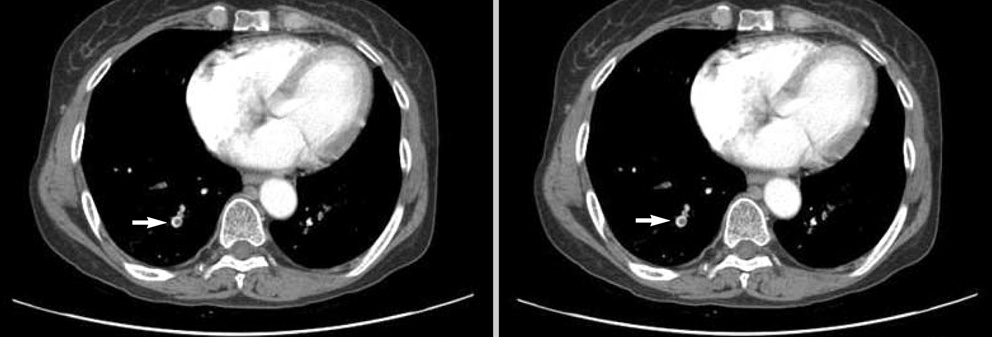
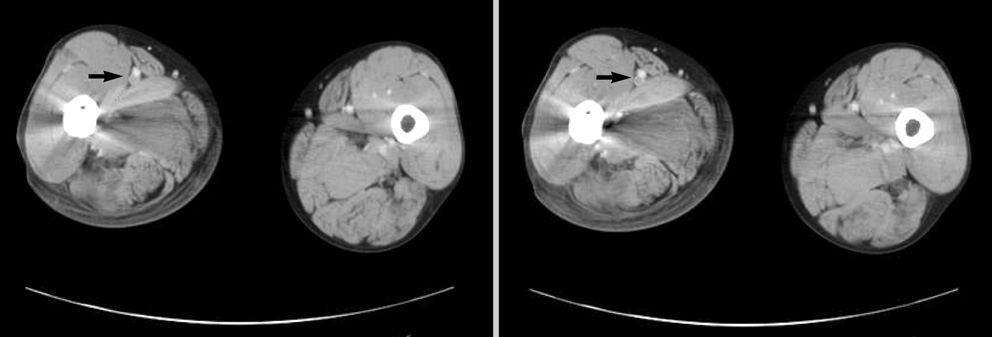
Venous Thromboembolism in Korean Patients Undergoing Major Orthopedic Surgery: A Prospective Observational Study using Computed Tomographic (CT) Pulmonary Angiography and Indirect CT Venography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. syukim@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713828
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.28
Abstract
- In patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery, data of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are lacking as studied by computed tomographic (CT) pulmonary angiography and indirect CT venography (CTPA-CTV). A prospective observational study was performed for 363 Korean patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery to determine the incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE), especially proximal DVT and PE. The incidence of VTE was 16.3% (n=59). Of them, 8 patients (2.2%) were symptomatic. The rate of VTE was the highest in patients who underwent total knee replacement (40.4%), followed by hip fracture surgery (16.4%), and total hip replacement (8.7%; P<0.001). The incidence of PE was 6.6% (n=24). Of them, 4 patients (1.1%) were symptomatic. Forty-one patients (11.3%) were in the proximal DVT or PE group. Based on multivariate analysis, total knee replacement and age > or =65 yr were significant risk factors for proximal DVT or PE in patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery (odds ratio [OR], 2.4; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.1-5.1; P=0.025; and OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.0-4.4; P=0.046, respectively). Taken together, the overall incidence of PE was 6.6% and rate of symptomatic PE rate was 1.1%. Knee joint replacement and age > or =65 yr were significant risk factors for proximal DVT or PE.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Arthroplasty, Replacement, Knee
Female
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Odds Ratio
*Orthopedic Procedures
Phlebography
Prospective Studies
Pulmonary Artery/radiography
Pulmonary Embolism/radiography/surgery
Republic of Korea
Risk Factors
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Venous Thromboembolism/*epidemiology/*radiography
Venous Thrombosis/radiography/surgery
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Korean Guidelines for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism
Soo-Mee Bang, Moon Ju Jang, Doyeun Oh, Yeo-Kyeoung Kim, In Ho Kim, Sung-Soo Yoon, Hwi-Joong Yoon, Chul-Soo Kim, Seonyang Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25(11):1553-1559. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.11.1553.The Efficacy of Low Molecular Weight Heparin for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism after Hip Fracture Surgery in Korean Patients
Kwang-Kyoun Kim, Yougun Won, Ye-Yeon Won
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(5):1209-1213. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.5.1209.Venous Thromboembolism and Superficial Femoral Artery Obstruction after Femur Intertrochanteric Fracture - A Case Report -
