Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis.
2014 Aug;21(2):81-95.
Antibody Responses in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Recipients after Vaccination Against Haemophilus Influenzae Type b and Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. kaykim@ewah.ac.kr
- 5Center for Vaccine Evaluation and Study, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) recipients are vulnerable to invasive infection by Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) and Streptococcus pneumoniae (Sp). This study was performed to evaluate immune responses after Hib and Sp vaccination in Korean pediatric HCT recipients.
METHODS
Patients were prospectively enrolled at Samsung Medical Center during 2009-2011. ELISA tests to detect anti-PRP IgG antibody and antibodies to Sp serotypes 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, and 23F were performed at the Center for Vaccine Evaluation and Study, Ewha Medical Research Institute.
RESULTS
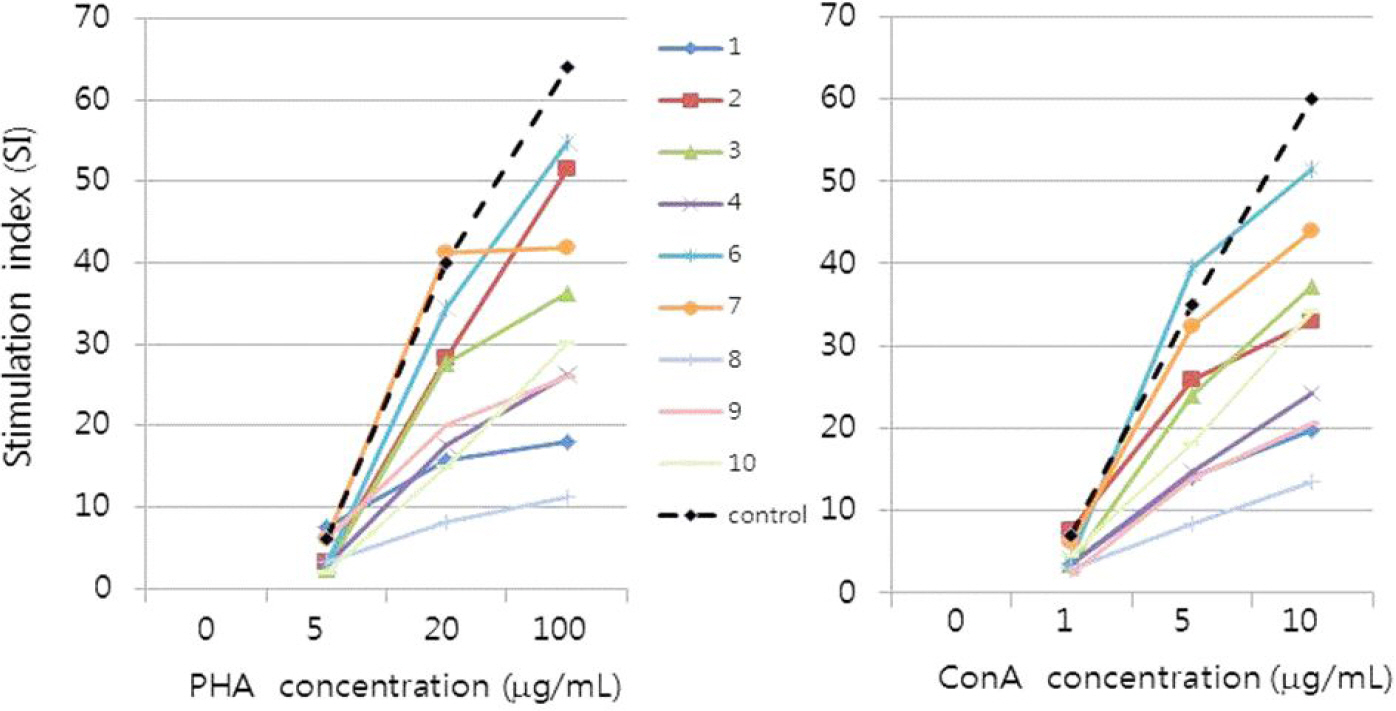
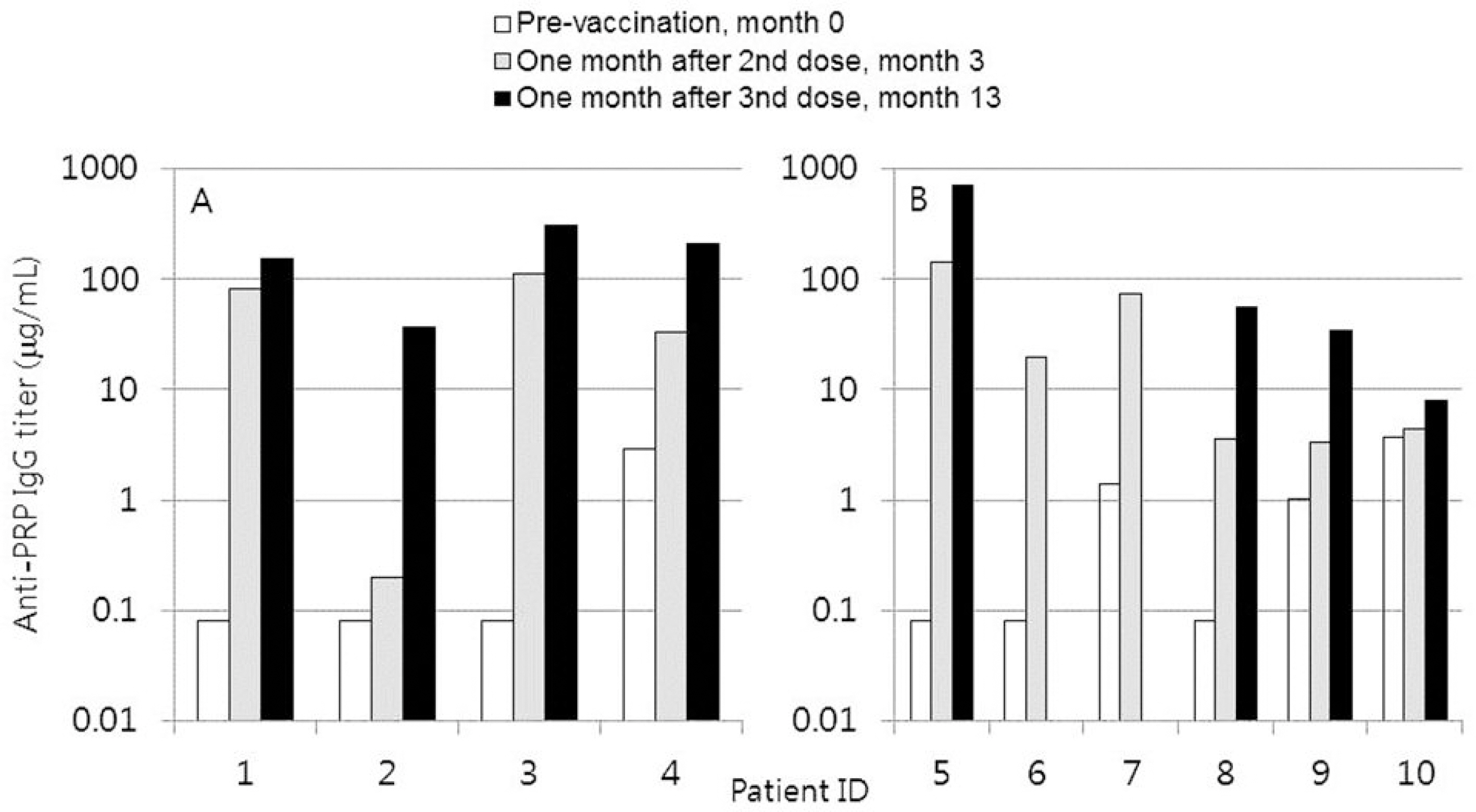
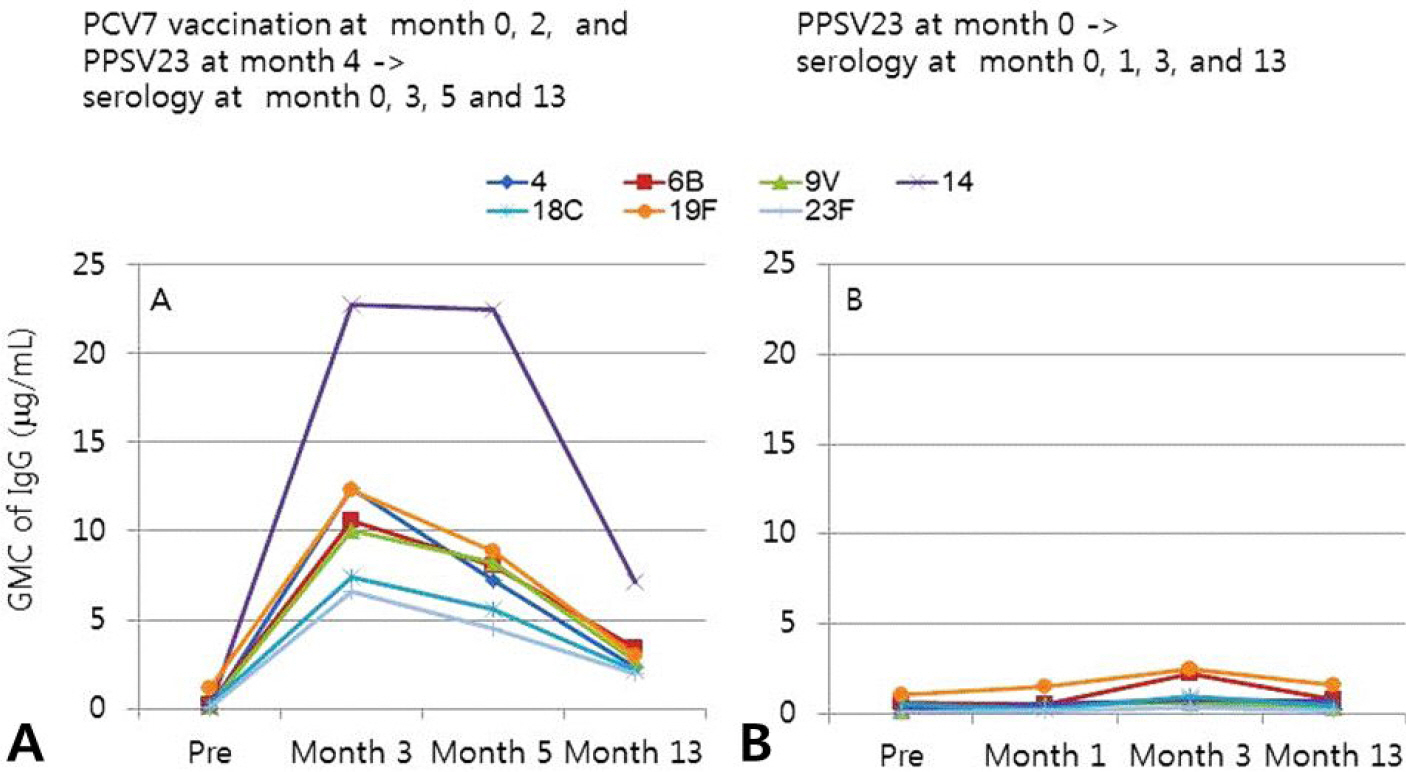
Ten patients (two allogeneic, eight autologous recipients) with median age 5.4 years (range 2.7-12.2 years) were enrolled. Before Hib vaccination, 60% of patients' anti-PRP IgG titers were below 0.15 microg/mL. After vaccination, 100% of patients' anti-PRP IgG titers increased above 0.15 microg/mL (cut-off value for detection) and 1.0 microg/mL (cut-off value for seroprotection). For pneumococcus, in 2-5 year-old patients, pre-vaccination geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) of IgG for six serotypes (4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, and 23F) were below 0.35 microg/mL and at 5 months post-vaccination GMCs of IgG for all seven serotypes increased to above 0.35 microg/mL. In patients older than 5 years, pre-vaccination GMCs of IgG for four serotypes (4, 9V, 14, and 23F) were below 0.35 microg/mL and at 3 months post-vaccination GMCs of IgG for all seven serotypes increased to above 0.35 microg/mL.
