Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Apr;57(4):213-220. 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.4.213.
The Effect of Aspirin Alone or Aspirin Plus Additional Antiplatelets Therapy on Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Medical Research Institute, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimse@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1718401
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.57.4.213
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
The increasing incidence of cardiovascular disease has led to an increase in the frequency of upper gastrointestinal (GI) hemorrhage due to the use of antiplatelet agents. This study examined the clinical characteristics of patients with upper GI hemorrhage who were administered aspirin alone or a combination treatment of antiplatelet agents.
METHODS
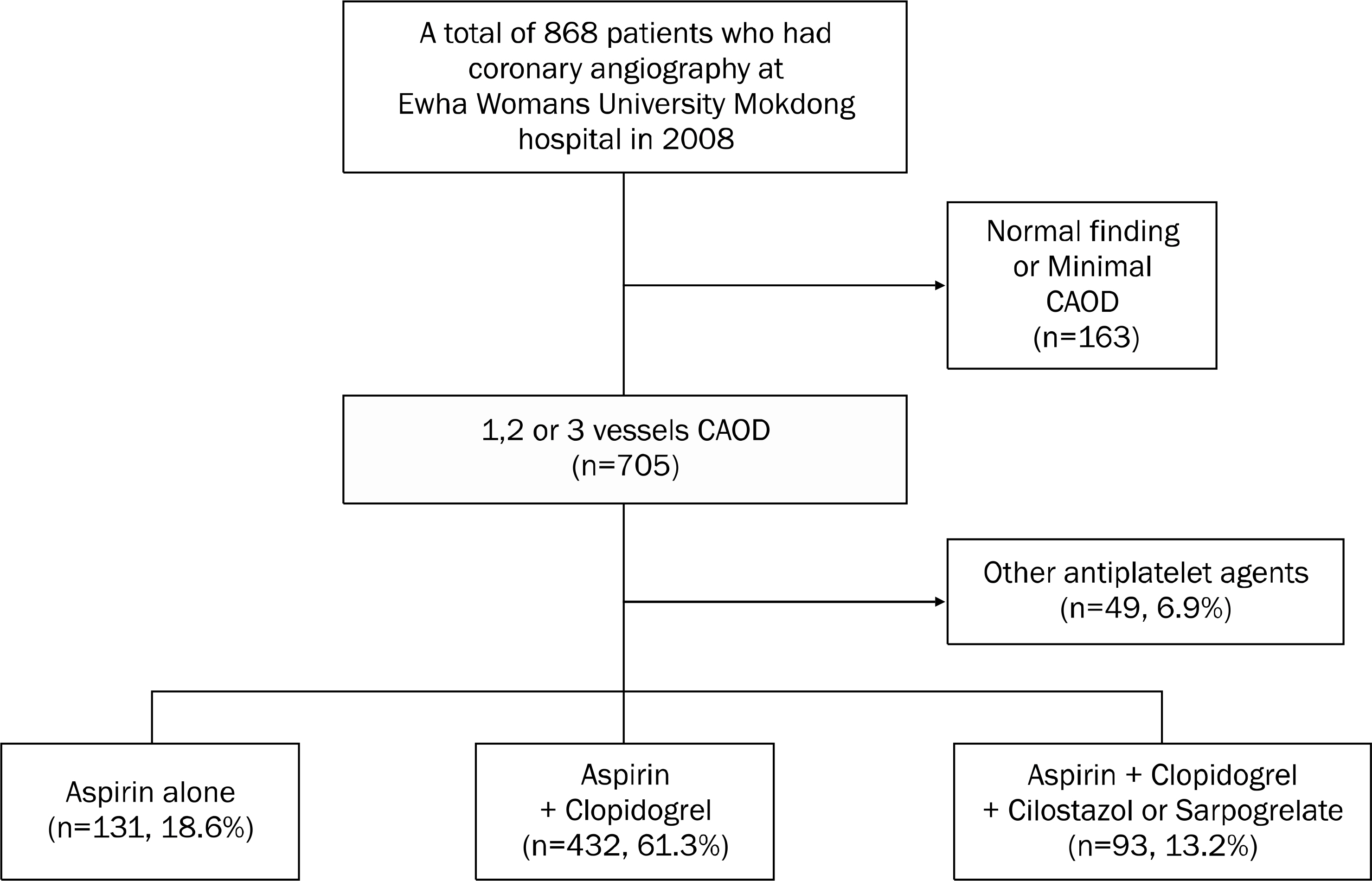
A 656 patients who underwent drug-eluting coronary stenting at Ewha Mokdong Hospital in 2008 were divided into three groups according to the antiplatetlet agents used after the intervention; groups of aspirin alone, aspirin plus clopidogrel, and aspirin, and clopidogrel plus another antiplatelet agent, respectively. Patients admitted with GI hemorrhage in the same period without a medication history of antiplatelet or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were used as the control hemorrhage group. The medical records were reviewed.
