J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Oct;19(5):729-734. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.729.
Endovascular Management of Iliofemoral Deep Venous Thrombosis due to Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome in Patients with Protein C and/or S Deficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, Gangneung, Korea. ypcho@gnah.co.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, Gangneung, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul Asan Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1733517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.729
Abstract
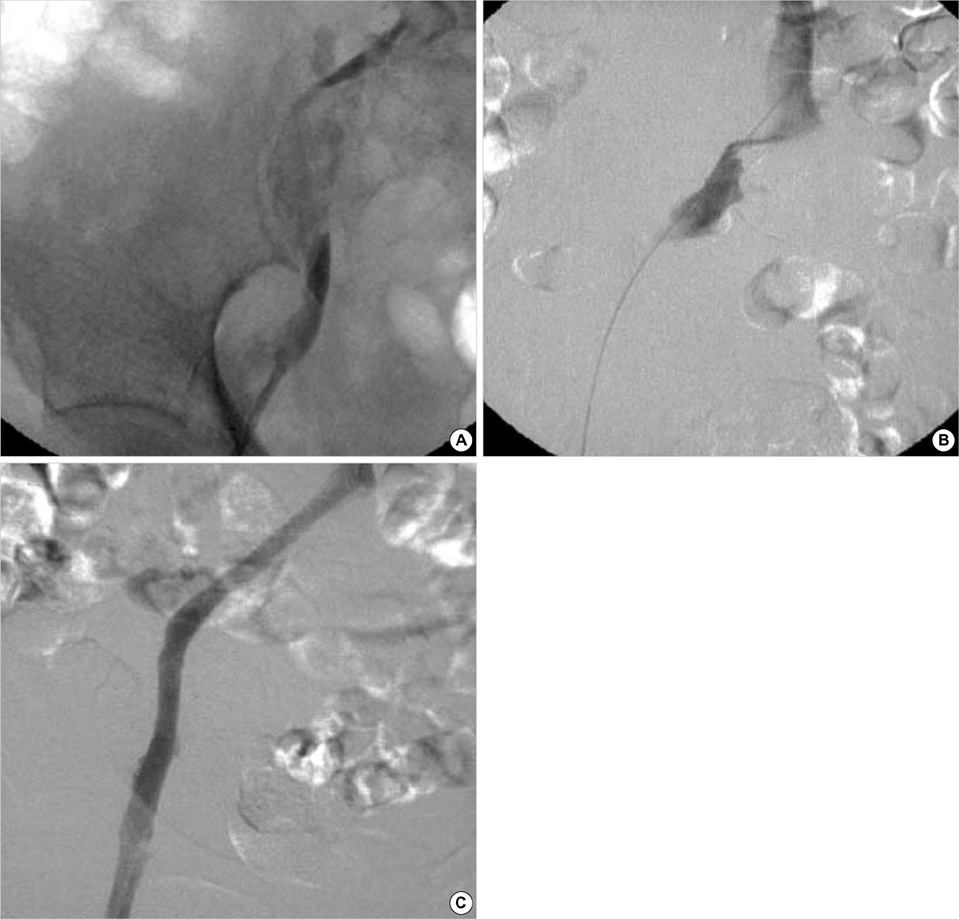
- The purpose of this study was to evaluate the early outcome of endovascular management in patients with iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis (DVT) due to iliac vein compression syndrome (IVCS) and protein C and/or S deficiency. Between September 2000 and January 2003, catheter-directed thrombolysis was performed in 11 patients with a diagnosis of acute iliofemoral DVT: 7 with protein C and/or S deficiency and 4 without protein C and/or S deficiency. After thrombolysis, the diagnosis of IVCS was confirmed in 6 patients: 4 with protein C and/or S deficiency and 2 without protein C and/or S deficiency. Further intervention consisted of angioplasty and stent placement was performed. Four patients with IVCS and protein C and/or S deficiency were included in this study. The immediate technical and clinical success rates were 100% in all 4 patients. There were no complications or clinically detectable pulmonary emboli. This initial experience suggests that endovascular management of iliofemoral DVT due to IVCS in patients with protein C and/or S deficiency is safe and effective.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Female
Humans
Iliac Vein
Male
Middle Aged
Plasminogen Activators/administration & dosage
Protein C Deficiency/*complications
Protein S Deficiency/*complications
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
*Thrombolytic Therapy
Treatment Outcome
Urinary Plasminogen Activator/administration & dosage
Venous Thrombosis/*complications/*drug therapy
Figure
Reference
-
1. Strandness DE Jr, Langlois Y, Cramer M, Randlett A, Thiele BL. Long-term sequelae of acute venous thrombosis. JAMA. 1983. 250:1289–1292.
Article2. O'Donnell TF Jr, Browse NL, Burnand KG, Thomas ML. The socioeconomic effects of an iliofemoral venous thrombosis. J Surg Res. 1977. 22:483–488.3. Prandoni P, Lensing AW, Cogo A, Cuppini S, Villalta S, Carta M, Cattelan AM, Polistena P, Bernardi E, Prins MH. The long-term clinical course of acute deep venous thrombosis. Ann Intern Med. 1996. 125:1–7.
Article4. Mewissen MW, Seabrook GR, Meissner MH, Cynamon J, Labropoulos N, Haughton SH. Catheter-directed thrombolysis for lower extremity deep venous thrombosis: report of a National Multicenter Registry. Radiology. 1999. 211:39–49.
Article5. Bjarnason H, Kruse JR, Asinger DA, Nazarian GK, Dietz CA Jr, Caldwell MD, Key NS, Hirsch AT, Hunter DW. Iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis: safety and efficacy outcome during 5 years of catheter-directed thrombolytic therapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1997. 8:405–418.