CONCLUSION
Most HCT recipients had low or no protective antibodies to Hib and Sp before vaccination, but showed good immune responses to protective levels after vaccination.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Infectious Disease Society of America, American Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Guidelines for preventing opportunistic infections among hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2000; 49:1–125. CE1–7.2. Plotkin SA, Walter AO, Paul AO. Vaccines. Vaccination of immunocompromised hosts. 6th ed.St. Louis, Mo.: Elsevier Saunders;2006. p. 1243–56.3. Ljungman P, Cordonnier C, Einsele H, Englund J, Machado CM, Storek J, et al. Vaccination of hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009; 44:521–6.
Article4. Ljungman P, Engelhard D, de la Camara R, Einsele H, Locasciulli A, Martino R, et al. Vaccination of stem cell transplant recipients: recommendations of the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005; 35:737–46.
Article5. Tomblyn M, Chiller T, Einsele H, Gress R, Sepkowitz K, Storek J, et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplant recipients: a global perspective. Preface. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009; 44:453–5.6. Aucouturier P, Barra A, Intrator L, Cordonnier C, Schulz D, Duarte F, et al. Long lasting IgG subclass and antibacterial polysaccharide antibody deficiency after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1987; 70:779–85.
Article7. Engelhard D, Cordonnier C, Shaw PJ, Parkalli T, Guenther C, Martino R, et al. Early and late invasive pneumococcal infection following stem cell transplantation: a European Bone Marrow Transplantation survey. Br J Haematol. 2002; 117:444–50.
Article8. Youssef S, Rodriguez G, Rolston KV, Champlin RE, Raad II, Safdar A. Streptococcus pneumoniae infections in 47 hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: clinical characteristics of infections and vaccine-break-through infections, 1989–2005. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007; 86:69–77.9. Atkinson K, Storb R, Prentice RL, Weiden PL, Wither-spoon RP, Sullivan K, et al. Analysis of late infections in 89 longterm survivors of bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1979; 53:720–31.
Article10. Cordonnier C, Bernaudin JF, Bierling P, Huet Y, Vernant JP. Pulmonary complications occurring after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. A study of 130 consecutive transplanted patients. Cancer. 1986; 58:1047–54.
Article11. Meisel R, Kuypers L, Dirksen U, Schubert R, Gruhn B, Strauss G, et al. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine provides early protective antibody responses in children after related and unrelated allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2007; 109:2322–6.
Article12. Pao M, Papadopoulos EB, Chou J, Glenn H, Castro-Malaspina H, Jakubowski AA, et al. Response to pneumococcal (PNCRM7) and Haemophilus influenzae conjugate vaccines (HIB) in pediatric and adult recipients of an allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo HCT). Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008; 14:1022–30.13. Patel SR, Ortin M, Cohen BJ, Borrow R, Irving D, Sheldon J, et al. Revaccination with measles, tetanus, poliovirus, Haemophilus influenzae type B, meningococcus C, and pneumococcus vaccines in children after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44:625–34.
Article14. Kim KH, Lim SY. Validation of enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human IgG antibodies specific for Haemophilus influenzae Type b capsular polysaccharide. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:143–50.
Article15. Phipps DC, West J, Eby R, Koster M, Madore DV, Qua-taert SA. An ELISA employing a Haemophilus influenzae type b oligosaccharide-human serum albumin conjugate correlates with the radioantigen binding assay. J Immunol Methods. 1990; 135:121–8.
Article16. Kayhty H, Peltola H, Karanko V, Makela PH. The protective level of serum antibodies to the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1983; 147:1100.
Article17. Concepcion NF, Frasch CE. Pneumococcal type 22f polysaccharide absorption improves the specificity of a pneumococcal-polysaccharide enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001; 8:266–72.
Article18. Wernette CM, Frasch CE, Madore D, Carlone G, Gold-blatt D, Plikaytis B, et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of human antibodies to pneumococcal polysaccharides. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003; 10:514–9.
