J Korean Med Sci.
2010 May;25(5):712-715. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.5.712.
Characteristics of P wave in Patients with Sinus Rhythm after Maze Operation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. seil@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713954
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.5.712
Abstract
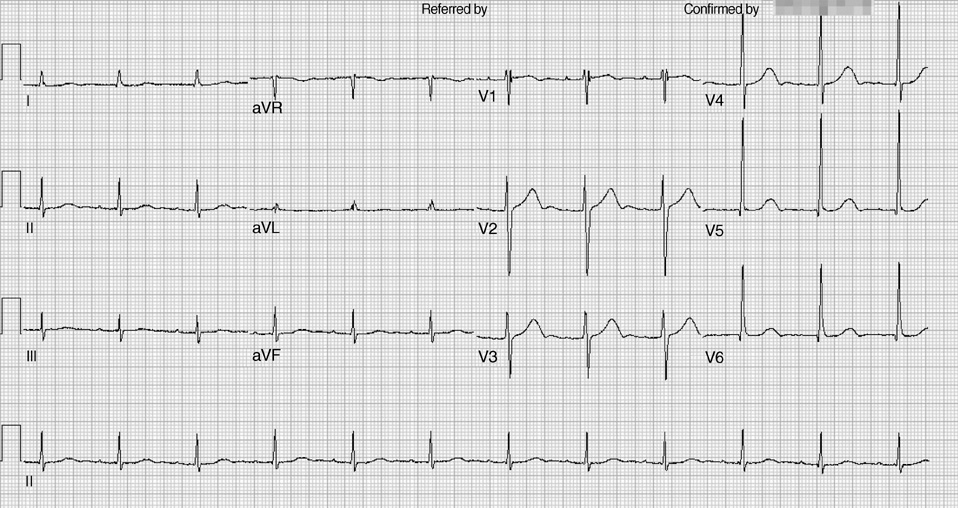
- Maze operation could alter P wave morphology in electrocardiogram (ECG), which might prevent exact diagnosis of the cardiac rhythm of patients. However, characteristics of P wave in patients with sinus rhythm after the operation have not been elucidated systematically. Consecutive patients who underwent the modified Cox Maze operation from January to December 2007 were enrolled. The standard 12-lead ECG and echocardiography were evaluated in patients who had sinus rhythm at 6 months after the operation. The average axis of P wave was 65+/-30 degrees. The average amplitude of P wave was less than 0.1 mV in all 12-leads, with highest amplitude in V1. The most common morphology of P wave was monophasic with positive polarity (49%), except aVR lead, which was different from those in patients with enlarged left atrium, characterized by large P-terminal force in the lead V1. There were no significant differences in P-wave characteristics and echocardiographic parameters between patients with LA activity (30.6%) versus without LA activity (69.4%) at 6 months after the operation. In conclusion, the morphology of P wave in patients after Maze operation shows loss of typical ECG pattern of P mitrale: P wave morphology is small in amplitude, monophasic and with positive polarity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cox JL, Schuessler RB, D'Agostino HJ Jr, Stone CM, Chang BC, Cain ME, Corr PB, Boineau JP. The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. III. Development of a definitive surgical procedure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1991. 101:569–583.2. Cox JL, Jaquiss RD, Schuessler RB, Boineau JP. Modification of the maze procedure for atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. II. Surgical technique of the maze III procedure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995. 110:485–495.3. Cox JL, Schuessler RB, Boineau JP. The development of the Maze procedure for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000. 12:2–14.
Article4. Stulak JM, Sundt TM 3rd, Dearani JA, Daly RC, Orsulak TA, Schaff HV. Ten-year experience with the Cox-maze procedure for atrial fibrillation: how do we define success? Ann Thorac Surg. 2007. 83:1319–1324.
Article5. Cox JL, Ad N, Palazzo T, Fitzpatrick S, Suyderhoud JP, DeGroot KW, Pirovic EA, Lou HC, Duvall WZ, Kim YD. Current status of the Maze procedure for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000. 12:15–19.
Article6. Chen MC, Chang JP, Chang HW, Chen CJ, Yang CH, Chen YH, Fu M. Clinical determinants of sinus conversion by radiofrequency maze procedure for persistent atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing concomitant mitral valvular surgery. Am J Cardiol. 2005. 96:1553–1557.
Article7. Ueshima K, Hashimoto K, Chiba M, Nakamura M, Nasu M, Hiramori K, Kamata J, Yagi Y, Kawazoe K. What are the predictors of restoration of sinus rhythm after combined treatment with surgical repair for organic heart disease and the Maze procedure for atrial fibrillation? J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 1999. 40:793–796.8. Kim YH, Lee SC, Oh HL, IL R, Lee SH, Hong KP, Park PW, Park JE, Seo JD. Predictors of sinus rhythm restoration after Maze operation and relationship between pre- and post-operative left atrial volume. Korean Circ J. 2004. 34:574–581.
Article9. Song BG, Cho SJ, Lee SY, Kim JH, Choi SM, Park YH, Choi JO, Lee SC, On YK, Park SW, Kim JS, Park P. Atrial mechanical function after Maze procedure for atrial fibrillation concomitant with mitral valve surgery. Korean Circ J. 2008. 38:606–611.
Article10. Lo HM, Lin JL, Lin FY, Tseng YZ. Characteristic P wave morphology in patients undergoing the atrial compartment operation for chronic atrial fibrillation with mitral valve disease. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003. 26:1864–1872.
Article11. Pasic M, Musci M, Edelmann B, Siniawski H, Bergs P, Hetzer R. Identification of P waves after the Cox-maze procedure: significance of right precordial leads V3R through V6R. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999. 67:1292–1294.
Article12. Kim YJ, Sohn DW, Choe SJ, Chung WY, Park DG, Oh BH, Lee MM, Park YB, Choi YS, Seo JD, Lee YW, Kim KB, Rho JR. Restoration of atrial mechanical function after Maze operation. Korean Circ J. 1996. 26:1137–1143.
Article13. Shyu KG, Cheng JJ, Chen JJ, Lin JL, Lin FY, Tseng YZ, Kuan P, Lien WP. Recovery of atrial function after atrial compartment operation for chronic atrial fibrillation in mitral valve disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994. 24:392–398.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mid-term Result of Operations for Atrial Fibrillation
- Restoration of Atrial Mechanical Function after Maze Operation
- The Long-term Results of a Modified Maze Procedure with Using Cryoablation
- Predictors of Sinus Rhythm Restoration after Maze Operation and Relationship between Pre- and Post-operative Left Atrial Volume
- Efficacy of the Maze Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation Associated with Atrial Septal Defect