Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Feb;63(2):114-119. 10.4166/kjg.2014.63.2.114.
Endoscopic Resection as a Possible Radical Treatment for Duodenal Gangliocytic Paraganglioma: A Report of Four Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dohoon.md@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1730918
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.63.2.114
Abstract
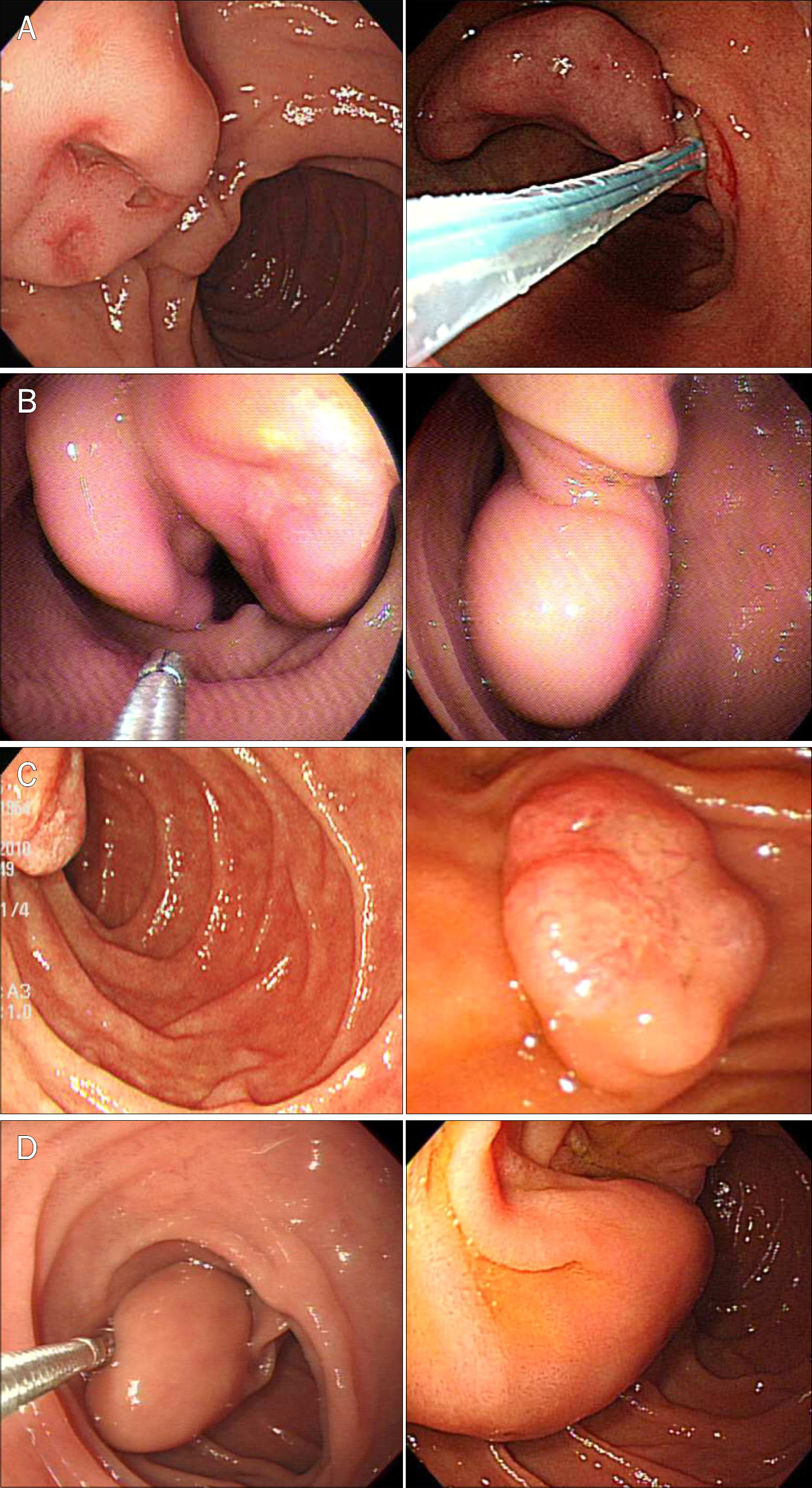
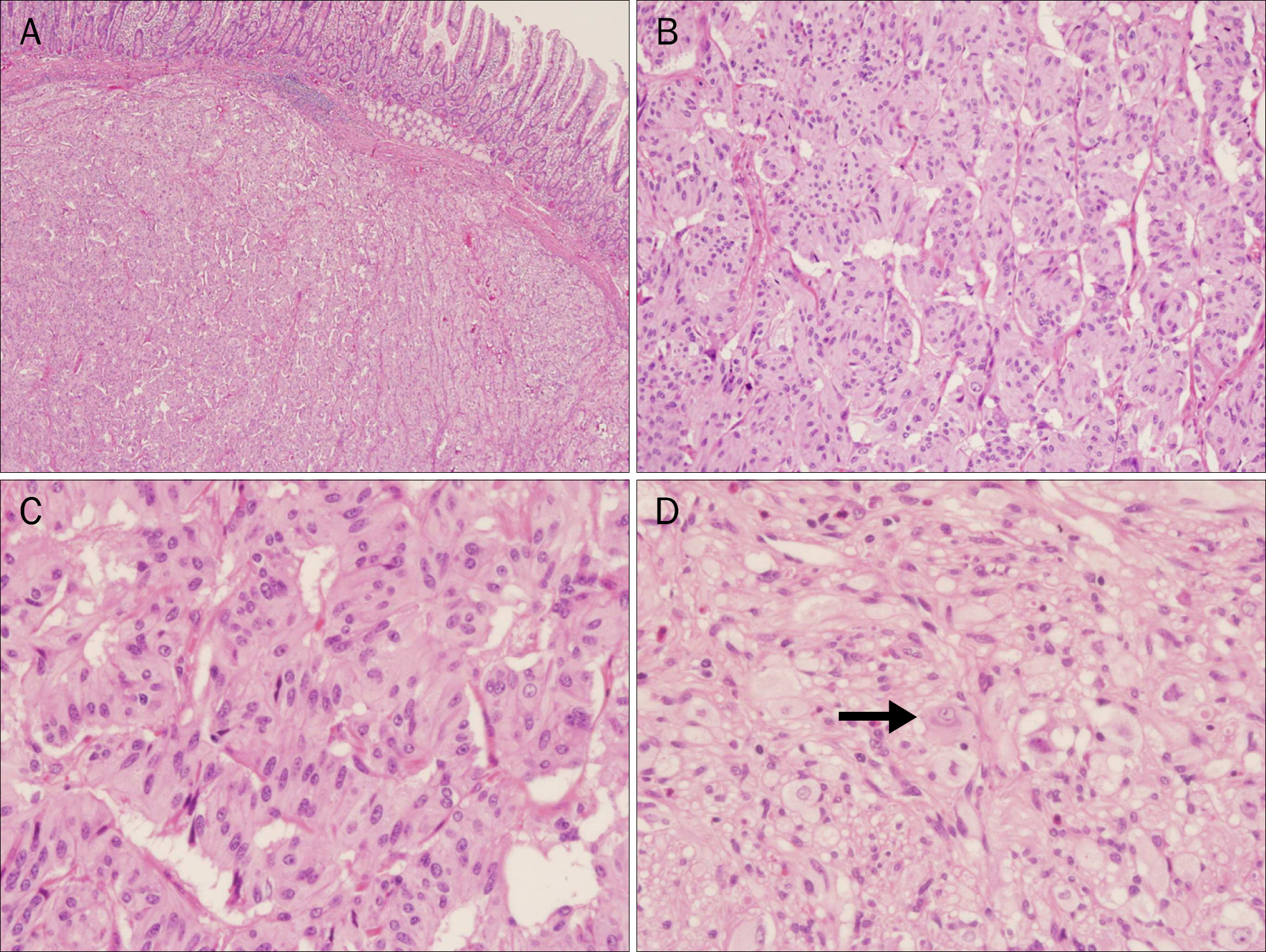
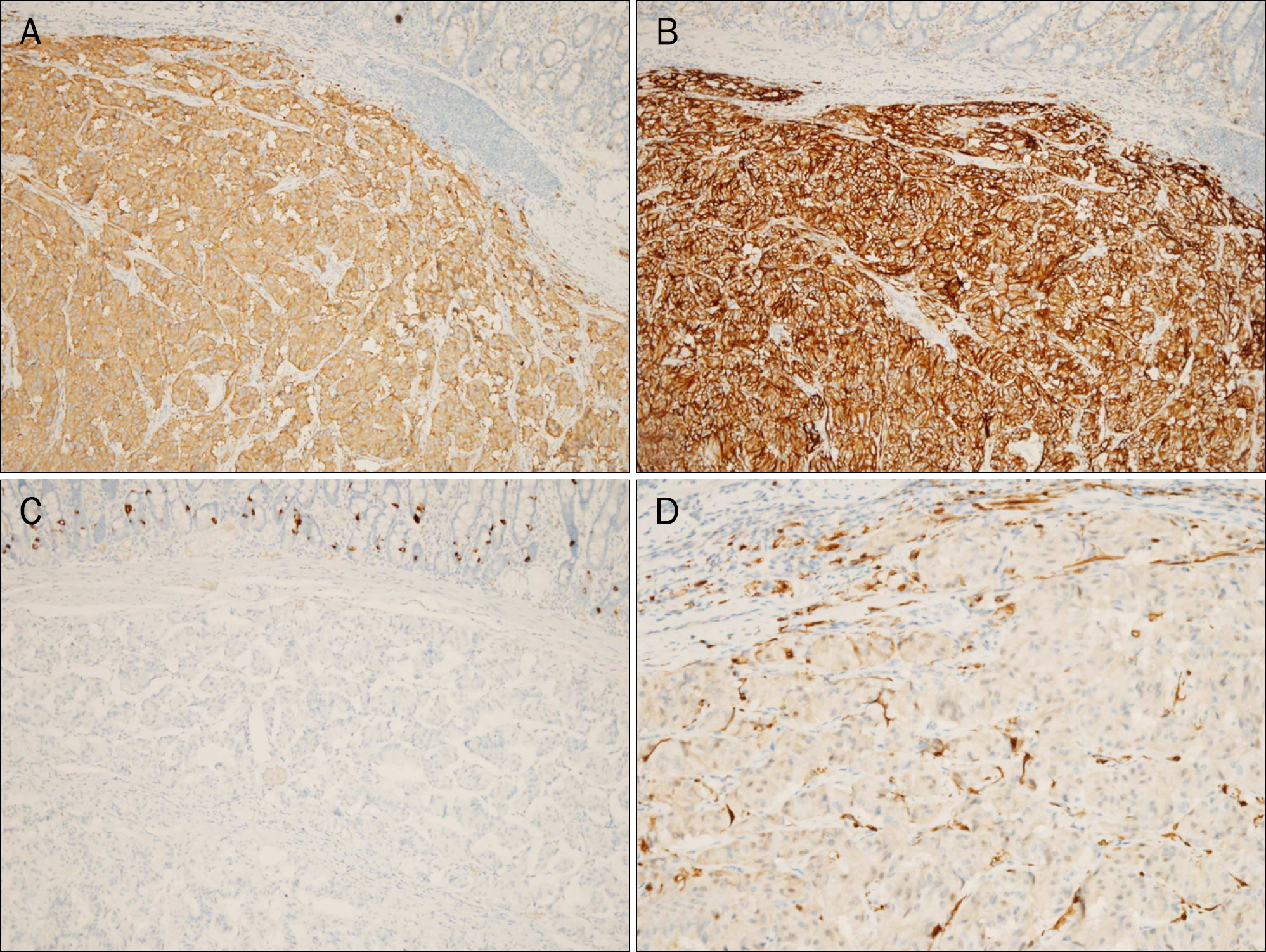
- Gangliocytic paraganglioma (GP) is a rare, benign tumor which is usually found in the duodenum. We here report four recent cases of GP, with successful endoscopic resection in three cases, including a lesion on the ampulla of Vater. In all cases, each lesion had a stalk that facilitated removal using an endoscopic approach. Endoscopic mucosal resection is a feasible and safe treatment if the location, depth, and lymph node status are all favorable and is also helpful for definite diagnosis of unknown duodenal mass. To avoid morbidity resulting from open surgical resection, careful inspection for the peduncle of the GP will help determine the feasibility of endoscopic resection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Ampulla of Vater/pathology