Chong-Kwan Kim, Byung-Woo Ahn, Sang-Min Kim, Seung-Hoon Kang, Kye-Young Han
Hip Pelvis. 2013;25(4):301-305. doi: 10.5371/hp.2013.25.4.301.Incidence and Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Severely Injured Patients with Lower Extremity Fracture
Ji Wan Kim, Ji Ho Choi, Jung Jae Kim
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2012;47(6):403-409. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2012.47.6.403.The Prophylaxis of Venous Thromboembolism in Korean Patients with Total Knee Replacement Arthroplasty
Jin-Kyu Lee, Kyu-Sung Chung, Seung-Wook Baek, Choong-Hyeok Choi
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2012;47(2):86-95. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2012.47.2.86.Detection of Deep Vein Thrombosis by Follow-up Indirect Computed Tomography Venography after Pulmonary Embolism
Hye Jin Lee, Seung-Ick Cha, Kyung-Min Shin, Jae-Kwang Lim, Seung-Soo Yoo, Shin-Yup Lee, Jaehee Lee, Chang-Ho Kim, Jae-Yong Park
Tuberc Respir Dis. 2018;81(1):49-58. doi: 10.4046/trd.2016.0056.
Reference
-
1. Leizorovicz A, Turpie AG, Cohen AT, Wong L, Yoo MC, Dans A. Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in Asian patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery without thromboprophylaxis. The SMART study. J Thromb Haemost. 2005. 3:28–34.
Article2. Geerts WH, Pineo GF, Heit JA, Bergqvist D, Lassen MR, Colwell CW, Ray JG. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest. 2004. 126:338S–400S.3. Leizorovicz A. Epidemiology of post-operative venous thromboembolism in Asian patients. Results of the SMART venography study. Haematologica. 2007. 92:1194–1200.
Article4. Piovella F, Wang CJ, Lu H, Lee K, Lee LH, Lee WC, Turpie AG, Gallus AS, Planes A, Passera R, Rouillon A. Deep-vein thrombosis rates after major orthopedic surgery in Asia. An epidemiological study based on postoperative screening with centrally adjudicated bilateral venography. J Thromb Haemost. 2005. 3:2664–2670.
Article5. Lotke PA, Ecker ML, Alavi A, Berkowitz H. Indications for the treatment of deep venous thrombosis following total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:202–208.
Article6. Stulberg BN, Insall JN, Williams GW, Ghelman B. Deep-vein thrombosis following total knee replacement. An analysis of six hundred and thirty-eight arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:194–201.
Article7. Dahl OE, Andreassen G, Aspelin T, Müller C, Mathiesen P, Nyhus S, Abdelnoor M, Solhaug JH, Arnesen H. Prolonged thromboprophylaxis following hip replacement surgery-results of a double-blind, prospective, randomised, placebo-controlled study with dalteparin (Fragmin). Thromb Haemost. 1997. 77:26–31.8. Gulsun Akpinar M, Goodman LR. Imaging of pulmonary thromboembolism. Clin Chest Med. 2008. 29:107–116.
Article9. Stein PD, Fowler SE, Goodman LR, Gottschalk A, Hales CA, Hull RD, Leeper KV Jr, Popovich J Jr, Quinn DA, Sos TA, Sostman HD, Tapson VF, Wakefield TW, Weg JG, Woodard PK. Multidetector computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:2317–2327.
Article10. Thomas SM, Goodacre SW, Sampson FC, van Beek EJ. Diagnostic value of CT for deep vein thrombosis: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Radiol. 2008. 63:299–304.
