Clin Orthop Surg.
2012 Dec;4(4):307-312. 10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.307.
Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing for Distal Femur Fracture with Osteoporosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ossbkang@gmail.com
- KMID: 1719299
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.307
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The incidence of distal femur fracture in the elderly has been increasing recently, and commonly occurs with osteoporosis. Retrograde intramedullary nailing has been considered a good surgical option for distal femur fracture. The purpose of the present study was to present our surgical results with retrograde intramedullary nailing for distal femur fractures with osteoporosis.
METHODS
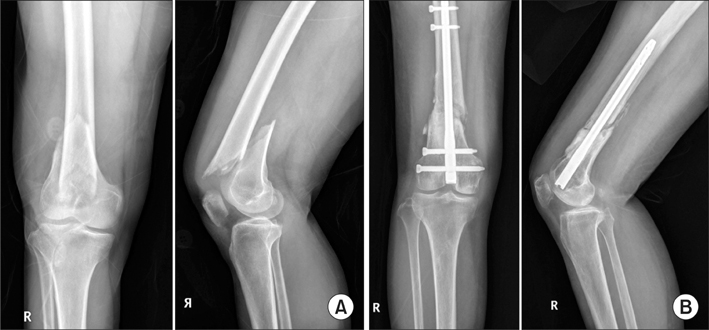
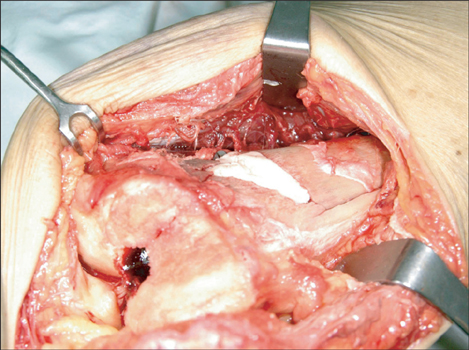
Thirteen patients diagnosed with extra-articular distal femur fracture and osteoporosis and managed with retrograde intramedullary nailing were retrospectively reviewed. Cement augmentation was used in four patients, shape memory alloy was used in eight patients and both were used in one patient. All patients were followed up for more than 2 years. Radiologic alignments. were scored and Tegner and the Lysholm activity score was used for a functional assessment.
RESULTS
The average time to clinical union was 13 weeks (range, 10 to 15 weeks). In 12 of our cases, the total alignment scores were excellent. At the last follow-up, the mean range of motion was 116degrees (range, 110degrees to 125degrees). The average functional score at postoperative 1 year was 2.6 (range, 1 to 5).
CONCLUSIONS
Retrograde intramedullary nailing is a good surgical option for distal femur fracture with osteoporosis. Cement augmentation and shape memory alloy can also be used for added mechanical stability. This surgical technique is very useful for distal femur fracture with osteoporosis as it promotes fracture healing and early rehabilitation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Alloys
Bone Cements
Female
Femoral Fractures/pathology/radiography/*surgery
Femur/pathology/radiography
Fracture Fixation, Intramedullary/instrumentation/*methods
Humans
Male
Osteoporosis, Postmenopausal/*pathology
Osteoporotic Fractures/pathology/radiography/*surgery
Range of Motion, Articular
Retrospective Studies
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006. 37(8):691–697.
Article2. Ng AC, Drake MT, Clarke BL, et al. Trends in subtrochanteric, diaphyseal, and distal femur fractures, 1984-2007. Osteoporos Int. 2012. 23(6):1721–1726.
Article3. Kannus P, Niemi S, Palvanen M, et al. Continuously rising problem of osteoporotic knee fractures in elderly women: nationwide statistics in Finland in 1970-1999 and predictions until the year 2030. Bone. 2001. 29(5):419–423.
Article4. Heiney JP, Barnett MD, Vrabec GA, Schoenfeld AJ, Baji A, Njus GO. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of trigen retrograde intramedullary (i.m.) nail, dynamic condylar screw (DCS), and locking compression plate (LCP) condylar plate. J Trauma. 2009. 66(2):443–449.
Article5. Scheerlinck T, Krallis P, Descamps PY, Hardy D, Delince P. The femoral supracondylar nail: preliminary experience. Acta Orthop Belg. 1998. 64(4):385–392.6. Wahnert D, Hoffmeier K, Frober R, Hofmann GO, Muckley T. Distal femur fractures of the elderly: different treatment options in a biomechanical comparison. Injury. 2011. 42(7):655–659.
Article7. Dall'Oca C, Maluta T, Moscolo A, Lavini F, Bartolozzi P. Cement augmentation of intertrochanteric fractures stabilised with intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2010. 41(11):1150–1155.8. Roth SE, Kreder H, Stephen D, Whyne CM. Biomechanical stability of intramedullary nailed high proximal third tibial fractures with cement augmented proximal screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19(7):457–461.
Article9. Han HS, Oh KW, Kang SB. Retrograde intramedullary nailing for periprosthetic supracondylar fractures of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009. 1(4):201–206.
Article10. Fracture and dislocation compendium. Orthopaedic Trauma Association Committee for Coding and Classification. J Orthop Trauma. 1996. 10:Suppl 1. v–ix. 1–154.11. Handolin L, Pajarinen J, Lindahl J, Hirvensalo E. Retrograde intramedullary nailing in distal femoral fractures: results in a series of 46 consecutive operations. Injury. 2004. 35(5):517–522.
Article12. Tegner Y, Lysholm J. Rating systems in the evaluation of knee ligament injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. (198):43–49.
Article13. Martinet O, Cordey J, Harder Y, Maier A, Buhler M, Barraud GE. The epidemiology of fractures of the distal femur. Injury. 2000. 31:Suppl 3. C62–C63.
Article14. Henderson CE, Kuhl LL, Fitzpatrick DC, Marsh JL. Locking plates for distal femur fractures: is there a problem with fracture healing? J Orthop Trauma. 2011. 25:Suppl 1. S8–S14.
Article15. Tejwani NC, Park S, Iesaka K, Kummer F. The effect of locked distal screws in retrograde nailing of osteoporotic distal femur fractures: a laboratory study using cadaver femurs. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19(6):380–383.
Article16. Ito K, Hungerbuhler R, Wahl D, Grass R. Improved intramedullary nail interlocking in osteoporotic bone. J Orthop Trauma. 2001. 15(3):192–196.
Article17. Gurkan V, Orhun H, Doganay M, et al. Retrograde intramedullary interlocking nailing in fractures of the distal femur. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2009. 43(3):199–205.
Article18. Armstrong R, Milliren A, Schrantz W, Zeliger K. Retrograde interlocked intramedullary nailing of supracondylar distal femur fractures in an average 76-year-old patient population. Orthopedics. 2003. 26(6):627–629.
Article19. Bei C, Wang R, Tang J, Li Q. Effect factors analysis of knee function recovery after distal femoral fracture operation. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009. 23(9):1053–1057.20. Papadokostakis G, Papakostidis C, Dimitriou R, Giannoudis PV. The role and efficacy of retrograding nailing for the treatment of diaphyseal and distal femoral fractures: a systematic review of the literature. Injury. 2005. 36(7):813–822.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of the Distal Femur Fracture with Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing Versus conventional Kuntscher Intramedullary Nailing for Fracture of the Femoral Shaft
- Factors Affecting Posterior Angulation in Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing for Distal Femoral Fractures
- Deformity Correction by Femoral Supracondylar Dome Osteotomy with Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing in Varus Deformity of the Distal Femur after Pathologic Fracture of Giant Cell Tumor
- Factors Affecting the Period of Bone Union When Treating Femoral Fractures with a Retrograde Intramedullary Nail