Yonsei Med J.
2006 Feb;47(1):131-134. 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.131.
Caroli's Syndrome with Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease in a Two Month Old Infant
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Kidney Disease, Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jsyonse@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1715883
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.131
Abstract
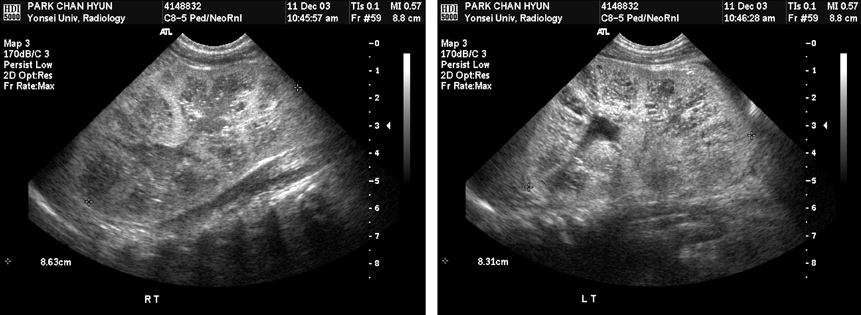
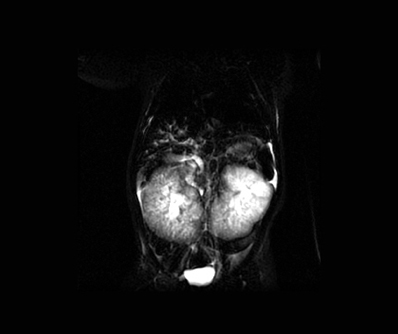
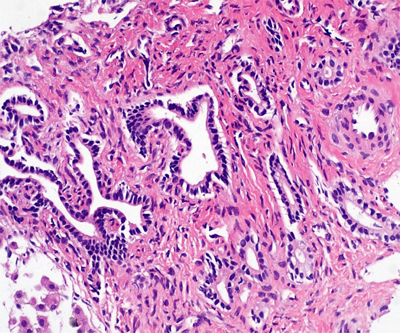
- Caroli's syndrome is a rare congenital disorder that involves intrahepatic bile duct ectasia and congenital hepatic fibrosis, frequently seen with concomitant autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Literature on infants with ARPKD is rare. Here, we present a case of a two month old boy who was diagnosed with Caroli's syndrome and ARPKD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Desmet VJ. Ludwig symposium on biliary disorders-part I. Pathogenesis of ductal plate anomalities. Mayo Clin Proc. 1998. 73:80–89.2. Levy AD, Rhormann CA Jr, Murakata LA, Lonergan GJ. Caroli's disease: radiologic spectrum with pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:1053–1057.3. Totkas S, Hohenberger P. Cholangiocellular carcinoma associated with segmental Caroli's disease. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2000. 26:520–521.4. Wu KL, Changchien CS, Kuo CM, Chuah SK, Chiu YC, Kuo CH. Caroli's disease - a report of two siblings. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. 14:1397–1399.5. Ribeiro A, Reddy RK, Bernstein D, Jeffers L, Schiff ER. Caroli's syndrome in twin sisters. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996. 91:1024–1026.6. Bergmann C, Senderek J, Sedlacek B, Pegiazoglou I, Puglia P, Eggermann T, et al. Spectrum of mutations in the gene for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD/PKHD1). J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. 14:76–89.7. Wang S, Luo Y, Wilson PD, Witman GB, Zhou J. The autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease protein is localized to primary cilia, with concentration in the basal body area. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. 15:592–602.8. Zerres K, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Senderek J, Eggermann T, Bergmann C. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). J Nephrol. 2003. 16:453–458.9. Huang SM, Yu Sc, Tsang Ym, Wei Tc, Hsu Sc, Chen KM. Complication of percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography and biliary drainage. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1989. 96:446–452.10. Harjai MM, Bal RK. Caroli syndrome. Pediatr Surg Int. 2000. 16:431–432.11. Ros E, Navarro S, Bru C, Gilabert R, Bianchi L, Bruguera M. Ursodeoxycholic acid treatment of primary hepatolithiasis in Caroli's syndrome. Lancet. 1993. 342:404–406.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Caroli Syndrome with Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Caroli's Disease Combined with Colon Cancer and Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease Confirmed to PKHD1 Gene Mutation: A Case of PKHD1 Gene Mutation
- Pulmonary hypertension in a child with juvenile-type autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
- Newly Detected PKHD1 Gene Mutation in a Newborn with Fatal Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease