J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Apr;19(2):218-222. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.218.
Molecular Analysis of X-linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease in Five Unrelated Korean Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hboh@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul, Korea.
- 3National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1733480
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.218
Abstract
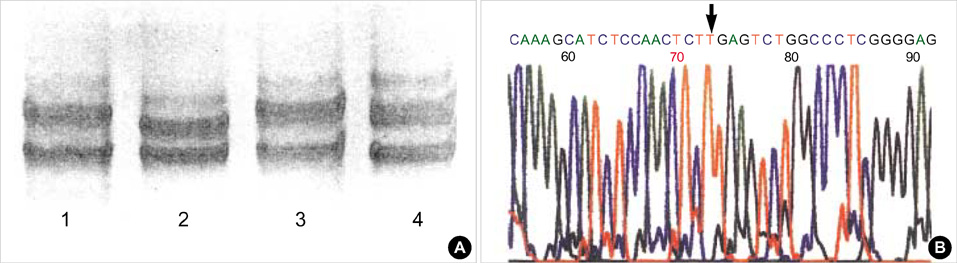
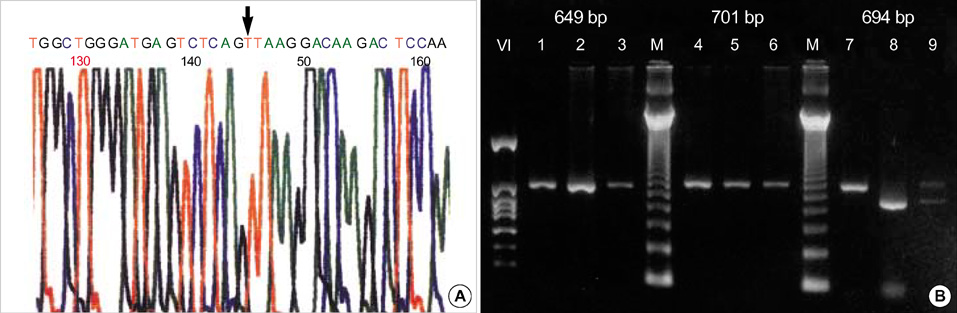
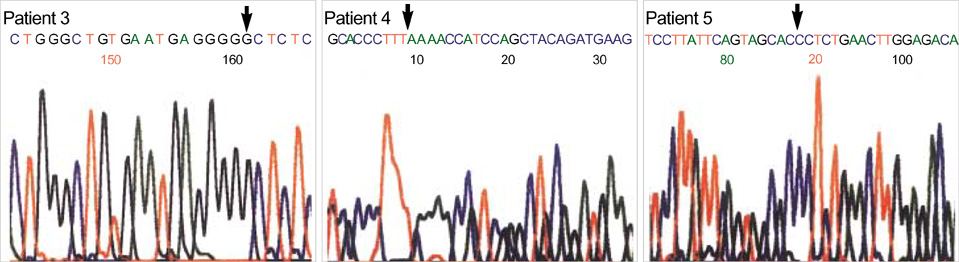
- Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a fatal genetic disorder in which phagocytes fail to produce antimicrobial superoxide because of NADPH oxidase deficiency. Molecular defects in CYBB gene causing X-linked CGD are responsible for about 70% of all cases. This study was done to confirm genetic defects of CYBB gene in five Korean patients who were highly suggestive of having CGD by clinical history. We performed initial screening for five unrelated Korean patients using single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) and then selective sequencing for the regions involving the abnormal bands. Activated NBT tests revealed that all patients were X-linked. SSCP analysis for CYBB gene showed abnormal bands in all patients. The molecular defects of five patients were as follows: c.1663insT, c.1111-1G>T, c.39_40insG, c.927delC and c.434T>C mutation. This result will help the families with prenatal diagnosis or genetic counseling.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Genetic Analysis of 10 Unrelated Korean Families with p22-phox-deficient Chronic Granulomatous Disease: An Unusually Identical Mutation of the CYBA Gene on Jeju Island, Korea
Young Mee Kim, Ji Eun Park, Jin Young Kim, Hee Kyung Lim, Jae Kook Nam, Moonjae Cho, Kyung-Sue Shin
J Korean Med Sci. 2009;24(6):1045-1050. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.6.1045.
