Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome and Its Association with Cardiovascular Diseases in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yshin@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1733476
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.195
Abstract
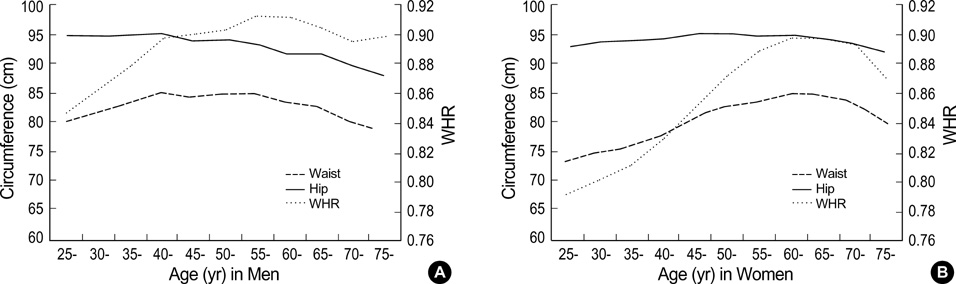
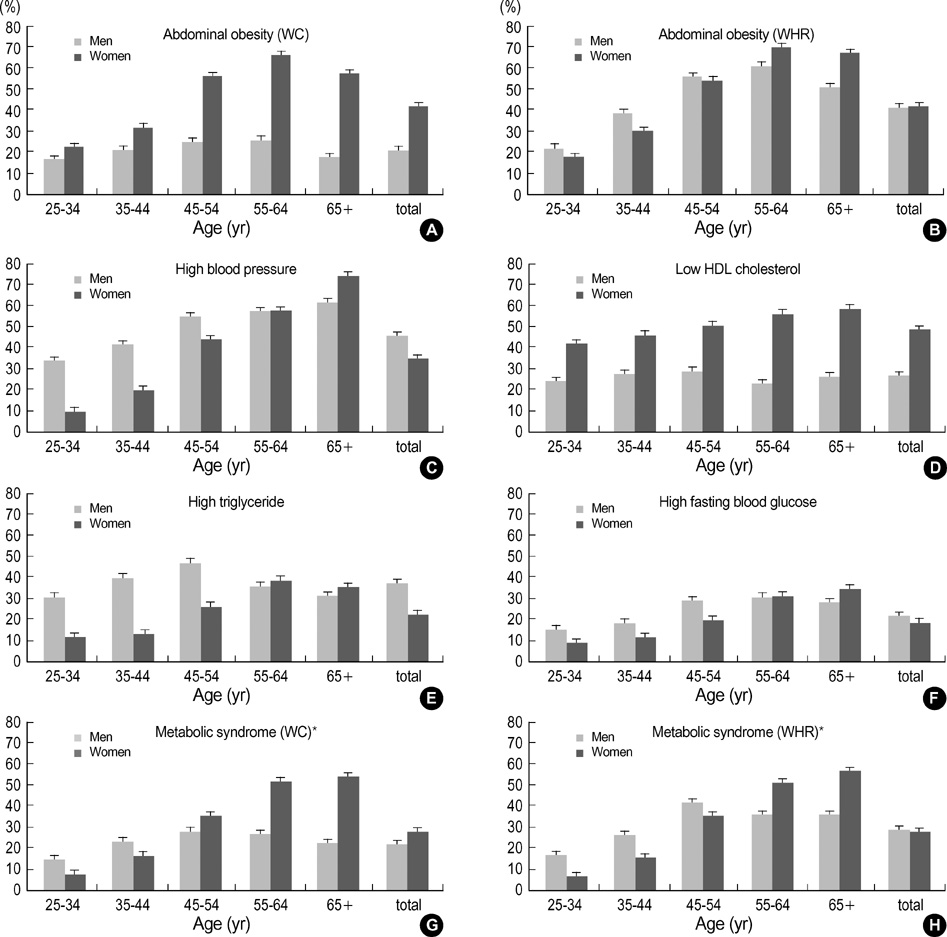
- This study aimed to estimate nationwide prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and to identify its association with cardiovascular diseases. The data on a national representative sample of 6,147 adults from 1998 Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey were analyzed. The syndrome was determined according to two kinds of modified definition from ATP III, in which abdominal obesity was determined by waist circumference (WC) standard for Asians and waist-to-hip ratio (WHR). Based on the former, prevalence was 22.1% in men and 27.8% in women. However, based on the latter, prevalence was 28.6% and 27.8%, respectively. Although age-specific prevalence was higher in men than in women among the younger group, it became higher in women among the older group because of its steeper rise with age. In multiple logistic regression, the syndrome was found to be positively associated with cardiovascular diseases (adjusted odds ratios (ORs)1.97 by WC and 1.48 by WHR in men, and 1.54 and 1.31 in women). Moreover, its effect size exceeded that of total cholesterol (adjusted ORs 1.21 in men, and 1.08 in women) or LDL cholesterol (1.58 in men and 1.22 in women). It is obvious that the metabolic syndrome prevails in Korea, and its importance regarding cardiovascular diseases is considerable. Prevention strategies should be implemented immediately to avoid cardiovascular epidemic in the near future.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
Achievement of LDL-C Targets Defined by ESC/EAS (2011) Guidelines in Risk-Stratified Korean Patients with Dyslipidemia Receiving Lipid-Modifying Treatments
Ye Seul Yang, Seo Young Lee, Jung-Sun Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Kang Wook Lee, Sang-Chol Lee, Jung Rae Cho, Seung-Jin Oh, Ji-Hyun Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):367-376. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.367.The Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Gout: A Multicenter Study
Young Hee Rho, Seong Jae Choi, Young Ho Lee, Jong Dae Ji, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Seung-hie Chung, Chae-Gi Kim, Jung-Yoon Choe, Sung Won Lee, Won Tae Chung, Gwan Gyu Song