Article11. Baldt MM, Zontsich T, Stümpflen A, Fleischmann D, Schneider B, Minar E, Mostbeck GH. Deep venous thrombosis of the lower extremity: efficacy of spiral CT venography compared with conventional venography in diagnosis. Radiology. 1996. 200:423–428.
Article12. Goodman LR, Stein PD, Matta F, Sostman HD, Wakefield TW, Woodard PK, Hull R, Yankelevitz DF, Beemath A. CT venography and compression sonography are diagnostically equivalent: data from PIOPED II. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007. 189:1071–1076.
Article13. Miyagi J, Funabashi N, Suzuki M, Asano M, Kuriyama T, Komuro I, Moriya H. Predictive indicators of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary arterial thromboembolism in 54 subjects after total knee arthroplasty using multislice computed tomography in logistic regression models. Int J Cardiol. 2007. 119:90–94.
Article14. Gladish GW, Choe DH, Marom EM, Sabloff BS, Broemeling LD, Munden RF. Incidental pulmonary emboli in oncology patients: prevalence, CT evaluation, and natural history. Radiology. 2006. 240:246–255.
Article15. Cham MD, Yankelevitz DF, Shaham D, Shah AA, Sherman L, Lewis A, Rademaker J, Pearson G, Choi J, Wolff W, Prabhu PM, Galanski M, Clark RA, Sostman HD, Henschke CI. Deep venous thrombosis: detection by using indirect CT venography. The Pulmonary Angiography-Indirect CT Venography Cooperative Group. Radiology. 2000. 216:744–751.16. Roders A, Walker N, Schug S, McKee A, Kehlet H, van Zundert A, Sage D, Futter M, Saville G, Clark T, MacMahon S. Reduction of postoperative mortality and morbidity with epidural or spinal anesthesia: results from overview of randomized trials. BMJ. 2000. 321:1493.17. Urwin SC, Parker MJ, Griffiths R. General versus regional anaesthesia for hip fracture surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Br J Anaesth. 2000. 84:450–455.
Article18. Byun SS, Kim JH, Kim YJ, Chun YS, Park CH, Kim WH. Evaluation of deep vein thrombosis with multidetector row CT after orthopedic arthroplasty: a prospective study for comparison with Doppler sonography. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:59–66.
Article19. Lim KE, Hsu WC, Hsu YY, Chu PH, Ng CJ. Deep venous thrombosis: comparison of indirect multidetector CT venography and sonography of lower extremities in 26 patients. Clin Imaging. 2004. 28:439–444.20. Kim YH, Suh JS. Low incidence of deep-vein thrombosis after cementless total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988. 70:878–882.
Article21. Kim YH, Choi IY, Park MR, Park TS, Cho JL. Prophylaxis for deep vein thrombosis with aspirin or low molecular weight dextran in Korean patients undergoing total hip replacement. A randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 1998. 22:6–10.22. Kim YH, Kim JS. The 2007 John Charnley Award. Factors leading to low prevalence of DVT and pulmonary embolism after THA: analysis of genetic and prothrombotic factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007. 465:33–39.23. Kim YH, Kim JS. Incidence and natural history of deep-vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002. 84:566–570.24. Leizorovicz A, Turpie AG, Cohen AT, Dhillon KS, Angchaisuksiri P, Wang CJ. Epidemiology of post-operative venous thromboembolism in Asian countries. Int J Angiol. 2004. 13:101–108.25. Kearon C. Natural history of venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2003. 107:23 Suppl 1. I22–I30.
Article26. White RH, Romano PS, Zhou H, Rodrigo J, Bargar W. Incidence and time course of thromboembolic outcomes following total hip or knee arthroplasty. Arch Intern Med. 1998. 158:1525–1531.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism Using 64 Channel Multidetector Row Computed Tomography-Indirect Venography and Anti-Coagulation Therapy after Total Knee Arthroplasty in Korea
- The Interobserver Agreement between Residents and Experienced Radiologists for Detecting Pulmonary Embolism and DVT with Using CT Pulmonary Angiography and Indirect CT Venography
- Detection of Deep Vein Thrombosis by Follow-up Indirect Computed Tomography Venography after Pulmonary Embolism
- Role of CT Venography in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Benign Thoracic Central Venous Obstruction
- Spiral CT Venography in Central Venous Obstruction