Yonsei Med J.
2006 Jun;47(3):354-358. 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.3.354.
Human Brain Astrocytes Mediate TRAIL-mediated Apoptosis after Treatment with IFN-gamma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Institute for Immunology and Immunological Diseases and Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Seoul, Korea. inhong@yumc.yonse.ac.kr
- KMID: 1715853
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2006.47.3.354
Abstract
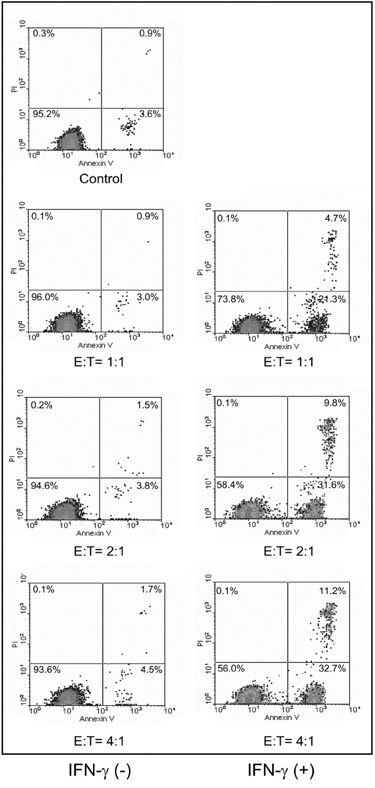
- TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) expressions were studied in primary human brain astrocytes in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines. When astrocytes were treated with IL-1beta TNF-alphaor IFN-gamma TRAIL was induced in cultured fetal astrocytes. In particular, IFN-gammainduced the highest levels of TRAIL in cultured astrocytes. When astrocytes were pre-reated with IFN-gamma they induced apoptosis in TRAIL-sensitive Peer cells. Our results suggest that IFN-gamma modulates the expression of TRAIL in astrocytes, which may enhance cytotoxic sensitivity of infiltrating immune cells or brain cells other than astrocytes during inflammation of brain.
MeSH Terms
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/genetics/*metabolism
TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand
Membrane Glycoproteins/genetics/*metabolism
Interferon Type II/*pharmacology
Humans
Cells, Cultured
Astrocytes/*cytology/drug effects/metabolism
Apoptosis Regulatory Proteins/genetics/*metabolism
Apoptosis/*drug effects/physiology
Antineoplastic Agents/*pharmacology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bach JH, Chae HS, Rah JC, Lee MW, Park CH, Choi SH, et al. C-terminal fragment of amyloid precursor protein induces astrocytosis. J Neurochem. 2001. 78:109–120.2. Andersson K, Olofsson A, Nielsen EH, Svehag SE, Lundgren E. Only amyloidogenic intermediates of transthyretin induce apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. 294:309–314.3. Dowling P, Shang G, Raval S, Menonna J, Cook S, Husar W. Involvement of the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) receptor/ligand system in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1996. 184:1513–1518.4. Shi B, De Girolami U, He J, Wang S, Lorenzo A, Busciglio J, et al. Apoptosis induced by HIV-1 infection of the central nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1996. 98:1979–1990.5. Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995. 3:673–682.6. Frank S, Kohler U, Schackert G, Schackert HK. Expression of TRAIL and its receptors in human brain tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. 257:454–459.7. Nakamura M, Rieger J, Weller M, Kim J, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H. APO2L/TRAIL expression in human brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2000. 99:1–6.8. Rieger J, Ohgaki H, Kleihues P, Weller M. Human astrocytic brain tumors express AP02L/TRAIL. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 1999. 97:1–4.9. Choi C, Park JY, Lee J, Shin EC, Ahn YS, Kim CH, et al. FasL and Fas are expressed constitutively in human astrocytes and the expression is increased with IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α or IFN-γ. J Immunol. 1999. 162:1889–1895.10. Lee J, Shin JS, Park JY, Kwon D, Choi SJ, Kim SJ, et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase modulates expression of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand induced by interferon-gamma in fetal brain astrocytes. J Neurosci Res. 2002. 74:884–890.11. Kayagaki N, Yamaguchi N, Nakayama M, Takeda K, Akiba H, Tsutsui H, et al. Expression and function of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand on murine activated NK cells. J Immunol. 1999. 163:1906–1913.12. Eddleston M, Mucke L. Molecular profile of reactive astrocytes: implications for their role in neurologic disease. Neuroscience. 1993. 54:15–36.13. Aloisi F, Borsellino G, Care A, Testa U, Gallo P, Russo C, et al. Cytokine regulation of astrocyte function: in-vitro studies using cells from the human brain. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1995. 13:265–274.14. Dorr J, Bechmann I, Waiczies S, Aktas O, Walczak H, Krammer PH, et al. Lack of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand but presence of its receptors in the human brain. J Neurosci. 2002. 22:RC209. (1-5).15. Falsig J, Latta M, Leist M. Defined inflammatory states in astrocyte cultures: correlation with susceptibility towards CD95-driven apoptosis. J Neurochem. 2004. 88:181–193.16. Langaas V, Shahzidi S, Johnsen JI, Smedsrod B, Sveinbjornsson B. Interferon-gamma modulates TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2001. 21:3733–3738.17. Griffith TS, Wiley SR, Kubin MZ, Sedger LM, Maliszewski CR, Fanger NA. Monocyte-mediated tumoricidal activity via the tumor necrosis factor-related cytokine. TRAIL. J Exp Med. 1999. 189:1343–1354.18. Smyth MJ, Cretney E, Takeda K, Wiltrout RH, Sedger LM, Kayagaki N, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) contributes to interferon gamma-dependent natural killer cell protection from tumor metastasis. J Exp Med. 2001. 193:661–670.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hydrogen Peroxide Upregulates TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) Expression in Human Astroglial Cells, and Augments Apoptosis of T Cells
- Effects of Cycloheximide and Dexamethasone on Fas - Mediated Apopthsis in Primary Human Astrocytes
- Paxilline enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of glioma cells via modulation of c-FLIP, survivin and DR5
- Activated stellate cells express the TRAIL receptor-2/death receptor-5 and undergo TRAIL-mediated apoptosis
- Sensitization of TNF alpha and Agonistic FAS/CD95 Antibody-Induced Apoptosis by INF gamma on Neuroblastoma Cells