J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Feb;22(1):122-126. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.122.
Neuroprotective Effects of Growth Hormone Against Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats: 1H Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mhchun@amc.seoul.kr
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4NMR Laboratory, Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713250
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.122
Abstract
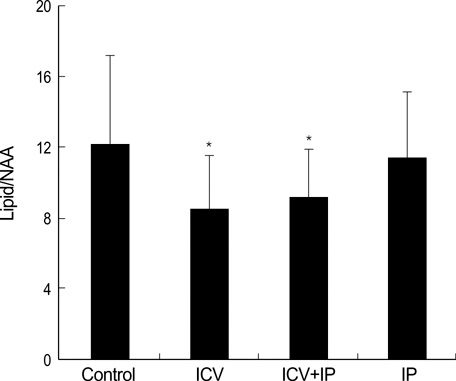
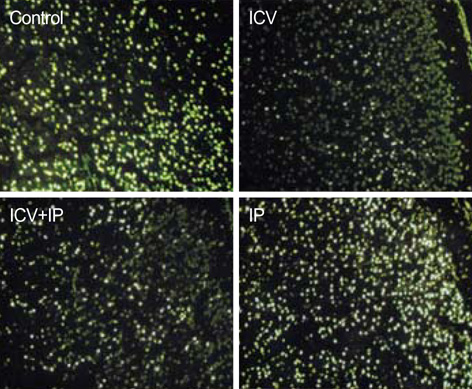
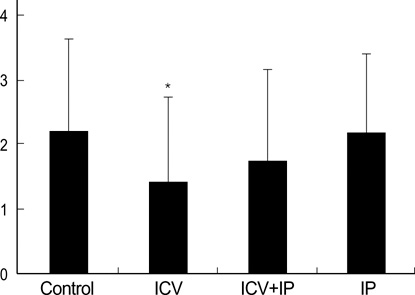
- Using 1H-MRS, we evaluated the effects of growth hormone (GH) as a caspase inhibitor on hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rat brains. The right common carotid arteries of rats were ligated, allowed to recover for 3 hr, and exposed to 8% oxygen for 2 hr. GH was given just prior to HI insult and animals were divided into four groups: control, intracerebroventricular (ICV), intracerebroventricular/intraperitoneal (ICV/IP), and intraperitoneal (IP). Localized in vivo 1H-MRS and TUNEL staining were performed 24 hr after HI injury. Lipid/N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) and lipid/creatine (Cr) ratios were used as apoptotic markers. Gross morphologic changes at 2 weeks were used to evaluate the effects of GH. The lipid/NAA ratio was lower in the ICV and ICV/IP groups than in the control, and the lipid/Cr ratio was lower in the ICV group than in the control. The number of TUNEL positive cells was decreased in the ICV and ICV/IP groups, and the degree of morphologic change indicative of brain injury was lower in the ICV group and somewhat lower in the ICV/IP group. The degree of morphologic change correlated with the lipid/NAA and lipid/Cr ratios. These findings suggest that GH exerts neuroprotective effects in cerebral hypoxicischemic injury.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vannucci RC. Current and potentially new management strategies for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 1990. 85:961–968.2. Holshouser BA, Ashwal S, Luh GY, Shu S, Kahlon S, Auld KL, Tomasi LG, Perkin RM, Hinshaw DB Jr. Proton MR spectroscopy after acute central nervous system injury: outcome prediction in neonates, infants, and children. Radiology. 1997. 202:487–496.
Article3. Novotny E, Ashwal S, Shevell M. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: An emerging technology in pediatric neurology research. Pediatr Res. 1998. 44:1–10.
Article4. Peden CJ, Cowan FM, Bryant DJ, Sargentoni J, Cox IJ, Menon DK, Gadian DG, Bell JD, Dubowitz LM. Proton MR spectroscopy of the brain in infants. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990. 14:886–894.
Article5. Shu SK, Ashwal S, Holshouser BA, Nystrom G, Hinshaw DB Jr. Prognostic value of 1H-MRS in perinatal CNS insults. Pediatr Neurol. 1997. 17:309–318.6. Beilharz EJ, Williams CE, Dragunow M, Sirimanne ES, Gluckman PD. Mechanisms of delayed cell death following hypoxic-ischemic injury in the immature rat: evidence for apoptosis during selective neuronal loss. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995. 29:1–14.
Article7. Cheng Y, Deshmukh M, D'Costa A, Demaro JA, Gidday JM, Shah A, Sun Y, Jacquin MF, Johnson EM, Holtzman DM. Caspase inhibitor affords neuroprotection with delayed administration in a rat model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. J Clin Invest. 1998. 101:1992–1999.
Article8. Pulera MR, Adams LM, Liu H, Santos DG, Nishimura RN, Yang FY, Cole GM, Wasterlain CG. Apoptosis in a neonatal rat model of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. Stroke. 1998. 29:2622–2630.
Article9. Adachi M, Sohma O, Tsuneishi S, Takeda S, Nakamura H. Combination effect of systemic hypothermia and caspase inhibitor administration against hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res. 2001. 20:590–595.
Article10. Gustafson K, Hagberg H, Bengtsson B, Brantsing C, Isgaard J. Possible protective role of growth hormones in hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res. 1999. 45:318–323.11. Scheepens A, Sirimanne ES, Breier BH, Clark RG, Gluckman PD, Williams CE. Growth hormone as a neuronal rescue factor during recovery from CNS injury. Neuroscience. 2001. 104:677–687.
Article12. Mitsunaka H, Dobashi H, Sato M, Tanaka T, Kitanaka A, Yamaoka G, Tokuda M, Matoba K, Hiraishi T, Ishida T. Growth hormone prevents Fas-induced apoptosis in lymphocytes through modulation of Bcl-2 and caspase-3. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2001. 9:256–262.
Article13. Tamatani M, Ogawa S, Tohyama M. Roles of Bcl-2 and caspases in hypoxia-induced neuronal cell death: a possible neuroprotective mechanism of peptide growth factors. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998. 58:27–39.
Article14. Kim KS, Park SJ, Lim KH, Kim EJ, Lee JH, Pi SY. In vivo 1H MR spectroscopic analysis of apoptosis in hypoxic-ischemic newborn rats. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2000. 8:1090. [abstract].15. Palmer C, Vannucci RC, Towfighi J. Reduction of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage with allopurinol. Pediatr Res. 1990. 27:332–336.
Article16. Ross B, Michaelis T. Clinical applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Q. 1994. 10:191–247.17. Groenendaal F, Veenhoven RH, van der Grond J, Jansen GH, Witkamp TD, de Vries LS. Cerebral lactate and N-acetyl-aspartate/choline ratios in asphyxiated full-term neonates demonstrated in vivo using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1994. 35:148–151.
Article18. Hanrahan JD, Sargentoni J, Azzopardi D, Manji K, Cowan FM, Rutherford MA, Cox IJ, Bell JD, Bryant DJ, Edwards AD. Cerebral metabolism within 18 hours of birth asphyxia: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Pediatr Res. 1996. 39:584–590.
Article19. Penrice J, Cady EB, Lorek A, Wylezinska M, Amess PN, Aldridge RF, Stewart A, Wyatt JS, Reynolds EO. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain in normal preterm and term infants, and early changes after perinatal hypoxia-ischemia. Pediatr Res. 1996. 40:6–14.
Article20. Penrice J, Lorek A, Cady EB, Amess PN, Wylezinska M, Cooper CE, D'Souza P, Brown GC, Kirkbride V, Edwards AD, Wyatt JS, Reynolds EO. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain during acute hypoxia-ischemia and delayed cerebral energy failure in the newborn piglet. Pediatr Res. 1997. 41:795–802.
Article21. Yue X, Mehmet H, Squier MV, Hope PL, Azzopardi D, Edwards AD. Apoptosis and necrosis in the brains of infants dying after birth asphyxia. Pediatr Res. 1995. 37:387.22. Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR. Apoptosis, a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972. 26:239–257.
Article23. Edwards AD, Mehmet H. Apoptosis in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic cerebral damage. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1996. 22:494–498.24. Bonfoco E, Krainc D, Ankarcrona M, Nicotera P, Lipton SA. Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced, respectively, by mild and intense insults with N-methyl-D-aspartate or nitric oxide/superoxide in cortical cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995. 92:7162–7166.
Article25. McDonald JW, Behrens MI, Chung C, Bhattacharyya T, Choi DW. Susceptibility to apoptosis is enhanced in immature cortical neurons. Brain Res. 1997. 759:228–232.
Article26. Pettmann B, Henderson CE. Neuronal cell death. Neuron. 1998. 20:633–647.
Article27. Deshmukh M, Vasilakos J, Deckwerth TL, Lampe PA, Shivers BD, Johnson EM Jr. Genetic and metabolic status of NGF-deprived sympathetic neurons saved by an inhibitor of ICE family proteases. J Cell Biol. 1996. 135:1341–1354.
Article28. Fink K, Zhu J, Namura S, Shimizu-Sasamata M, Endres M, Ma J, Dalkara T, Yuan J, Moskowitz MA. Prolonged therapeutic window for ischemic brain damage caused by delayed caspase activation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998. 18:1071–1076.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neuroprotective Effect of Growth Hormone in Neonatal Rat with Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury
- The Protective Effect of Ischemic and Hypoxic Preconditioning on Hypoxic-ischemic Brain Injury in the Neonatal Rat: 1H Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Study
- Early Prediction of Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage in Newbon Rats Using Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Neuroprotective Effect of EGb 761
- Effect of the Heme Oxygenase Inhibitor on the Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury in the Neonatal Rat
- Effects of Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor on Hypoxic-ischemic Injury in the Neonatal Rat Brain: 1H Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Study