J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Apr;19(2):223-228. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.223.
The Role of the Lactate Dehydrogenase and the Effect of Prone Position during Ventilator-induced Lung Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. lscmd@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1733481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.223
Abstract
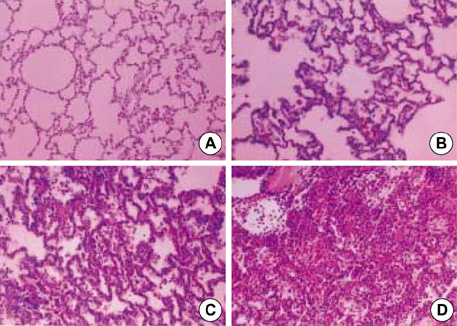
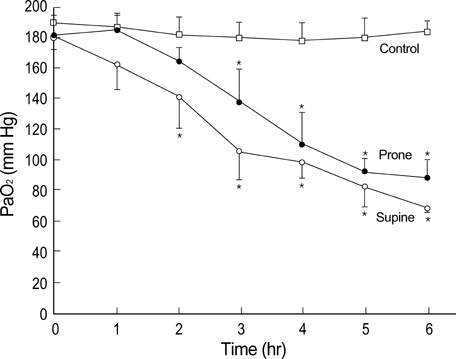
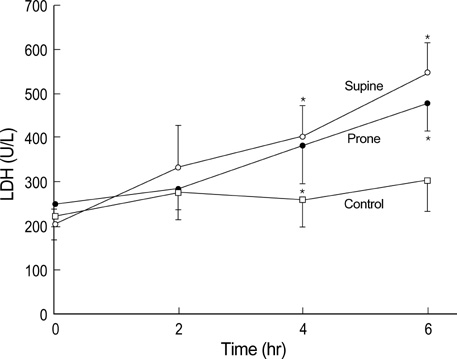
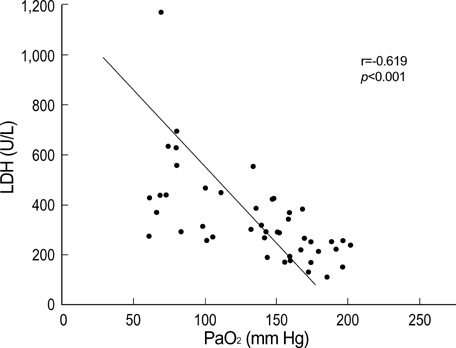
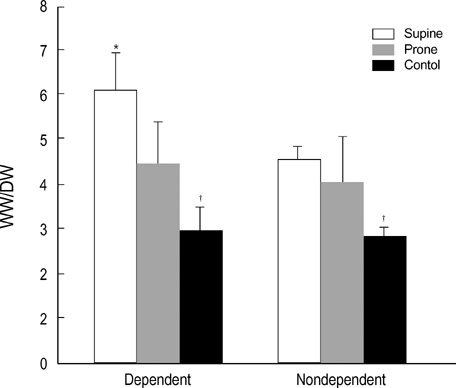
- To examine the impact of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as an early marker of ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) and the effect of prone position during the VILI, we ventilated 28 normal white rabbits (10 supine, 10 prone, 8 controls) for 6 hr or until PaO2/FIO2 ratio was<200 mmHg. We applied an identical injurious ventilatory pattern (peak inspiratory pressure of 35 cmH2O with a PEEP of 3 cmH2O, I:E ratio of 1:2, and FIO2 of 0.40) in the supine and prone group. VILI was assessed by oxygenation, gravimetric analysis and histologic grading. Serum levels of LDH progressively increased significantly during the VILI (supine and prone groups) as compared with controls. There was a significant negative correlation between oxygenation and LDH levels (r=-0.619, p<0.001). Wet weight/dry weight ratios (WW/DW) and histologic scores for dependent regions were significantly higher in the supine than the prone group. There were no differences in WW/DW and histologic scores for nondependent regions between the supine and prone group. These findings suggest that serum LDH levels might be an early marker of severity of lung injury. The prone position resulted in a less severe and more homogenous distribution of VILI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parker JC, Hernandez LA, Peevy KJ. Mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury. Crit Care Med. 1993. 21:131–143.
Article2. Dreyfuss D, Saumon G. Ventilator-induced lung injury: lessons from experimental studies. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 157:294–323.3. Amato MB, Barbas CS, Medeiros DM, Magaldi RB, Schettino GP, Lorenzi-Filho G, Kairalla RA, Deheinzelin D, Munoz C, Oliveira R, Takagaki TY, Carvalho CR. Effect of a protective-ventilation strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1998. 338:347–354.
