The Interval Between Initiation of Anti-tuberculosis Treatment in Patients with Culture-positive Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Receipt of Drug-susceptibility Test Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine and Lung Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yimjj@snu.ac.kr
- 2Korean Institute of Tuberculosis, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713225
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.26
Abstract
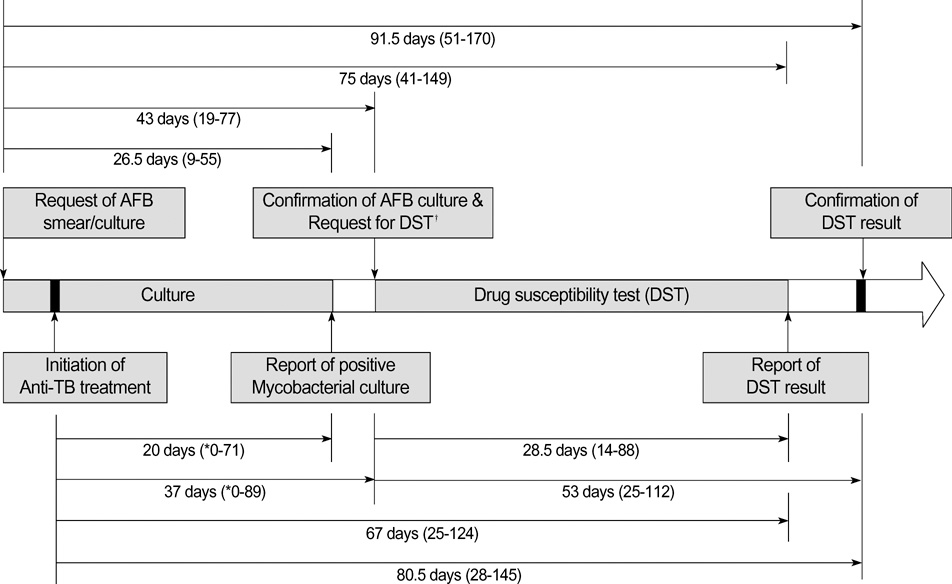
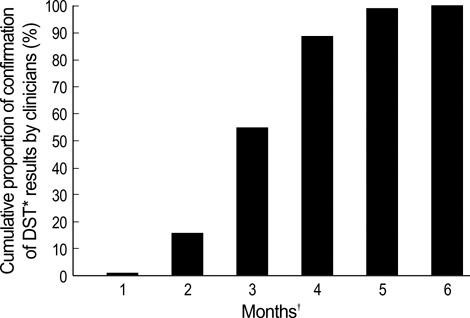
- Although mycobacterial culture and the subsequent drug-susceptibility test (DST) for anti-tuberculosis (TB) drugs take several months to complete using solid media, there are no reports on the turnaround times of these tests under clinical conditions. The aim of this study was to determine the interval between initiation of anti-TB treatment and receipt of DST requested at an outpatient clinic. We prospectively enrolled patients with culture-positive pulmonary TB at Seoul National University Hospital from September 2002 to December 2004. Patients were followed up monthly. Mycobacterial cultures were done using Ogawa media at Seoul National University Hospital. DST were performed at the Korean Institute of Tuberculosis. Of the 104 patients enrolled, 54 were male. The median age was 41 yr. The median interval from initiation of anti-TB treatment to receipt of mycobacterial culture results by clinicians was 37 days (range, 0-89 days). The median interval from initiation of treatment to confirmation of DST by requesting clinicians was 80.5 days (range, 28-145 days). Clinicians only received the results of DST more than two months after initiation of treatment when they followed up patients monthly and mycobacterial culture was performed using solid media.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 9 articles
-
Impact of Molecular Drug Susceptibility Testing on the Time to Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis Treatment Initiation
Doosoo Jeon, Hyungseok Kang, Yong-Soo Kwon, Jae-Joon Yim, Tae Sun Shim
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(35):e284. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e284.The Incidence and Clinical Implication of Sputum with Positive Acid-Fast Bacilli Smear But Negative in Mycobacterial Culture in a Tertiary Referral Hospital in South Korea
Jae Seok Lee, Eui-Chong Kim, Sei Ick Joo, Sang-Min Lee, Chul-Gyu Yoo, Young Whan Kim, Sung Koo Han, Young-Soo Shim, Jae-Joon Yim
J Korean Med Sci. 2008;23(5):767-771. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.5.767.Multidrug-resistant Pulmonary Tuberculosis Among Young Korean Soldiers in a Communal Setting
Sei Won Lee, Kyeongman Jeon, Kwang Hyun Kim, Kyung Hoon Min
J Korean Med Sci. 2009;24(4):592-595. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.592.What Strategy Can be Applied to the Patients with Culture Positive Tuberculosis to Reduce Treatment Delay in a Private Tertiary Healthcare Center?
