Yonsei Med J.
2005 Aug;46(4):449-455. 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.4.449.
Obesity, Insulin Resistance and Cancer Risk
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Epidemiology and Health Promotion, Graduate School of Public Health, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. jsunha@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, MD, USA.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1716512
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2005.46.4.449
Abstract
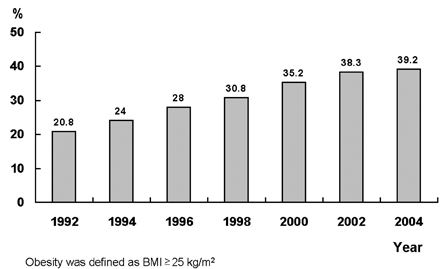
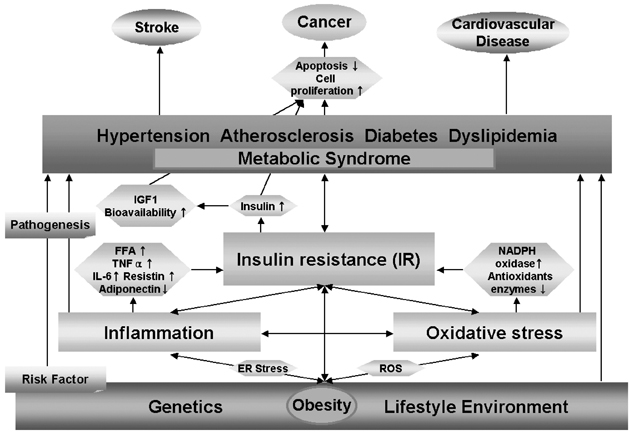
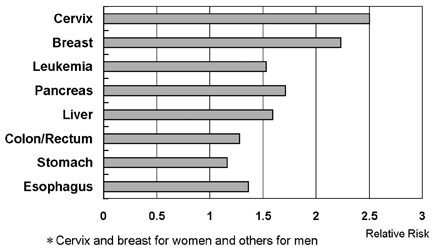
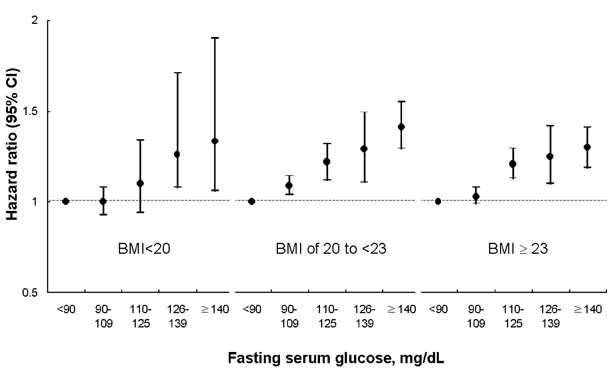
- Obesity is a known cause of metabolic syndrome which includes Type II diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. It is well documented that insulin resistance contributes to the mortality and the incidence of metabolic syndromes including central obesity, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia and hypertension. Both obesity and diabetes are emerging topics for researchers to consider as having a possible causal association with cancer since the two factors have been viewed as risk factors for cancer. The present paper introduced the hypothesis of a possible causal relationship between obesity, insulin resistance and cancer and reviews relevant existing studies in this area. More efforts and studies are needed to clarify the mechanisms and the common risk factors which might be incorporated into interventions to prevent cancer and cardiovascular diseases as top causes of death.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Blockade of Oxidative Stress by Vitamin C Ameliorates Albuminuria and Renal Sclerosis in Experimental Diabetic Rats
Eun Young Lee, Mi Young Lee, Soon Won Hong, Choon Hee Chung, Sae Yong Hong
Yonsei Med J. 2007;48(5):847-855. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.847.