Reference
-
1. Segal BH, Leto TL, Gallin JI, Malech HL, Holland SM. Genetic, biochemical and clinical features of chronic granulomatous disease. Medicine. 2000. 79:170–200.
Article2. Winkelstein JA, Marino MC, Johnston RB Jr, Boyle J, Curnutte J, Gallin JI, Malech HL, Holland SM, Ochs H, Quie P, Buckley RH, Foster CB, Chanock SJ, Dickler H. Chronic granulomatous disease. Report on a national registry of 368 patients. Medicine. 2000. 79:155–169.
Article3. Roos D. X-CGDbase: a database of X-CGD-causing mutations. Immunol Today. 1996. 17:517–521.
Article4. Meerhof LJ, Roos D. Heterogeneity in chronic granulomatous disease detected with an improved nitroblue tetrazolium slide test. J Leukoc Biol. 1986. 39:699–711.
Article5. Patino PJ, Perez JE, Lopez JA, Condino-Neto A, Grumach AS, Botero JH, Curnutte JT, Garcia de Olarte D. Molecular analysis of chronic granulomatous disease caused by defects in gp91-phox. Hum Mutat. 1999. 13:29–37.6. Bannai M, Tokunaga K, Lin L, Kuwata S, Mazda T, Amaki I, Fujisawa K, Juji T. Discrimination of human HLA-DRB1 alleles by PCR-SSCP (single-strand conformation polymorphism) method. Eur J Immunogenet. 1994. 21:1–9.
Article7. Dinauer MC, Curnutte JT, Rosen H, Orkin SH. A missense mutation in the neutrophil cytochrome b heavy chain in cytochrome-positive X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1989. 84:2012–2016.
Article8. Gerard B, El Benna J, Alcain F, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Grandchamp B, Chollet-Martin S. Characterization of 11 novel mutations in the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (CYBB gene). Hum Mutat. 2001. 18:163.9. Curnutte JT. Chronic granulomatous disease: the solving of clinical riddle at the molecular level. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993. 67:S2–S15.10. Jones AM, Dodd ME, Webb AK. Burkholderia cepacia: current clinical issues, environmental controversies and ethical dilemmas. Eur Respir J. 2001. 17:295–301.
Article11. Rae J, Newburger PE, Dinauer MC, Noack D, Hopkins PJ, Kuruto R, Curnutte JT. X-linked chronic granulomatous disease: mutations in the CYBB gene encoding the gp91-phox component of respiratory-burst oxidase. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. 62:1320–1331.
Article12. de Boer M, Bolscher BG, Dinauer MC, Orkin SH, Smith CI, Ahlin A, Weening RS, Roos D. Splice site mutations are a common cause of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1992. 80:1553–1558.
Article13. Roos D. The genetic basis of chronic granulomatous disease. Immunol Rev. 1994. 138:121–157.
Article14. Roos D, de Boer M, Kuribayashi F, Meischl C, Weening RS, Segal AW, Ahlin A, Nemet K, Hossle JP, Bernatowska-Matuszkiewicz E, Middleton-Price H. Mutations in the X-linked and autosomal recessive forms of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1996. 87:1663–1681.
Article15. Skalnik DG, Strauss EC, Orkin SH. CCAAT displacement protein as a repressor of the myelomonocytic-specific gp91-phox gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991. 266:16736–16744.
Article16. Ariga T, Sakiyama Y, Furuta H, Matsumoto S. Molecular genetic studies of two families with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease: mutation analysis and definitive determination of carrier status in patients' sisters. Eur J Haematol. 1994. 52:99–102.
Article17. Hayashi K. PCR-SSCP: a simple and sensitive method for detection of mutation in the genomic DNA. PCR Methods Appl. 1991. 1:34–38.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Genetic Analysis of 10 Unrelated Korean Families with p22-phox-deficient Chronic Granulomatous Disease: An Unusually Identical Mutation of the CYBA Gene on Jeju Island, Korea
- A Case of X-linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease Diagnosed in Identical Twin
- 2 Cases of X-linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease Diagnosed by Flow Cytometry using 2'7'-dichIorofIuorescein diacetate
- A case of chronic granulomatous disease
- Clinical Study on Chronic Granulomatous Disease in Korea