J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Oct;19(5):693-697. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.693.
The Prognostic Effect of VEGF Expression in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix Treated with Radiation Therapy Alone
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Medical College, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. kangjino@khmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1733511
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.693
Abstract
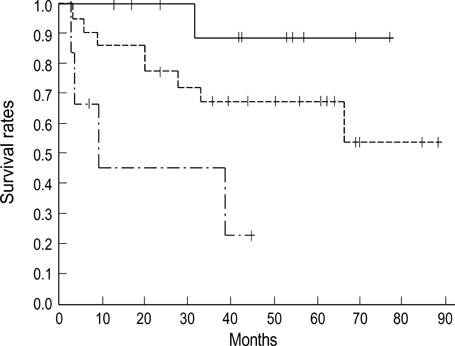
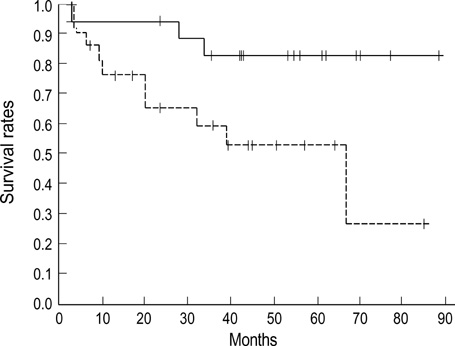
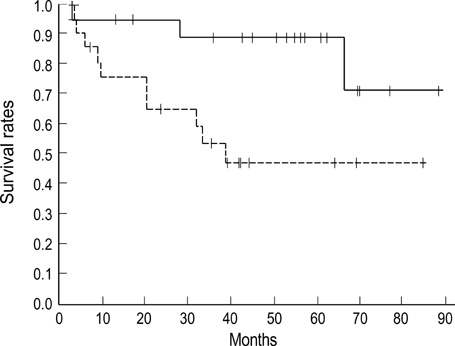
- We investigated the relationship between vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and clinical outcome in squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix treated with radiotherapy alone. The immunohistochemical study was performed for fortytwo paraffin embedded specimens with anti-VEGF mouse monoclonal antibody. Staining was defined as positive for VEGF when more than 10% of the tumor cells were stained from 500 cells counted. Positive VEGF expression was observed in twenty-one among forty-two patients. VEGF expression according to stage (p=0.101), lymph node status (p=0.621), parametrial invasion (p=0.268), and age (p=0.5) revealed no significant difference. But the VEGF expression was significantly higher in tumors larger than 4 cm (p=0.031). Five year survival rates according to VEGF expression status were 89% for VEGF negative group and 47% for VEGF positive group (p=0.02). FIGO stage (p=0.007), tumor size (p=0.025) and the duration of external beam radiation therapy (p=0.006) were also significant prognostic factors for overall survival. We suggest that VEGF expression may be a prognotic factor of the cervix cancer patients treated with radiation therapy alone.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Huh SJ, Kim BK, Lim DH, Shin SS, Lee JE, Kang MK, Ahn YC. Treatment results of radical radiotherapy in uterine cervix cancer. J Korean Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 2002. 20:237–245.2. Hockel M, Schlenger K, Mitze M, Schaffer U, Vaupel P. Hypoxia and Radiation Response in Human Tumors. Semin Radiat Oncol. 1996. 6:3–9.3. Shweiki D, Neeman M, Itin A, Keshet E. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by hypoxia and by glucose deficiency in multicell spheroids: implications for tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995. 92:768–772.
Article4. Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991. 324:1–8.5. Gupta VK, Jaskowiak NT, Beckett MA, Mauceri HJ, Grunstein J, Johnson RS, Calvin DA, Nodzenski E, Pejovic M, Kufe DW, Posner MC, Weichselbaum RR. Vascular endothelial growth factor enhances endothelial cell survival and tumor radioresistance. Cancer J. 2002. 8:47–54.
Article6. Gorski DH, Beckett MA, Jaskowiak NT, Calvin DP, Mauceri HJ, Salloum RM, Seetharam S, Koons A, Hari DM, Kufe DW, Weichselbaum RR. Blockage of the vascular endothelial growth factor stress response increases the antitumor effects of ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:3374–3378.7. Lee IJ, Park KR, Lee KK, Song JS, Lee KG, Lee JY, Cha DS, Choi HI, Kim DH, Deung YK. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor in Stage IB carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. 54:768–779.
Article8. Loncaster JA, Cooper RA, Logue JP, Davidson SE, Hunter RD, West CM. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression is a prognostic factor for radiotherapy outcome in advanced carcinoma of the cervix. Br J Cancer. 2000. 83:620–625.
Article9. Cheng WF, Chen CA, Lee CN, Chen TM, Hsieh FJ, Hsieh CY. Vascular endothelial growth factor in cervical carcinoma. Obstet Gynecol. 1999. 93(5 Pt 1):761–765.
Article10. Bachtiary B, Selzer E, Knocke TH, Potter R, Obermair A. Serum VEGF levels in patients undergoing primary radiotherapy for cervical cancer: impact on progression-free survival. Cancer Lett. 2002. 179:197–203.
Article11. Santin AD, Hermonat PL, Ravaggi A, Pecorelli S, Cannon MJ, Parham GP. Secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Obstet Gynecol. 1999. 94:78–82.
Article12. Tokumo K, Kodama J, Seki N, Nakanishi Y, Miyagi Y, Kamimura S, Yoshinouchi M, Okuda H, Kudo T. Different angiogenic pathways in human cervical cancers. Gynecol Oncol. 1998. 68:38–44.
Article13. Lee JS, Kim HS, Jung JJ, Lee MC, Park CS. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in adenocarcinomas of the uterine cervix and its relation to angiogenesis and p53 and c-erbB-2 protein expression. Gynecol Oncol. 2002. 85:469–475.
Article14. Ferrara N. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in pathological angiogenesis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995. 36:127–137.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Implications of VEGF and p53 Expression in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix Treated with Radiation Therapy
- Lectins Binding in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker
- Correlation between CD44 Variants Expression, Microvessel Density and VEGF Expression and HPV 16/18 Subtypes in Squamous Neoplasia of the Uterine Cervix
- Expressions of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), Phospholipase C-gammal and Ki-67 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma and High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion of Uterine Cervix
- Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma