Korean J Radiol.
2013 Aug;14(4):653-661. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.4.653.
Anterior Commissure - Posterior Commissure Revisited
- Affiliations
-
- 1Neuroscience Research Institute, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon 405-760, Korea. zcho@gachon.ac.kr
- KMID: 1715771
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.4.653
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
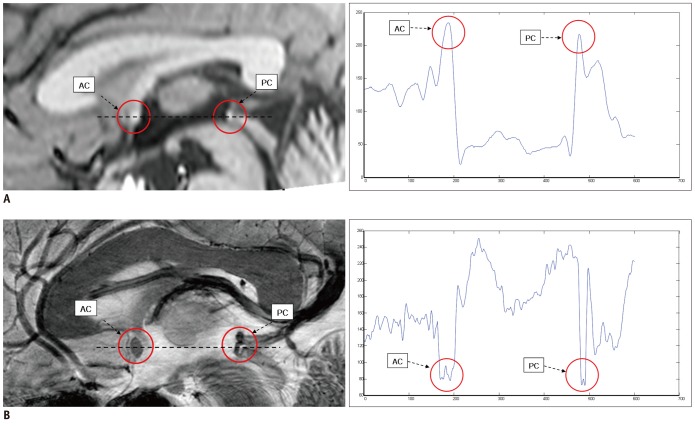
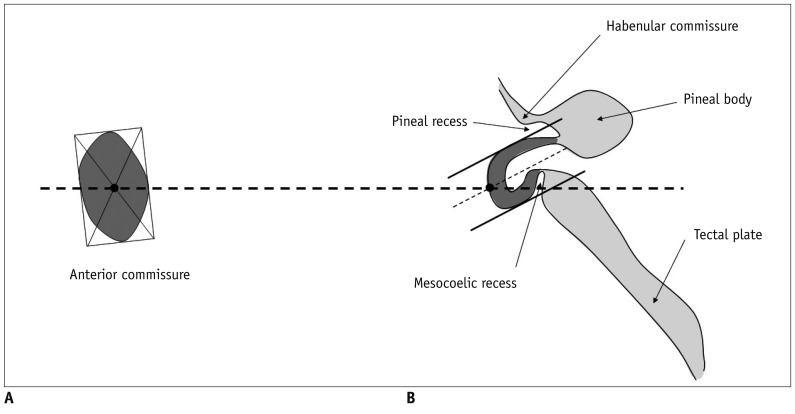
The anterior commissure (AC) and posterior commissure (PC) are the two distinct anatomic structures in the brain which are difficult to observe in detail with conventional MRI, such as a 1.5T MRI system. However, recent advances in ultra-high resolution MRI have enabled us to examine the AC and PC directly. The objective of the present study is to standardize the shape and size of the AC and PC using a 7.0T MRI and to propose a new brain reference line.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
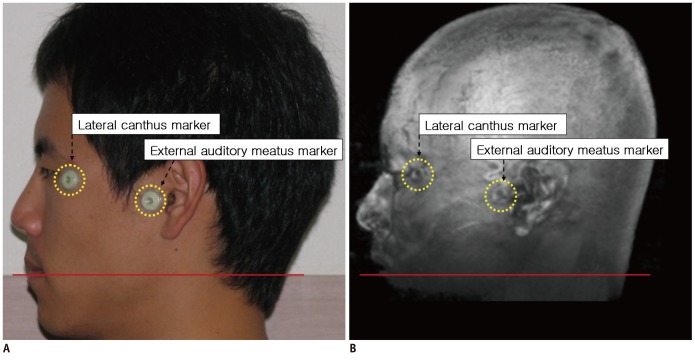
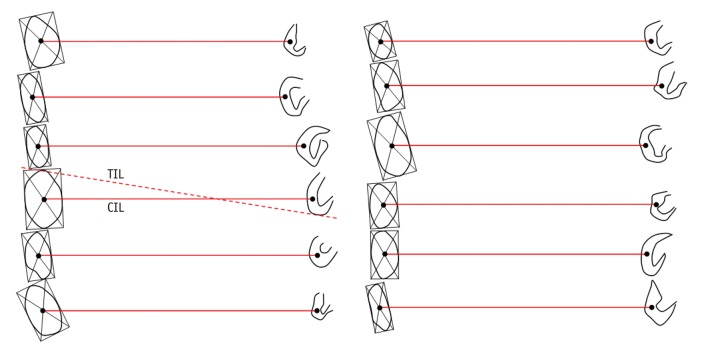
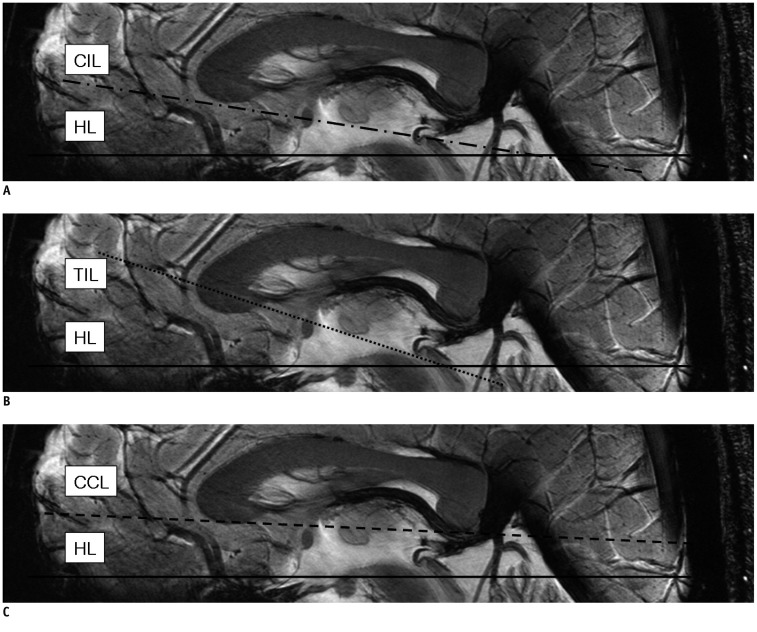
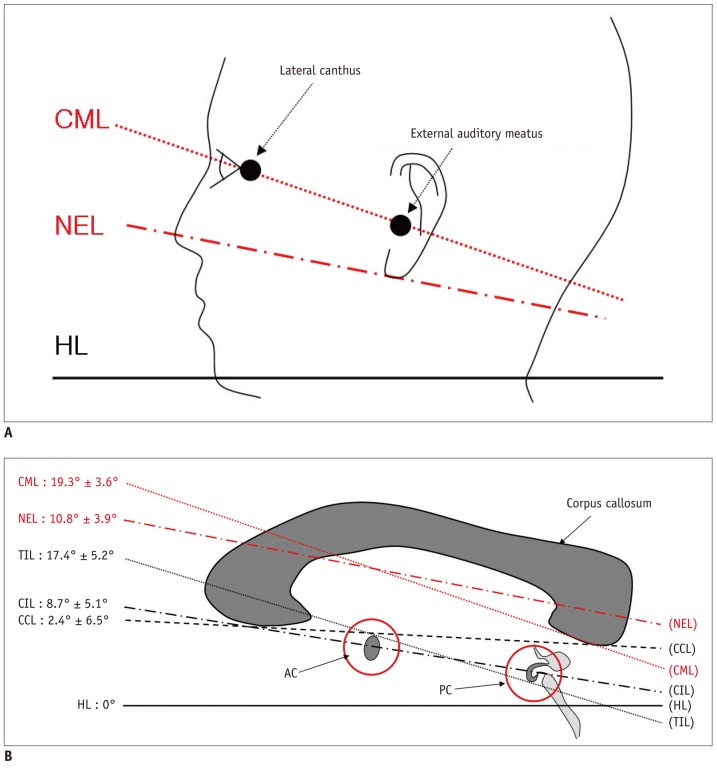
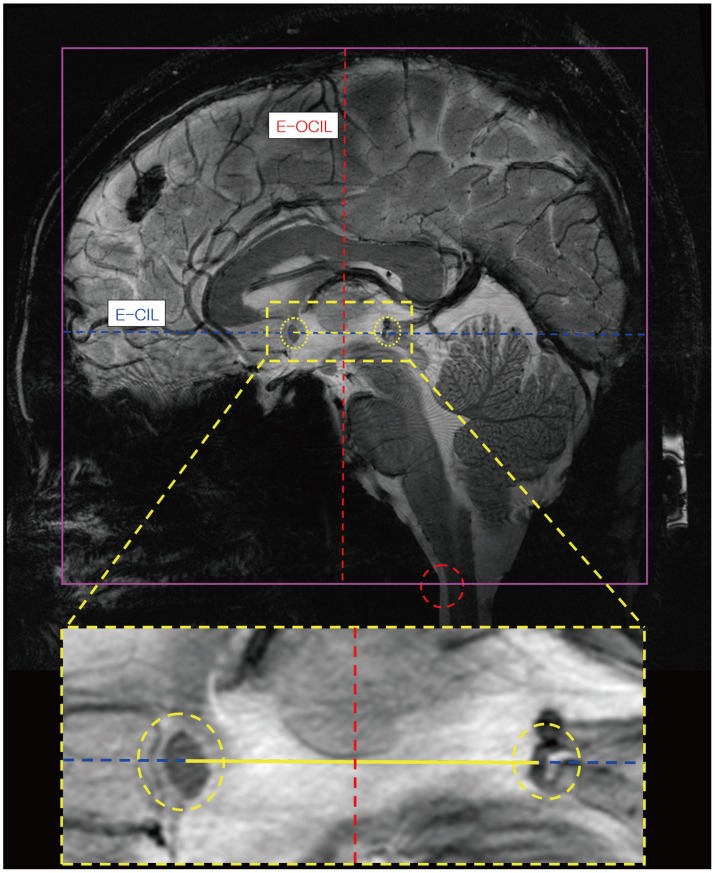
Thirty-four, 21 males and 13 females, healthy volunteers were enrolled in this study. After determining the center of each AC and PC, we defined the connection of these centers as the central intercommissural line (CIL). We compared the known extra- and intra-cerebral reference lines with the CIL to determine the difference in the angles. Additionally, we obtained horizontal line from flat ground line of look front human.