RESULTS
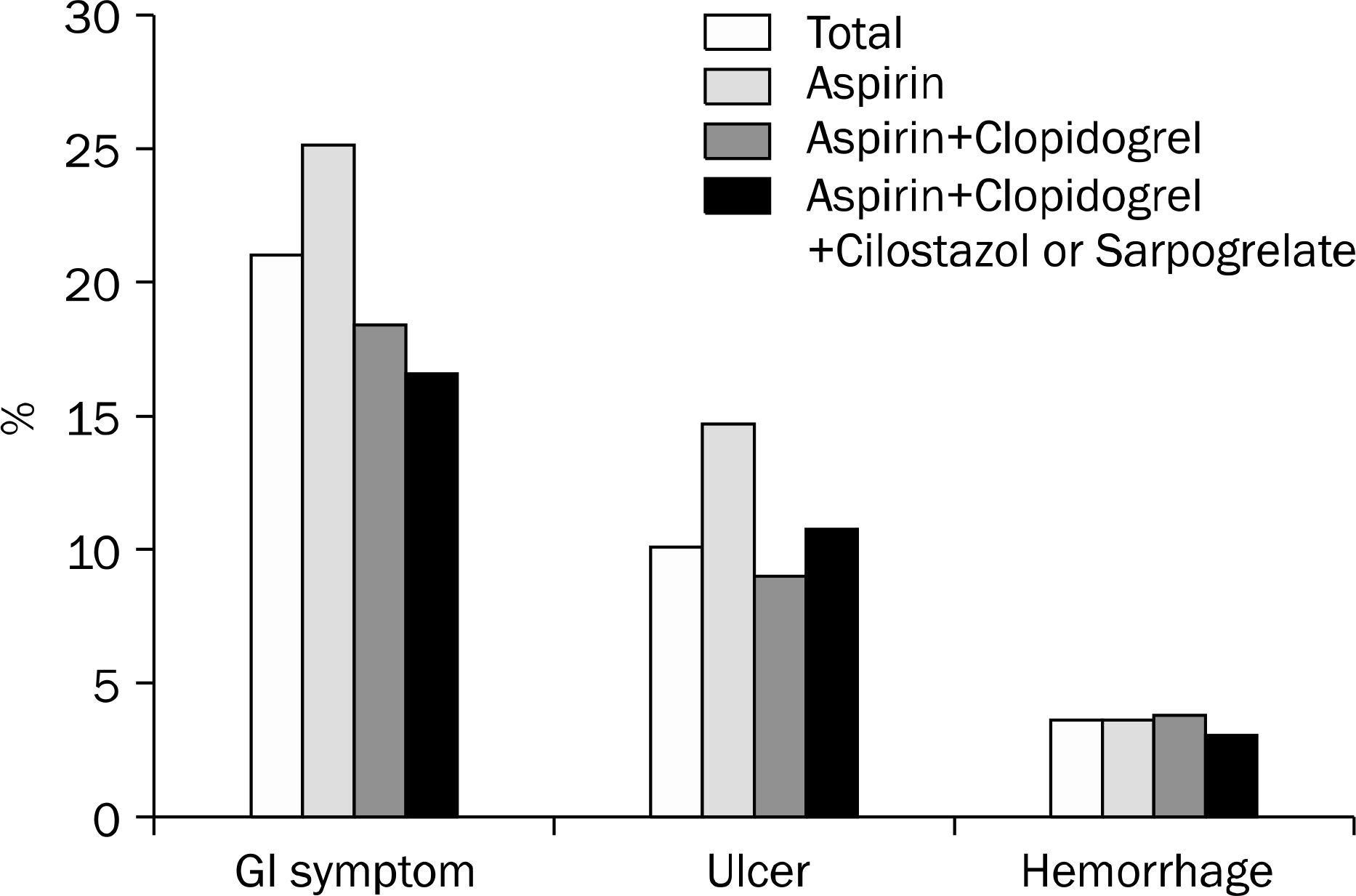
Significant GI symptoms were observed in 21.1% of total patients, of whom 48.2% had ulcers. The upper GI hemorrhage rate was 3.8%. There was no significant difference in the hemorrhage rate between three groups. Compared to the control hemorrhage group, the endoscopic variables of the antiplatelet-related hemorrhage group were not significantly different. However, the Helicobacter pylori infection rate was lower, the admission period was longer, and the mortality rate was higher in the antiplatelet-related hemorrhage group (p<0.05, respectively). There was no direct association between restarting or discontinuance of antiplatelets after the hemorrhage event and mortality.