Chromogranin A/metabolism
Colonoscopy
Duodenal Neoplasms/pathology/*surgery
Endoscopy, Gastrointestinal
Female
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Intestinal Mucosa/pathology/surgery
Male
Middle Aged
Neuroendocrine Tumors/pathology/surgery
Paraganglioma/pathology/*surgery
S100 Proteins/metabolism
Synaptophysin/metabolism
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Chromogranin A
S100 Proteins
Synaptophysin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Concurrent Ampullary Adenoma and Gangliocytic Paraganglioma at the Minor Papilla Treated with Endoscopic Resection
Jun Kwon Ko, Do Hyun Park, Hee Sang Hwang
Clin Endosc. 2019;52(4):382-386. doi: 10.5946/ce.2018.198.
Reference
-
References
1. Dahl EV, Waugh JM, Dahlin DC. Gastrointestinal ganglioneur-omas; brief review with report of a duodenal ganglioneuroma. Am J Pathol. 1957; 33:953–965.2. Okubo Y, Wakayama M, Nemoto T, et al. Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of gangliocytic paraganglioma. BMC Cancer. 2011; 11:187.
Article3. Wong A, Miller AR, Metter J, Thomas CR Jr. Locally advanced duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma treated with adjuvant radiation therapy: case report and review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol. 2005; 3:15.
Article4. Barret M, Rahmi G, Duong van Huyen JP, Landi B, Cellier C, Berger A. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma with lymph node metastasis and an 8-year follow-up: a case report. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 24:90–94.5. Sundararajan V, Robinson-Smith TM, Lowy AM. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma with lymph node metastasis: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003; 127:e139–e141.
Article6. Kwon J, Lee SE, Kang MJ, Jang JY, Kim SW. A case of gangliocytic paraganglioma in the ampulla of Vater. World J Surg Oncol. 2010; 8:42.
Article7. Plaza JA, Vitellas K, Marsh WL Jr. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma: a radiological-pathological correlation. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2005; 9:143–147.
Article8. Nagai T, Torishima R, Nakashima H, et al. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma treated with endoscopic hemostasis and resection. J Gastroenterol. 2004; 39:277–283.
Article9. Morita T, Tamura S, Yokoyama Y, et al. Endoscopic resection of a duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma. Dig Dis Sci. 2007; 52:1400–1404.
Article10. El Idrissi-Lamghari A, Rioux-Leclercq N, Pagenault M, Bretagne JF. Voluminous juxtapapillary gangliocytic paraganglioma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:445–446.
Article11. Witkiewicz A, Galler A, Yeo CJ, Gross SD. Gangliocytic paraganglioma: case report and review of the literature. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:1351–1354.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periampullary Gangliocytic Paraganglioma Successfully Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- A Incidentally Diagnosed Duodenal Subepithelial Mass: Gangliocytic Paraganglioma Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- A Case of Concurrent Ampullary Adenoma and Gangliocytic Paraganglioma at the Minor Papilla Treated with Endoscopic Resection
- A case of juxtapapillary gangliocytic paraganglioma treated with endoscopic resection
- Gangliocytic Paraganglioma of the Duodenum