Article19. World Health Organization. 2009. Recommendations to assure the quality, safety and efficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. Available from:. http://www.who. int/biologicals/areas/vaccines/pneumo/Pneumo_final_23APRIL_2010.pdf.20. Ljungman P, Fridell E, Lonnqvist B, Bolme P, Bottiger M, Gahrton G, et al. Efficacy and safety of vaccination of marrow transplant recipients with a live attenuated measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1989; 159:610–5.
Article21. Parkkali T, Ruutu T, Stenvik M, Kuronen T, Kayhty H, Hovi T, et al. Loss of protective immunity to polio, diphtheria and Haemophilus influenzae type b after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. APMIS. 1996; 104:383–8.22. Chan CY, Molrine DC, Antin JH, Wheeler C, Guinan EC, Weinstein HJ, et al. Antibody responses to tetanus toxoid and Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccines following autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT). Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997; 20:33–8.
Article23. Hammarstrom V, Pauksen K, Bjorkstrand B, Simonsson B, Oberg G, Ljungman P. Tetanus immunity in autologous bone marrow and blood stem cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998; 22:67–71.
Article24. Molrine DC, Hibberd PL. Vaccines for transplant recipients. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2001; 15:273–305. xii.
Article25. Guinan EC, Molrine DC, Antin JH, Lee MC, Weinstein HJ, Sallan SE, et al. Polysaccharide conjugate vaccine responses in bone marrow transplant patients. Trans-plantation. 1994; 57:677–84.26. Parkkali T, Kayhty H, Ruutu T, Volin L, Eskola J, Ruutu P. A comparison of early and late vaccination with Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines after allogeneic BMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996; 18:961–7.27. Winston DJ, Ho WG, Schiffman G, Champlin RE, Feig SA, Gale RP. Pneumococcal vaccination of recipients of bone marrow transplants. Arch Intern Med. 1983; 143:1735–7.
Article28. de Roux A, Schmole-Thoma B, Siber GR, Hackell JG, Kuhnke A, Ahlers N, et al. Comparison of pneumococcal conjugate polysaccharide and free polysaccharide vaccines in elderly adults: conjugate vaccine elicits improved antibacterial immune responses and immunological memory. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46:1015–23.
Article29. Avanzini MA, Carra AM, Maccario R, Zecca M, Pignatti P, Marconi M, et al. Antibody response to pneumococcal vaccine in children receiving bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Immunol. 1995; 15:137–44.
Article30. Hammarstrom V, Pauksen K, Azinge J, Oberg G, Ljungman P. Pneumococcal immunity and response to immunization with pneumococcal vaccine in bone marrow transplant patients: the influence of graft versus host reaction. Support Care Cancer. 1993; 1:195–9.
Article31. Cordonnier C, Labopin M, Chesnel V, Ribaud P, Camara Rde L, Martino R, et al. Immune response to the 23-valent polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccine after the 7-valent conjugate vaccine in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: results from the EBMT IDWP01 trial. Vaccine. 2010; 28:2730–4.
Article32. Cordonnier C, Labopin M, Chesnel V, Ribaud P, De La Camara R, Martino R, et al. Randomized study of early versus late immunization with pneumococcal conjugate vaccine after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 48:1392–401.
Article33. Cordonnier C, Labopin M, Jansen KU, Pride M, Chesnel V, Bonnet E, et al. Relationship between IgG titers and opsonocytophagocytic activity of anti-pneumococcal antibodies after immunization with the 7-valent conjugate vaccine in allogeneic stem cell transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010; 45:1423–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vaccination of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients: Perspective in Korea
- Natural Anti-PRP Antibody Levels ot Haemophilus Influenzae Type b(Hib) and Changs of Antibody Levels after Three Doses of Vacination
- Pneumococcal Sepsis 8 Years after Splenectomy for Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Case of Vaccinated 12-year-old Patient
- Considering the epidemiology of invasive Haemophilus influenzae infection and vaccination in Korea
- A Case of Neurologic Sequelae and a Case of Peripheral Gangrene of Extremities Associated with Haemophilus influenzae Type b Meningitis