Ji Eun Lee, Yang-Ki Kim, Tae Hyong Kim, Kyung Ha Kim, Eun Jung Lee, Soo Taek Uh, Tae Youn Choi
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(1):42-47. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.1.42.Clinical Usefulness of rpoB Gene Sequence Analysis in Lymph Node Tuberculosis
Ji-Young Park, Ki Tae Kwon
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(5):357-361. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.5.357.Rifampin-resistant Relapsed Tuberculosis Confirmed by Molecular Technique
Song Mi Moon, Sang-Oh Lee, Sang-Ho Choi, Yang Soo Kim, Jun Hee Woo, Sung-Han Kim
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(6):485-490. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.6.485.Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis
Byung Woo Jhun, Hee Jae Huh, Won-Jung Koh
J Korean Med Assoc. 2019;62(1):18-24. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2019.62.1.18.Rapid Diagnosis of Tuberculosis and Multidrug Resistance Using a MGIT 960 System
Won-Jung Koh, Yousang Ko, Chang-Ki Kim, Kyung Sun Park, Nam Yong Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2012;32(4):264-269. doi: 10.3343/alm.2012.32.4.264.Detection of Isoniazid and Rifampicin Resistance by Sequencing of
katG, inhA , andrpoB Genes in Korea
Eun Hae Cho, Hye Kyung Bae, Seong Ki Kang, Eun Hee Lee
Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29(5):455-460. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.5.455.
Reference
-
1. Kim SJ. Drug-susceptibility testing in tuberculosis: methods and reliability of results. Eur Respir J. 2005. 25:564–569.
Article2. Muralidhar S, Srivastava L. Evaluation of three methods to determine the antimicrobial susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res. 2004. 120:463–467.3. Schaberg T, Reichert B, Schulin T, Lode H, Mauch H. Rapid drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using conventional solid media. Eur Respir J. 1995. 8:1688–1693.4. WHO. Treatment of tuberculosis; Guidelines for National Programmes 2003.5. Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE, Daley CL, Etkind SC, Friedman LN, Fujiwara P, Grzemska M, Hopewell PC, Iseman MD, Jasmer RM, Koppaka V, Menzies RI, O'Brien RJ, Reves RR, Reichman LB, Simone PM, Starke JR, Vernon AA. American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003. 167:603–662.6. British Thoracic Society. Chemotherapy and management of tuberculosis in the United Kingdom: recommendations 1998. Joint Tuberculosis Committee of the British Thoracic Society. Thorax. 1998. 53:536–548.7. Seung KJ, Bai GH, Kim SJ, Lew WJ, Park SK, Kim JY. The treatment of tuberculosis in South Korea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2003. 7:912–919.8. Korean Society of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis 2005.9. Seung KJ, Gelmanova IE, Peremitin GG, Golubchikova VT, Pavlova VE, Sirotkina OB, Yanova GV, Strelis AK. The effect of initial drug resistance on treatment response and acquired drug resistance during standardized short-course chemotherapy for tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 39:1321–1328.
Article10. Koh WJ, Kwon OJ, Park YK, Lew WJ, Bai GH. Development of multidrug resistance during treatment of isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis. Eur Respir J. 2005. 26:557.
Article11. Anargyros P, Astill DS, Lim IS. Comparison of improved BACTEC and Lowenstein-Jensen media for culture of mycobacteria from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990. 28:1288–1291.
Article12. Steadham JE, Stall SK, Simmank JL. Use of the BACTEC system for drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. kansasii, and M. avium complex. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985. 3:33–40.
Article13. Roberts GD, Goodman NL, Heifets L, Larsh HW, Lindner TH, McClatchy JK, McGinnis MR, Siddiqi SH, Wright P. Evaluation of the BACTEC radiometric method for recovery of mycobacteria and drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from acid-fast smear-positive specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983. 18:689–696.
Article14. Tortoli E, Mattei R, Savarino A, Bartolini L, Beer J. Comparison of Mycobacterium tuberculosis susceptibility testing performed with BACTEC 460TB (Becton Dickinson) and MB/BacT (Organon Teknika) systems. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000. 38:83–86.
Article15. Ruiz P, Zerolo FJ, Casal MJ. Comparison of susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using the ESP culture system II with that using the BACTEC method. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:4663–4664.
Article16. Tortoli E, Benedetti M, Fontanelli A, Simonetti MT. Evaluation of automated BACTEC MGIT 960 system for testing susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to four major antituberculous drugs: comparison with the radiometric BACTEC 460TB method and the agar plate method of proportion. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. 40:607–610.
Article17. Ardito F, Posteraro B, Sanguinetti M, Zanetti S, Fadda G. Evaluation of BACTEC Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube (MGIT 960) automated system for drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 39:4440–4444.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Prevalence of Initial Drug Resistance among Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients
- Clinical Meaning of INNO-LiPA Test in the Diagnosis of Rifampin Resistant Tuberculosis
- Clinical Outcome after Treatment with the First-line Drugs in Patients with Persistent Positive Sputum Smear and Negative Sputum Culture Results
- Clinical Manifestations of Persistent Smear Positive and Culture Negative Sputum Tests 5 Months after First-line Anti-Tuberculous Chemotherapy
- Pediatric tuberculosis and drug resistance