Article4. Brochard L, Roudot-Thoraval F, Roupie E, Delclaux C, Chastre J, Fernandez-Mondejar E, Clementi E, Mancebo J, Factor P, Matamis D, Ranieri M, Blanch L, Rodi G, Mentec H, Dreyfuss D, Ferrer M, Brun-Buisson C, Tobin M, Lemaire F. The Multicenter Trial Group on Tidal Volume reduction in ARDS. Tidal volume reduction for prevention of ventilator-induced lung injury in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 158:1831–1838.5. Broccard AF, Shapiro RS, Schmitz LL, Ravenscraft SA, Marini JJ. Influence of prone position on the extent and distribution of lung injury in a high tidal volume oleic acid model of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 1997. 25:16–27.
Article6. Pelosi P, D'Andrea L, Vitale G, Pesenti A, Gattinoni L. Vertical gradient of regional lung inflation in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994. 149:8–13.
Article7. Montgomery AB, Stager MA, Carrico CJ, Hudson LD. Causes of mortality in patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985. 132:485–489.
Article8. Ghosh A, Greenberg ME. Calcium signaling in neurons: molecular mechanisms and cellular consequences. Science. 1995. 268:239–247.
Article9. Slutsky AS. Lung injury caused by mechanical ventilation. Chest. 1999. 116:9S–15S.
Article10. Behnia R, Molteni A, Waters CM, Panos RJ, Ward WF, Schnaper HW, TS'Ao CH. Early markers of ventilator-induced lung injury in rats. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1996. 26:437–450.11. Slutsky AS, Tremblay LN. Multiple system organ failure. Is mechanical ventilation a contributing factor? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 157:1721–1725.12. Tremblay LN, Slutsky AS. Ventilator-induced injury: from barotrauma to biotrauma. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1998. 110:482–488.13. Chernoff AE, Granowitz EV, Shapiro L, Vannier E, Lonnemann G, Angel JB, Kennedy JS, Rabson AR, Wolff SM, Dinarello CA. A randomized, controlled trial of IL-10 in humans. Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production and immune responses. J Immunol. 1995. 154:5492–5499.14. Ranieri VM, Suter PM, Tortorella C, De Tullio R, Dayer JM, Brienza A, Bruno F, Slutsky AS. Effect of mechanical ventilation on inflammatory mediators in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999. 282:54–61.
Article15. Messerole E, Peine P, Wittkopp S, Marini JJ, Albert RK. The pragmatics of prone positioning. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 165:1359–1363.
Article16. Piehl MA, Brown RS. Use of extreme position changes in acute respiratory failure. Crit Care Med. 1976. 4:13–14.
Article17. Douglas WW, Rehder K, Beynen FM, Sessler AD, Marsh HM. Improved oxygenation in patients with acute respiratory failure: the prone position. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977. 115:559–566.18. Albert RK, Leasa D, Sanderson M, Robertson HT, Hlastala MP. The prone position improves arterial oxygenation and reduces shunt in oleic-acid-induced acute lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987. 135:628–633.19. Lamm WJ, Graham MM, Albert RK. Mechanism by which the prone position improves oxygenation in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994. 150:184–193.
Article20. Broccard A, Shapiro RS, Schmitz LL, Adams AB, Nahum A, Marini JJ. Prone positioning attenuates and redistributes ventilator-induced lung injury in dogs. Crit Care Med. 2000. 28:295–303.
Article21. Dreyfuss D, Soler P, Basset G, Saumon G. High inflation pressure pulmonary edema. Respective effects of high airway pressure, high tidal volume, and positive end-expiratory pressure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988. 137:1159–1164.
Article22. Dreyfuss D, Martin-Lefevre L, Saumon G. Hyperinflation-induced lung injury during alveolar flooding in rats: effect of perfluorocarbon instillation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 159:1752–1757.23. Bone RC, Fisher CJ Jr, Clemmer TP, Slotman GJ, Metz CA. Early methylprednisolone treatment for septic syndrome and the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Chest. 1987. 92:1032–1036.
Article24. Imai Y, Parodo J, Kajikawa O, de Perrot M, Fischer S, Edwards V, Cutz E, Liu M, Keshavjee S, Martin TR, Marshall JC, Ranieri VM, Slutsky AS. Injurious mechanical ventilation and end-organ epithelial cell apoptosis and organ dysfunction in an experimental model of acute respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA. 2003. 289:2104–2112.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury
- Biotrauma in Ventilator Induced Lung Injury
- Follicular Lactate Dehydrogenase Activity and Steroid Concentrations in the Immature Gilt Ovary
- A study on the serum and cell lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme in hematologic malignancies
- The Respiratory and Hemodynamic Effects of Prone Position According to the Level of PEEP in a Dog Acute Lung Injury Model