Article6. Semba CP, Dake MD. Iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis: aggressive therapy with catheter-directed thrombolysis. Radiology. 1994. 191:487–494.
Article7. Sherry S. Thrombolytic therapy for noncoronary diseases. Ann Emerg Med. 1991. 20:396–404.
Article8. Semba CP, Dake MD. Catheter-directed thrombolysis for iliofemoral venous thrombosis. Semin Vasc Surg. 1996. 9:26–33.9. Cho YP, Jang HJ, Lee DH, Ahn J, Han MS, Kim JS, Kim YH, Lee SG. Deep venous thrombosis associated with protein C and/or S deficiency: management with catheter-directed thrombolysis. Br J Radiol. 2003. 76:380–384.
Article10. May R, Thurner J. The cause of the predominantly sinistral occurrence of thrombosis of the pelvic veins. Angiology. 1957. 8:419–427.
Article11. Cho YP, Lee DH, Jang HJ, Kim JS, Han MS, Lee SG. Peripheral arterial insufficiency associated with protein C deficiency. Br J Radiol. 2002. 75:843–846.
Article12. Eldrup-Jorgensen J, Flanigan DP, Brace L, Sawchuk AP, Mulder SG, Anderson CP, Schuler JJ, Meyer JR, Durham JR, Schwarcz TH. Hypercoagulable states and lower limb ischemia in young adults. J Vasc Surg. 1989. 9:334–341.
Article13. Lane DA, Mannucci PM, Bauer KA, Bertina RM, Bochkov NP, Boulyjenkov V, Chandy M, Dahlback B, Ginter EK, Miletich JP, Rosendaal FR, Seligsohn U. Inherited thrombophilia: Part 1. Thromb Haemost. 1996. 76:651–662.
Article14. Lane DA, Mannucci PM, Bauer KA, Bertina RM, Bochkov NP, Boulyjenkov V, Chandy M, Dahlback B, Ginter EK, Miletich JP, Rosendaal FR, Seligsohn U. Inherited thrombophilia: Part 2. Thromb Haemost. 1996. 76:824–834.
Article15. De Stefano V, Finazzi G, Mannucci PM. Inherited thrombophilia: pathogenesis, clinical syndromes, and management. Blood. 1996. 87:3531–3544.16. Allaart CF, Poort SR, Rosendaal FR, Reitsma PH, Bertina RM, Briet E. Increased risk of venous thrombosis in carriers of hereditary protein C deficiency defect. Lancet. 1993. 341:134–138.
Article17. De Stefano V, Leone G, Mastrangelo S, Tripodi A, Rodeghiero F, Castaman G, Barbui T, Finazzi G, Bizzi B, Mannucci PM. Clinical manifestations and management of inherited thrombophilia: retrospective analysis and follow-up after diagnosis of 238 patients with congenital deficiency of antithrombin III, protein C, protein S. Thromb Haemost. 1994. 72:352–358.
Article18. Sakata T, Kario K, Katayama Y, Matsuyama T, Kato H, Miyata T. Studies on congenital protein C deficiency in Japanese: prevalence, genetic analysis, and relevance to the onset of arterial occlusive diseases. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000. 26:11–16.
Article19. Sakata T, Kario K, Katayama Y, Matsuyama T, Kato H, Miyata T. Analysis of 45 episodes of arterial occlusive disease in Japanese patients with congenital protein C deficiency. Thromb Res. 1999. 94:69–78.
Article20. Akesson H, Brudin L, Dahlstrom JA, Eklof B, Ohlin P, Plate G. Venous function assessed during a five year period after acute iliofemoral venous thrombosis treated with anticoagulation. Eur J Vasc Surg. 1990. 4:43–48.21. Cockett FB, Thomas ML. The iliac compression syndrome. Br J Surg. 1965. 52:816–821.
Article22. Okrent D, Messersmith R, Buckman J. Transcatheter fibrinolytic therapy and angioplasty for left iliofemoral venous thrombosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1991. 2:195–197.
Article23. Berger A, Jaffe JW, York TN. Iliac compression syndrome treated with stent placement. J Vasc Surg. 1995. 21:510–514.
Article24. Cockett FB, Lea Thomas M, Negus D. Iliac vein compression: its relation to iliofemoral thrombosis and the post-thrombotic syndrome. Br Med J. 1967. 2:14–19.25. O'Sullivan GJ, Semba CP, Bittner CA, Kee ST, Razavi MK, Sze DY, Dake MD. Endovascular management of iliac vein compression (May-Thurner) syndrome. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000. 11:823–836.26. Patel NH, Stookey KR, Ketcham DB, Cragg AH. Endovascular management of acute extensive iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis caused by May-Thurner syndrome. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000. 11:1297–1302.
Article27. Clouse LH, Comp PC. The regulation of hemostasis: the protein C system. N Engl J Med. 1986. 314:1298–1304.
Article28. Gruber A, Pál A, Kiss RG, Sas G, Griffin JH. Generation of activated protein C during thrombolysis. Lancet. 1993. 342:1275–1276.
Article29. Plate G, Ohlin P, Eklof B. Pulmonary embolism in acute ilio-femoral venous thrombosis. Br J Surg. 1985. 72:912–915.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Left Iliac Vein Thrombosis with May-Thurner Syndrome
- May-Thurner Syndrome Treated with Endovascular Wall Stent
- Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome in Spinal Cord Injury
- Interventional Radiologic Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis in Lower Extremity
- May-Thurner Syndrome with Coexisting Arteriovenous Fistula Treated Using an Endovascular Procedure