Clin Orthop Surg.
2010 Dec;2(4):209-213. 10.4055/cios.2010.2.4.209.
Early Union of Grafted Bone in Ankylosing Spondylitis: Comparative Study with Degenerative Spinal Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang Universtiy College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. hyparkys@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hospital for Rheumatic Disease, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1719320
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2010.2.4.209
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) achieve early bone union compared to those with other spinal diseases. This study compared the time to bone union after surgery between AS patients and degenerative spinal disease patients.
METHODS
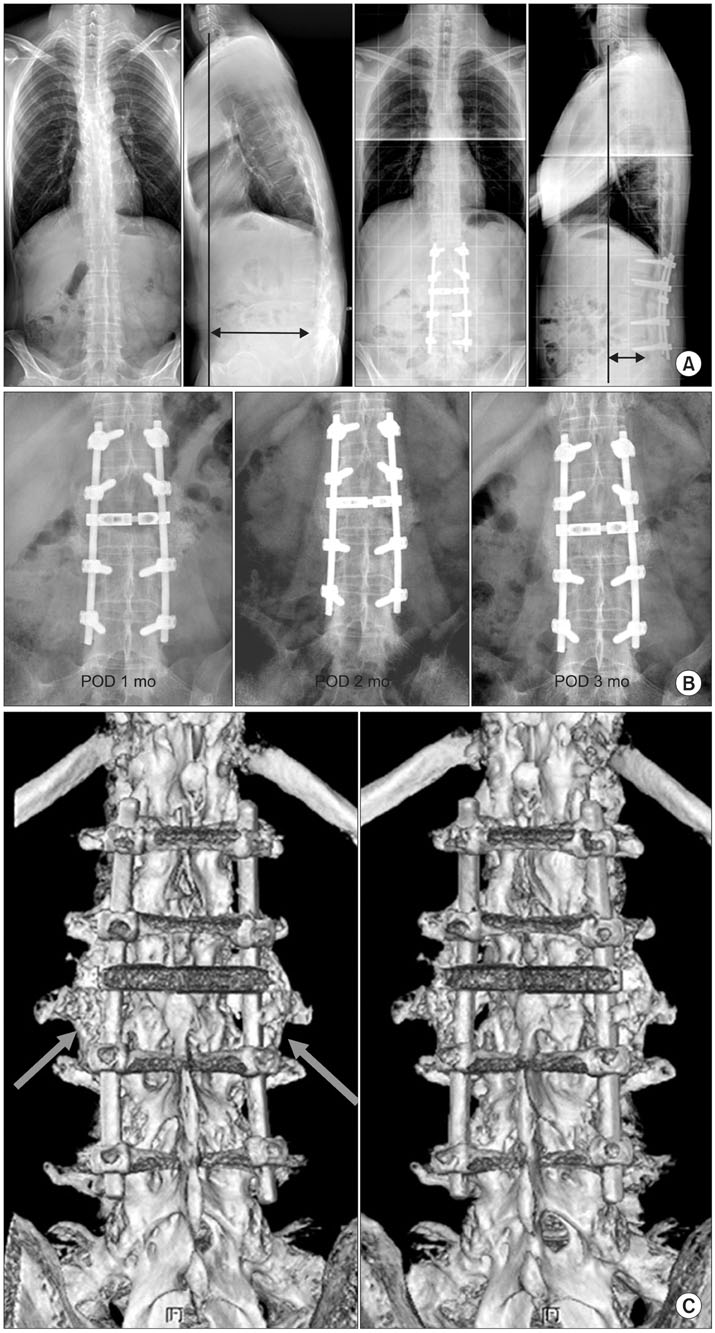
Patients with degenerative spinal diseases (control group) and AS (experimental group) underwent pedicle subtraction osteotomy followed by posterolateral fusion, and decompression and posterolateral fusion, respectively. There were 10 patients in the experimental group. The control group included 26 patients who were less than 50 years of age and underwent two-level autogenous grafting after decompression and spinal fusion. Autogenous grafts and a range of bone substitutes were used in the experimental group, whereas only autogenous grafts were used in the control group. Bone union was determined on the radiographs and 3-dimensional CT scan images. The level of union was assessed using the Lenke's and Christensen's classification systems.
