Incidence of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. beyil@snu.ac.kr
- 2Statistical Research Committee, The Korean Society of Neonatology, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1714204
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.914
Abstract
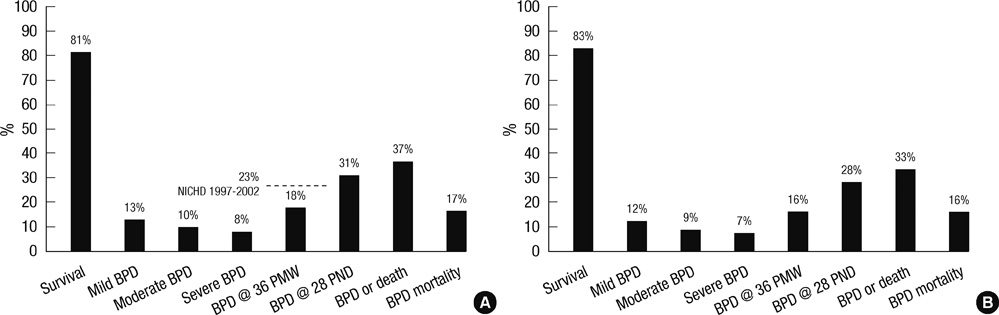
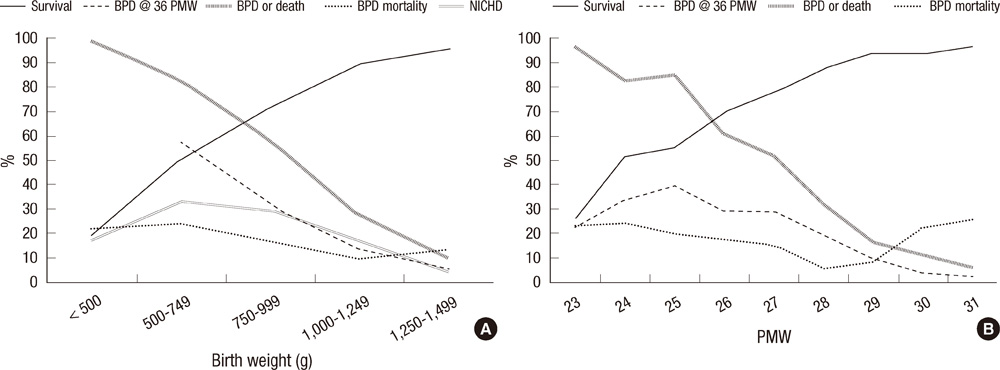
- A nationwide survey was conducted to determine the incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in Korea and the intercenter differences in survival and BPD rates among preterm infants. Questionnaires were sent to all registered neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). The questionnaires inquired about the survival and BPD rates of very low birth weight (VLBW, < 1,500 g) infants who had been admitted to each NICU from 2007 to 2008. BPD was defined as requiring oxygen at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age. Almost all level III NICUs replied. During the study period, 3,841 VLBW infants were born in the NICUs that responded to the survey. The survival rate was 81% and the BPD rate was 18%. Combined outcome of BPD or death rate was 37%. The BPD rate and combined outcome of BPD or death rate varied considerably from 5% to 50% and 11% to 73%, respectively across the centers. There was no significant correlation between the survival rate and the BPD rate across the centers. In conclusion, the incidence of BPD among VLBW infants in Korea during the study period was 18%, and a considerable intercenter difference in BPD rates was noted.