J Korean Med Sci. 2005;20(6):1029-1033. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.6.1029.Menopause experience and the relationship between metabolic syndrome components and periodontitis
Ye Hwang Kim, Jung Hwa Lee
J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2019;43(2):56-62. doi: 10.11149/jkaoh.2019.43.2.56.Prevalence and Gender-Related Characteristics of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Community
Kyung-Taek Park, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Myung-A Kim, Euijae Lee, Jonghanne Park, Sang-Ho Jo, Sung Rae Kim, Jaetaek Kim, Chee Jeong Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Hyun Ho Shin
J Lipid Atheroscler. 2014;3(2):89-96. doi: 10.12997/jla.2014.3.2.89.The Effects of Lifestyle Factors on Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adults
Mee Young Im, Young-Ran Lee, Suk Jung Han, Chung-Min Cho
J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2012;23(1):13-21. doi: 10.12799/jkachn.2012.23.1.13.The Effects of Lifestyle Factors on Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adults
Mee Young Im, Young-Ran Lee, Suk Jung Han, Chung-Min Cho
J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2012;23(1):13-21. doi: 10.12799/jkachn.2012.23.1.13.Impact of fish consumption by subjects with prediabetes on the metabolic risk factors: using data in the 2015 (6th) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Kyoung-yun Kim, Jeong Seop Park
Nutr Res Pract. 2018;12(3):233-242. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2018.12.3.233.
Reference
-
1. National Institutes of Health. NIH Publication 01-3670. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). 2001. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health.2. Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988: Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988. 37:1595–1607.
Article3. Wilson PW, Kannel WB, Silbershatz H, D'Agostino RB. Clustering of metabolic factors and coronary heart disease. Arch Int Med. 1999. 159:1104–1109.
Article4. Trevisan M, Liu J, Bahsas FB, Menotti A. for the Risk factors and Life Expectancy Research Group. Syndrome X and mortality: a population-based study. Am J Epidemiol. 1998. 148:958–966.
Article5. Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, Forsen B, Lahti K, Nissen M, Taskinen MR, Groop L. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2001. 24:683–689.