RESULTS
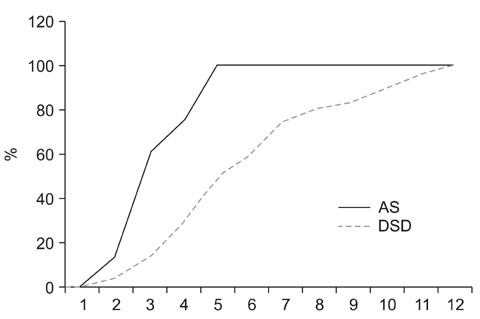
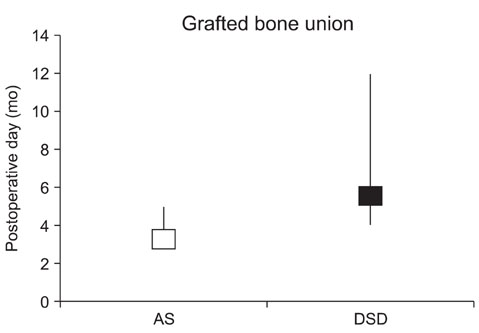
In the experimental group, the mean age was 41.3 years (range, 30 to 67 years), the mean follow-up period was 21.7 months (range, 12 to 43 months), and bone union was confirmed at an average of 3.5 months (range, 3 to 5 months) after surgery. In the control group, the mean age was 43.1 years (range, 35 to 50 years), the mean follow-up period was 21.8 months (range, 12 to 74 months), and bone union was observed at an average of 5.6 months (range, 4 to 12 months) after surgery. The difference in the time to bone union between the two groups was significant (p = 0.023).
CONCLUSIONS
The union of grafted bone was obtained earlier in patients with AS than in those with degenerative spinal diseases. Therefore, future studies should examine the factors affecting the early union in AS patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goel MK. Vertebral osteotomy for correction of fixed flexion deformity of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968. 50(2):287–294.
Article2. Kim KT, Lee SU, Kim YW, Kwon OS, Cho CH. Posterior closed wedge lumbar osteotomy in the kyphotic deformity of ankylosing spondylitis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1997. 32(7):1756–1765.
Article3. Urist MR. Osteotomy of the cervical spine: report of a case of ankylosing rheumatoid spondylitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958. 40(4):833–843.4. Meenan RF, Gertman PM, Mason JH, Dunaif R. The arthritis impact measurement scales: further investigations of a health status measure. Arthritis Rheum. 1982. 25(9):1048–1053.
Article5. Herbert JJ. Vertebral osteotomy for kyphosis, especially in Marie-Strumpell arthritis: a report on fifty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959. 41(2):291–302.6. Thomasen E. Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. (194):142–152.
Article7. Chang KW, Chen YY, Lin CC, Hsu HL, Pai KC. Closing wedge osteotomy versus opening wedge osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis with thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30(14):1584–1593.
Article8. Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bullis D, Betz RR, Baldus C, Schoenecker PL. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord. 1992. 5(4):433–442.
Article9. Christensen FB, Laursen M, Gelineck J, Eiskjaer SP, Thomsen K, Bunger CE. Interobserver and intraobserver agreement of radiograph interpretation with and without pedicle screw implants: the need for a detailed classification system in posterolateral spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26(5):538–543.
Article10. Zhang X, Aubin JE, Inman RD. Molecular and cellular biology of new bone formation: insights into the ankylosis of ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003. 15(4):387–393.
Article11. Polzer K, Diarra D, Zwerina J, Schett G. Inflammation and destruction of the joints: the Wnt pathway. Joint Bone Spine. 2008. 75(2):105–107.
Article12. Goldring SR, Goldring MB. Eating bone or adding it: the Wnt pathway decides. Nat Med. 2007. 13(2):133–134.
Article13. Bodine PV, Komm BS. Wnt signaling and osteoblastogenesis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2006. 7(1-2):33–39.14. Gregory CA, Gunn WG, Reyes E, et al. How Wnt signaling affects bone repair by mesenchymal stem cells from the bone marrow. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. 1049:97–106.
Article15. Diarra D, Stolina M, Polzer K, et al. Dickkopf-1 is a master regulator of joint remodeling. Nat Med. 2007. 13(2):156–163.
Article16. Uderhardt S, Diarra D, Katzenbeisser J, et al. Blockade of Dickkopf (DKK)-1 induces fusion of sacroiliac joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. 69(3):592–597.
Article17. Park MC, Park YB, Lee SK. Relationship of bone morphogenetic proteins to disease activity and radiographic damage in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2008. 37(3):200–204.
Article18. Wendling D, Cedoz JP, Racadot E, Dumoulin G. Serum IL-17, BMP-7, and bone turnover markers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Joint Bone Spine. 2007. 74(3):304–305.
Article19. Lories RJ, Derese I, Luyten FP. Modulation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling inhibits the onset and progression of ankylosing enthesitis. J Clin Invest. 2005. 115(6):1571–1579.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Cervical Cord Injury with Ankylosing Spondylitis: Case Report
- Relationship between Union of Grafted Autologous Bone and Clinical Results of Operative Treatment of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis by Posterolateral Fusion
- Clinieal Values of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ( SPECT ) in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Prevention And Surgical Correction Of Deformity
- Paraplegia after Open Reduction of the Femoral Trochanteric Fracture in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Case Report