CONCLUSIONS
Adding other antiplatelet agents to aspirin did not increase the hemorrhage rate. However, active diagnostic and therapeutic efforts are recommended in patients with GI symptoms during antiplatelet therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aspirin/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Cardiovascular Diseases/prevention & control
Drug Therapy, Combination
Drug-Eluting Stents
Endoscopy, Gastrointestinal
Female
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage/*chemically induced/mortality/prevention & control
Helicobacter Infections/complications/epidemiology
Helicobacter pylori
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Peptic Ulcer/complications/epidemiology
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Ticlopidine/adverse effects/analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Does Combination Therapy of Aspirin Plus Antiplatelet Therapy Increase the Risk of Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage?
Jie-Hyun Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011;57(4):205-206. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.4.205.Does Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Increase the Risk of Peptic Ulcer Disease?
Jin Joo Kim, Nayoung Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2014;64(2):67-69. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.2.67.
Reference
-
References
1. Vallurupalli NG, Goldhaber SZ. Gastrointestinal complications of dual antiplatelet therapy. Circulation. 2006; 113:e655–e658.
Article2. Cutlip DE, Baim DS, Ho KK, et al. Stent thrombosis in the modern era: a pooled analysis of multicenter coronary stent clinical trials. Circulation. 2001; 103:1967–1971.3. Wang F, Stouffer GA, Waxman S, Uretsky BF. Late coronary stent thrombosis: early vs. late stent thrombosis in the stent era. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2002; 55:142–147.
Article4. Steinhubl SR, Berger PB, Mann JT, et al. Early and sustained dual oral antiplatelet therapy following percutaneous coronary intervention: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2002; 288:2411–2420.5. Patrono C, Bachmann F, Baigent C, et al. Expert consensus document on the use of antiplatelet agents. The task force on the use of antiplatelet agents in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease of the European society of cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2004; 25:166–181.
Article6. Ng FH, Wong SY, Chang CM, et al. High incidence of clopidogrel-associated gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with previous peptic ulcer disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 18:443–449.
Article7. Moukarbel GV, Signorovitch JE, Pfeffer MA, et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding in high risk survivors of myocardial infarction: the VALIANT Trial. Eur Heart J. 2009; 30:2226–2232.
Article8. Deepak LB, Keith AA, Ch. B, et al. Clopidogrel and aspirin versus aspirin alone for the prevention of atherothrombotic events. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:1706–1717.9. Mehta SR, Yusuf S, Peters RJ, et al. Effects of pretreatment with clopidogrel and aspirin followed by long-term therapy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: the PCI-CURE study. Lancet. 2001; 358:527–533.
Article10. Bhatt DL, Scheiman J, Abraham NS, et al. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. Circulation. 2008; 118:1894–1909.11. Gilard M, Arnaud B, Cornily JC, et al. Influence of omeprazole on the antiplatelet action of clopidogrel associated with aspirin: the randomized, double-blind OCLA (Omeprazole CLopidogrel Aspirin) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:256–260.12. Rao SV, O'Grady K, Pieper KS, et al. Impact of bleeding severity on clinical outcomes among patients with acute coronary syndromes. Am J Cardiol. 2005; 96:1200–1206.
Article13. Twomley KM, Rao SV, Becker RC. Proinflammatory, immunomodulating, and prothrombotic properties of anemia and red blood cell transfusions. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2006; 21:167–174.
Article14. Biondi-Zoccai GG, Lotrionte M, Agostoni P, et al. A systematic review and metaanalysis on the hazards of discontinuing or not adhering to aspirin among 50,279 patients at risk for coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 2006; 27:2667–2674.15. Iakovou I, Schmidt T, Bonizzoni E, et al. Incidence, predictors, and outcome of thrombosis after successful implantation of drug-eluting stents. JAMA. 2005; 293:2126–2130.
Article16. Seddighzadeh A, Wolf AT, Parasuraman S, et al. Gastrointestinal complications after 3 months of dual antiplatelet therapy for drug-eluting stents as assessed by wireless capsule endoscopy. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2009; 15:171–176.
Article17. O'Donoghue ML, Braunwald E, Antman EM, et al. Pharmacodynamic effect and clinical efficacy of clopidogrel and prasugrel with or without a proton-pump inhibitor: an analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet. 2009; 374:989–997.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Does Combination Therapy of Aspirin Plus Antiplatelet Therapy Increase the Risk of Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage?
- Endoscopic Sphincterotomy and Aspirin
- A Comparative Study of Therapeutic Effect of Intravenous Gammaglobulin plus Aspirin Versus Aspirin Alone in Kawasaki Syndrome
- A Case of Dieulafoy's Lesion Presenting Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding in a Child in the Acute Phase of Kawasaki Disease
- Chemoprevention of Gastric Cancer: Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Including Aspirin