Ewha Med J.
2013 Dec;36(Suppl):S14-S16. 10.12771/emj.2013.36.S.S14.
Eosinophilic Enteritis with Eosinophilic Ascites without Eosinophilia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Daerim Saint Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jyjeong76@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Daerim Saint Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1726728
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2013.36.S.S14
Abstract
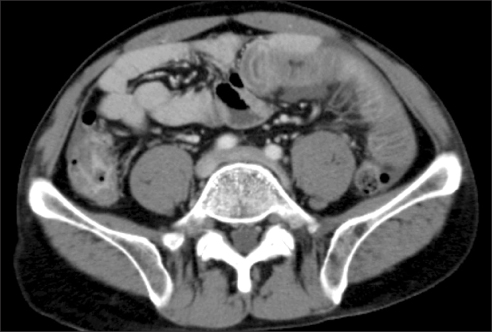
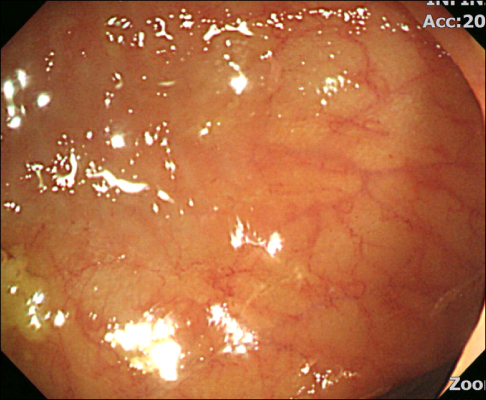
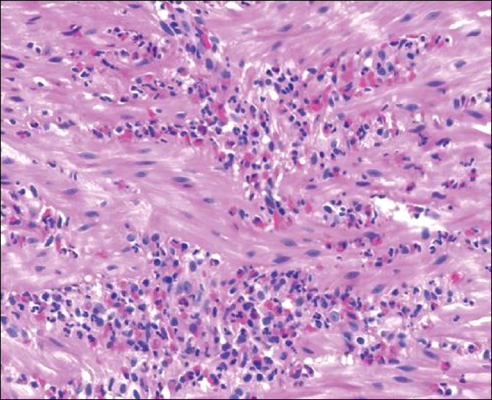
- Eosinophilic enteritis is an uncommon disease of unknown cause characterized by eosinophilic infiltration in various areas of the gastrointestinal tract with symptoms. It is generally classified according to the layer of the gastrointestinal tract involved. Eosinophilic infiltration of the serosa is the rarest form of presentation and may manifest eosinophilic ascites. We report a case of a 47-year-old man who experienced progressing abdominal pain. A diffuse erythematous change of the gastric mucosa was observed on gastrofibroscopy. An abdominal computed tomography and colonoscopy showed diffuse wall thickening of the small bowel and colon with a small amount of ascites. Eosinophilic infiltration was confirmed by multiple biopsies of the gastrointestinal tract and peritoneal fluid analysis. The patient was treated with corticosteroid and responded dramatically.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Feldman M, Friedman LS, Sleisenger MH. Sleisenger and Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders;2002.2. Kuri K, Lee M. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis manifesting with ascites. South Med J. 1994; 87:956–957.3. Cello JP. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a complex disease entity. Am J Med. 1979; 67:1097–1104.4. Kim NI, Jo YJ, Song MH, Kim SH, Kim TH, Park YS, et al. Clinical features of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004; 44:217–223.5. Caldwell JH, Mekhjian HS, Hurtubise PE, Beman FM. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with obstruction. Immunological studies of seven patients. Gastroenterology. 1978; 74(5 Pt 1):825–828.6. Fenoglio LM, Benedetti V, Rossi C, Anania A, Wulhfard K, Trapani M, et al. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with ascites: a case report and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48:1013–1020.7. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:11–28.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Eosinophilic Enteritis Presenting as Massive Ascites after Influenza A Virus Infection in a Young Female
- Eosinophilic Enteritis Diagnosed by Laparoscopic Biopsy
- A Case of Eosinophilic Enteritis with Ascites
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis in a Child
- A Case of Anisakiasis Diagnosed after Partial Resection of Ileum Due to Eosinophilic Ascites and Ileal Abscess