RESULTS
The difference in angle of the CIL and the tangential intercommissural line (TIL) from the horizontal line was 8.7 +/- 5.1 (11 +/- 4.8) and 17.4 +/- 5.2 (19.8 +/- 4.8) degrees in males and females, respectively. The difference in angle between the CIL and canthomeatal line was 10.1 in both male and female, and there was no difference between both sexes. Likewise, there was no significant difference in angle between the CIL and TIL between both sexes (8.3 +/- 1.1 in male and 8.8 +/- 0.7 in female).
CONCLUSION
In this study, we have used 7.0T MRI to define the AC and PC quantitatively and in a more robust manner. We have showed that the CIL is a reproducible reference line and serves as a standard for the axial images of the human brain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cho ZH, Chung MS, Chi JG, Na DL. 7.0 Tesla MRI Brain Atlas: In Vivo Atlas with Cryomacrotome Correlation. Heidelberg: Springer;2010.2. Cho ZH, Kim YB, Han JY, Min HK, Kim KN, Choi SH, et al. New brain atlas-mapping the human brain in vivo with 7.0 T MRI and comparison with postmortem histology: will these images change modern medicine? Int J Imaging Syst Technol. 2008; 18:2–8.
Article3. Weiss KL, Pan H, Storrs J, Strub W, Weiss JL, Jia L, et al. Clinical brain MR imaging prescriptions in Talairach space: technologist- and computer-driven methods. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:922–929. PMID: 12748095.4. Nowinski WL. Modified Talairach landmarks. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001; 143:1045–1057. PMID: 11685613.
Article5. Choi DY, Chung SC, Lee BY, Eom JS, Sohn JH. Development of Korean standard brain templates according to gender and age. Korean J Anat. 2004; 37:255–261.6. Talairach J, Tournoux P. Co-planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain. New York: Thieme;1988.7. Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W, Hassler RG. Atlas of Stereotaxy of the Human Brain. 2nd ed. Thieme: Stuttgart;1977.8. Lee U, Kim YB, Kim MH, Ahn SG, Kang DS, Park CW. Basic estimation of intracerebral reference points: data analysis from 169 Korean people. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 1995; 24:1056–1060.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Normal Width of the Anterior Commissure of the True Vocal Cord in Korean Adults Measured by Helical CT
- Avulsion of Aortic Commissure: Rare Cause of Aortic Regurgitation: 2 case reports
- A Rare Midbrain Syndrome with Bilateral Cerebellar Ataxia and Isolated Superior Rectus Palsy: Wernekinck Commissure Syndrome
- Interthalamic adhesion in humans: a gray commissure?
- A New 'Y' Shape Partial Laryngectomy for Supraglottic Carcinoma with Anterior Commissure Invasion or Encroachment