MeSH Terms
-
Anti-Inflammatory Agents/therapeutic use
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia/drug therapy/*epidemiology/mortality
Demography
Dexamethasone/therapeutic use
Gestational Age
Humans
Incidence
Infant, Newborn
Infant, Premature
Infant, Very Low Birth Weight
Intensive Care Units, Neonatal
Questionnaires
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Survival Rate
Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Dexamethasone
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Changes in neonatal outcomes in Korea
So Young Kim
J Korean Med Assoc. 2016;59(7):498-505. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2016.59.7.498.Clinical characteristics of lower respiratory infections in preterm children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Na Hyun Lee, Se Jin Kim, Hee Joung Choi
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(2):92-98. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.2.92.Characteristics of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Very Low Birth Weight Infants according to the Timing of Dexamethasone Administration
Hae Yun Lee, Hyoung Jin Lee, Ji Won Koh, In Gu Song, Sae Yun Kim, Young Hwa Jung, Seung Han Shin, Chang Won Choi, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim, Beyong Il Kim, Jung-Hwan Choi
Korean J Perinatol. 2015;26(4):321-328. doi: 10.14734/kjp.2015.26.4.321.The Incidence and Survival Rate of Very Low Birth Weight Infants in Korea (2013–2016): A Comparison of the Statistics Korea and the Korean Neonatal Network and Improvements
Jisu Kim, Hye-Eun Kim, Kyung-Suk Lee, Sung-Hoon Chung, Yong-Sung Choi, Chong-Woo Bae, Korean Neonatal Network
Perinatology. 2019;30(1):1-7. doi: 10.14734/PN.2019.30.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Hahn WH, Chang JY, Chang YS, Shim KS, Bae CW. Recent trends in neonatal mortality in very low birth weight Korean infants: in comparison with Japan and the USA. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. 26:467–473.2. Vohr BR, Wright LL, Dusick AM, Perritt R, Poole WK, Tyson JE, Steichen JJ, Bauer CR, Wilson-Costello DE, Mayes LC. Neonatal Research Network. Center differences and outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2004. 113:781–789.3. Cotten CM, Oh W, McDonald S, Carlo W, Fanaroff AA, Duara S, Stoll B, Laptook A, Poole K, Wright LL, Goldberg RN. NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Prolonged hospital stay for extremely premature infants: risk factors, center differences, and the impact of mortality on selecting a best-performing center. J Perinatol. 2005. 25:650–655.4. Payne NR, Lacorte M, Sun S, Karna P, Lewis-Hunstiger M, Goldsmith JP. Evaluation and development of potentially better practices to reduce bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2006. 118:S65–S72.5. Lim IS, Choi CW, Kim BI, Kim DH, Sim SY, Kim EK, Kim HS, Choi JH. Clinical usefulness of the new definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2006. 13:9–16.6. Na BM, Kim MJ, Kim WH. Recent outcomes of very low birth weight infants at Cheongju area. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2006. 13:128–138.7. Sung KH, Kim MH, Kim ER, Shim JW, Lee JJ, Im JW, Jin HS. Epidemiology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in Korea: multi-center study. Korean J Perinatol. 2009. 20:225–233.8. Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 163:1723–1729.9. Wang SW, Lee YA, Park SE, Shin JB, Hong YR, Park JJ, Lee JA, Son SH, Byun SO, Kim JP. Changes in the outcomes of very low birth weight infants in Busan Area. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2007. 14:206–214.10. Kim SH, Lee KH, Lee SH, You DK, Choi SJ, Hwang JH, Choi CW, Shim JW, Yoon HK, Yang SH, et al. The comparison of severity according to preceding causes of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very low birth weight infants. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2003. 10:47–54.11. Fanaroff AA, Stoll BJ, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Stark AR, Bauer CR, Donovan EF, Korones SB, Laptook AR, et al. Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007. 196:147.e1–147.e8.12. Payne NR, LaCorte M, Karna P, Chen S, Finkelstein M, Goldsmith JP, Carpenter JH. Breathsavers Group, Vermont Oxford Network Neonatal Intensive Care Quality Improvement Collaborative. Reduction of bronchopulmonary dysplasia after participation in the Breathsavers Group of the Vermont Oxford Network Neonatal Intensive Care Quality Improvement Collaborative. Pediatrics. 2006. 118:S73–S77.13. Zeitlin J, Draper ES, Kollée L, Milligan D, Boerch K, Agostino R, Gortner L, Van Reempts P, Chabernaud JL, Gadzinowski J, et al. Differences in rates and short-term outcome of live births before 32 weeks of gestation in Europe in 2003: results from the MOSAIC cohort. Pediatrics. 2008. 121:e936–e944.14. de Kleine MJ, den Ouden AL, Kollée LA, Ilsen A, van Wassenaer AG, Brand R, Verloove-Vanhorick SP. Lower mortality but higher neonatal morbidity over a decade in very preterm infants. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2007. 21:15–25.15. van Marter LJ. Abman SH, editor. Epidemiology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. 2010. New York: Informa Healthcare USA Inc;223–266.16. Avery ME, Tooley WH, Keller JB, Hurd SS, Bryan MH, Cotton RB, Epstein MF, Fitzhardinge PM, Hansen CB, Hansen TN, et al. Is chronic lung disease in low birth weight infants preventable? A survey of eight centers. Pediatrics. 1987. 79:26–30.17. Walsh MC, Wilson-Costello D, Zadell A, Newman N, Fanaroff A. Safety, reliability, and validity of a physiologic definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol. 2003. 23:451–456.18. Walsh MC, Yao Q, Gettner P, Hale E, Collins M, Hensman A, Everette R, Peters N, Miller N, Muran G, et al. Impact of a physiologic definition on bronchopulmonary dysplasia rates. Pediatrics. 2004. 114:1305–1311.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- Prevention and Treatment of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- Radiological analysis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- The effects of early surfactant treatment and minimal ventilation on prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in respiratory distress syndrome
- Prevention of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia