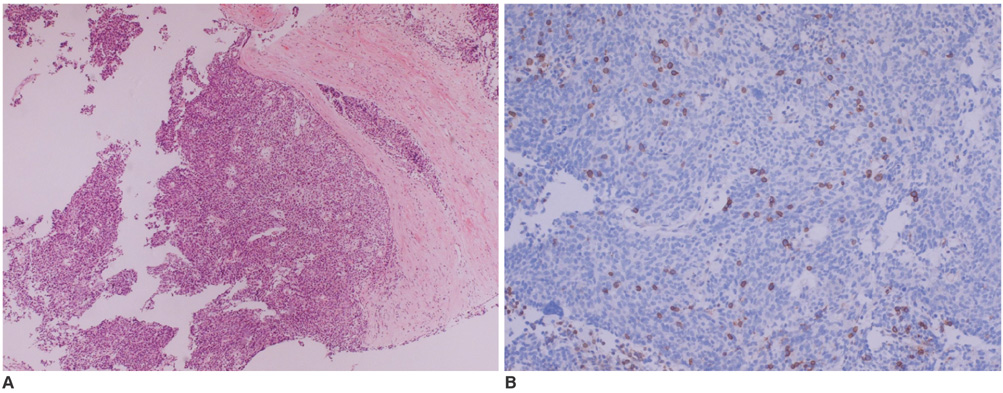
- Breast metastasis from nonmammary malignant neoplasms is uncommon, and it accounts for approximately 2% of all breast tumors. Distant metastasis of thymoma is very rare, and especially to extrathorcic areas. We report a female who had a metastatic thymoma in her breast 20 years after undergoing resection for a non-invasive thymoma. She presented with a palpable mass in her left breast. Mammography and ultrasonogram showed a lobular mass at the anterior glandular portion. Histological examination after surgical excision revealed a metastatic thymoma.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yeh CN, Lin CH, Chen MF. Clinical and ultrasonographic characteristics of breast metastases from extramammary malignancies. Am Surg. 2004. 70:287–290.2. Toombs BD, Kalisher L. Metastatic disease to the breast: clinical, pathologic, and radiographic features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977. 129:673–676.3. Amichetti M, Perani B, Boi S. Metastases to the breast from extramammary malignancies. Oncology. 1990. 47:257–260.4. Nomori H, Watanabe K, Ohtsuka T, Naruke T, Suemasu K, Orikasa H, et al. Pulmonary metastasis 12 years after resection of thymoma with microscopic capsule invasion. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2004. 34:630–633.5. Youk JH, Kim EK, Kim MJ, Oh KK, Park YN. Metastatic breast lesion from thymic carcinoma. J Ultrasound Med. 2006. 25:1339–1342.6. Jochimsen PR, Brown RC. Metastatic melanoma in the breast masquerading as fibroadenoma. JAMA. 1976. 236:2779–2780.7. Cardenosa G. Breast Imaging. 2004. Lippincott: Williams & Wilkins.8. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK, Harris CC, editors. Pathology & Genetics Tumours of the Lung, Pleuera, Thymus and Heart. 2004. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer.9. Han J, Lee KS, Yi CA, Kim TS, Shim YM, Kim J, et al. Thymic epithelial tumors classified according to a newly established WHO scheme: CT and MR findings. Korean J Radiol. 2003. 4:46–53.10. Sadohara J, Fujimoto K, Müller NL, Kato S, Takamori S, Ohkuma K, et al. Thymic epithelial tumors: comparison of CT and MR imaging findings of low-risk thymomas, high-risk thymomas, and thymic carcinomas. Eur J Radiol. 2006. 60:70–79.11. Lewis JE, Wick MR, Scheithauer BW, Bernatz PE, Taylor WF. Thymoma. A clinicopathologic review. Cancer. 1987. 60:2727–2743.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fine needle aspiration cytology of malignant thymoma: two cases of invasive thymoma and thymic carcinoma
- A Large Solitary Liver Metastasis of Thymoma
- Congenital Urinary Tract Anomalies Associated with Urinary Tract Infection in Infants and Children
- Cytologic Features of Metastatic Thymoma in the Liver: A Cese Report
- Myasthenia Gravis Appearing After Thymectomy: a Case Report and Review of the Literature