Article6. Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001. 414:782–787.
Article7. Kim SW, Kim JY, Kim ES, Kim YI, Lee MS, Kim HH, Park JY, Hong SK, Lee KU. Prevalence of insulin resistance syndrome in subjects living in Jungup district, Korea. J Korean Diabet Assoc. 1999. 23:70–78.8. Lee HJ, Yoon JS, Shin DH. Patterns of insulin resistance syndrome in the Taegu community for the development of nutritional service improvement programs. Korean J Community Nutrition. 2001. 6:97–107.9. Kim BS. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome for Koreans: Among the clients of comprehensive medical examination in one university hospital. Korean J Health Promotion Disease Prevention. 2002. 2:17–26.10. Park SH, Lee WY, Kim SW. The relative risks of the metabolic syndrome defined by adult treatment panel III according to insulin resistance in Korean population. Korean J Med. 2003. 64:552–560.11. Lym YL, Hwang SW, Shim HJ, Oh EH, Chang YS, Cho BL. Prevalence and risk factors of the metabolic syndrome as defined by NCEP-ATP III. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2003. 24:135–143.12. Chung HW, Kim DJ, Jin HD, Choi SH, Ahn CW, Cha BS, Lee HC, Huh KB. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome according to the new criteria for obesity. J Korean Diabet Assoc. 2002. 26:431–442.13. Park JS, Park HD, Yun JW, Jung CH, Lee WY, Kim SW. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome as defined by NCEP-ATP III among the urban Korean population. Korean J Med. 2002. 63:290–298.14. Korea Institute of Health and Social Affairs. Summary Report: National Health and Nutrition Survey in 1998, Korea. 1999. Seoul: Ministry of Health & Welfare.15. Okosun IS, Liao Y, Rotimi CN, Prewitt TE, Cooper RS. Abdominal adiposity and clustering of multiple metabolic syndrome in white, black, and hispanic Americans. Ann Epidemiol. 2000. 10:263–270.
Article16. Inoue S, Zimmet P, Catersen I, Chunming C, Ikeda Y, Khalid AK, Kim YS, Basesett J. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment: Health Communication Australia Pty. 2000.17. Bjorntorp P. Body fat distribution, insulin resistance, and metabolic diseases. Nutrition. 1997. 13:795–803.
Article18. Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complication. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus, provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Medicine. 1998. 15:539–553.19. Ford ES, Giles WH. A comparison of the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome using two proposed definitions. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:575–581.
Article20. Brunner EJ, Marmot MG, Nanchahal K, Shipley MJ, Stansfeld SA, Juneja M, Alberti KGMM. Social inequality in coronary risk: central obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Evidence from the Whitehall II study. Diabetologia. 1997. 40:1341–1349.
Article21. Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: Findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2002. 287:356–359.
Article22. Araneta MRG, Wingard DL, Barrett-Connor E. Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome in Filipina-American women: A high-risk non-obese population. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:494–499.23. Fujimoto WY, Bergstrom RW, Boyko EJ, Chen K, Kahn SE, Leonetti DL, McNeely MJ, Newell LL, Shofer JB, Wahl PW. Type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in Japanese Americans. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000. 50:S73–S76.
Article24. Kosaka K, Kuzuya T, Yoshinaga H, Hagura R. A prospective study of health check examination for the development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: relationship of the incidence of diabetes with initial insulinogenic index and degree of obesity. Diabetic Medicine. 1996. 13:s120–s126.25. McKeigue PM, Shah B, Marmot MG. Relation of central obesity and insulin resistance with high diabetes prevalence and cardiovascular risk in South Asians. Lancet. 1991. 337:382–386.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome in Korea: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2021
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescent
- Epidemiology of the metabolic syndrome among Korean children and adolescents
- Association between Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Patients
- Interrelationship of Uric Acid, Gout, and Metabolic Syndrome: Focus on Hypertension, Cardiovascular Disease, and Insulin Resistance