Reference
-
1. Garrison RJ, Higgins MW, Kannel WB. Obesity and coronary heart disease. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1996. 7:199–202.2. Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, et al. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2002. 288:2709–2716.3. Calle EE, Kaaks R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004. 4:579–591.4. Komninou D, Ayonote A, Richie JP Jr, Rigas B. Insulin resistance and its contribution to colon carcinogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2003. 228:396–405.5. Renehan AG, Howell A. Preventing cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. Lancet. 2005. 365:1449–1451.6. Dandona P, Aljada A, Chaudhuri A, Mohanty P, Garg R. Metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive perspective based on interactions between obesity, diabetes, and inflammation. Circulation. 2005. 111:1448–1454.7. Maddux BA, See W, Lawrence JC Jr, Goldfine AL, Goldfine ID, Evans JL. Protection against oxidative stress-induced insulin resistance in rat L6 muscle cells by mircomolar concentrations of alpha-lipoic acid. Diabetes. 2001. 50:404–410.8. Matsuoka T, Kajimoto Y, Watada H, Kaneto H, Kishimoto M, Umayahara Y, et al. Glycation-dependent, reactive oxygen species-mediated suppression of the insulin gene promoter activity in HIT cells. J Clin Invest. 1997. 99:144–150.9. Nakazono K, Watanabe N, Matsuno K, Sasaki J, Sato T, Inoue M. Does superoxide underlie the pathogenesis of hypertension? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991. 88:10045–10048.10. Ohara Y, Peterson TE, Harrison DG. Hypercholesterolemia increases endothelial superoxide anion production. J Clin Invest. 1993. 91:2546–2551.11. Keaney JF Jr, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Wilson PW, Lipinska I, Corey D, et al. Obesity and systemic oxidative stress: clinical correlates of oxidative stress in the Framingham Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003. 23:434–439.12. Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, et al. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2004. 114:1752–1761.13. Giovannucci E. Insulin and colon cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 1995. 6:164–179.14. Weiderpass E, Partanen T, Kaaks R, Vainio H, Porta M, Kauppinen T, et al. Occurrence, trends and environment etiology of pancreatic cancer. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1998. 24:165–174.15. Kaaks R, Lukanova A, Kurzer MS. Obesity, endogenous hormones, and endometrial cancer risk: a synthetic review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002. 11:1531–1543.16. Kaaks R. Nutrition, hormones, and breast cancer: is insulin the missing link? Cancer Causes Control. 1996. 7:605–625.17. Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A, Friend KE. The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev. 2000. 21:215–244.18. Chapman IM, Hartman ML, Pieper KS, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Hintz RL, et al. Recovery of growth hormone release from suppression by exogenous insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I): evidence for a suppressive action of free rather than bound IGF-I. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. 83:2836–2842.19. The DECODE Study Group. Age- and sex-specific prevalences of diabetes and impaired glucose regulation in 13 European cohorts. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:61–69.20. Weiderpass E, Gridley G, Persson I, Nyren O, Ekbom A, Adami HO. Risk of endometrial and breast cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int J Cancer. 1997. 71:360–363.21. Hu FB, Manson JE, Liu S, Hunter D, Colditz GA, Michels KB, et al. Prospective study of adult onset diabetes mellitus (type 2) and risk of colorectal cancer in women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999. 91:542–547.22. Hjalgrim H, Frisch M, Ekbom A, Kyvik KO, Melbye M, Green A. Cancer and diabetes--a follow-up study of two population-based cohorts of diabetic patients. J Intern Med. 1997. 241:471–475.23. Wolf I, Sadetzki S, Catane R, Karasik A, Kaufman B. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005. 6:103–111.24. Jee SH, Ohrr H, Sull JW, Yun JE, Ji M, Samet JM. Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. JAMA. 2005. 293:194–202.25. Cooney KA, Gruber SB. Hyperglycemia, Obesity, and Cancer Risk on the Horizon. JAMA. 2005. 293:235–236.26. Key TJ, Verkasalo PK, Banks E. Epidemiology of breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2001. 2:133–140.27. Yancik R, Wesley MN, Ries LA, Havlik RJ, Edwards BK, Yates JW. Effect of age and comorbidity in postmenopausal breast cancer patients aged 55 years and older. JAMA. 2001. 285:885–892.28. Will JC, Galuska DA, Vinicor F, Calle EE. Colorectal cancer: another complication of diabetes mellitus? Am J Epidemiol. 1998. 147:816–825.29. Nilsen TI, Vatten LJ. Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk and physical activity, diabetes, hyperinsulinemia hypothesis. Br J Cancer. 2001. 417–422.30. Kono S, Honjo S, Todoroki I, Nishiwaki M, Hamada H, Nishikawa H, et al. Glucose intolerance and adenomas of the sigmoid colon in Japanese men (Japan). Cancer Causes Control. 1998. 9:441–446.31. La Vecchia C, Negri E, Decarli A, Franceschi S. Diabetes mellitus and colorectal cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 1997. 6:1007–1010.32. Lee SY, Kim MT, Jee SH, Im JS. Does hypertension increase mortality risk from lung cancer? A prospective cohort study on smoking, hypertension and lung cancer risk among Korean men. J Hypertens. 2002. 20:617–622.33. Choi MY, Jee SH, Sull JW, Nam CM. The effect of hypertension on the risk for kidney cancer in Korean men. Kidney Int. 2005. 67:647–652.34. Tsushima M, Nomura AM, Lee J, Stemmermann GN. Prospective study of the association of serum triglyceride and glucose with colorectal cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. 50:499–505.35. Han C, Zhang HT, Du L, Liu X, Jing J, Zhao X, et al. Serum levels of leptin, insulin, and lipids in relation to breast cancer in China. Endocrine. 2005. 26:19–24.36. Dandona P, Aljada A, Mohanty P. The anti-inflammatory and potential anti-atherogenic effect of insulin: a new paradigm. Diabetologia. 2002. 45:924–930.