Emerging Need for Vaccination against Hepatitis A Virus in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Medical Research Institute, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. thkm@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713168
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.218
Abstract
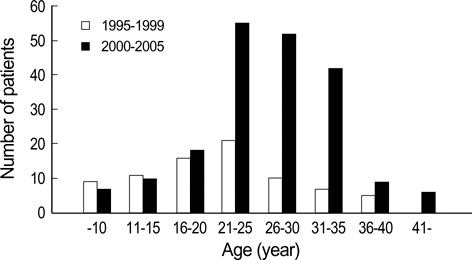
- Vaccination against hepatitis A virus (HAV) is recommended for patients with chronic liver disease (CLD), but this has been deemed unnecessary in Korea since the immunity against HAV was almost universal in adults. However, this practice has never been reevaluated with respect to the changing incidence of adult acute hepatitis A. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 278 patients with acute hepatitis A diagnosed from January 1995 to November 2005 and prospectively tested 419 consecutive CLD patients from July to December 2005 for the presence of IgG anti-HAV. The number of patients with acute hepatitis A has markedly increased recently, and the proportion of adult patients older than 30 yr has been growing from 15.2% during 1995-1999, to 28.4% during 2000-2005 (p=0.019). Among 419 CLD patients, the seroprevalences of IgG anti-HAV were 23.1% for those between 26 and 30 yr, 64% between 31 and 35 yr, and 85.0% between 36 and 40 yr. These data demonstrate that immunity against HAV is no more universal in adult and substantial proportion of adult CLD patients are now at risk of HAV infection in Korea. Therefore, further study on seeking proper strategy of active immunization against HAV is warranted in these populations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Risk Factors
Risk Assessment/methods
Middle Aged
Male
Liver Diseases/*epidemiology/*prevention & control
Korea/epidemiology
Infant, Newborn
Infant
Incidence
Humans
Hepatitis A Vaccines/*therapeutic use
Hepatitis A/*epidemiology/*prevention & control
Female
Disease Outbreaks/*prevention & control/*statistics & numerical data
Comorbidity
Communicable Diseases, Emerging/epidemiology/prevention & control
Chronic Disease
Child, Preschool
Child
Aged, 80 and over
Aged
Adult
Adolescent
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Clinical Features of Re-Emerging Hepatitis A: An Analysis of Patients Hospitalized during an Urban Epidemic in Korea
Hee Kyoung Choi, Young Goo Song, Chang Oh Kim, So Youn Shin, Bum Sik Chin, Sang Hoon Han, Sung Joon Jin, Yun Tae Chae, Ji-Hyeon Baek, Sun Bean Kim, Do Young Kim, Jun Yong Park, June Myung Kim, Jun Yong Choi
Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(4):686-691. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.4.686.Recent Epidemiological Status and Vaccination of Hepatitis A in Korea
Jong-Hyun Kim
J Korean Med Assoc. 2008;51(2):110-118. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2008.51.2.110.Hepatitis A Virus Seropositivity among Healthcare Workers at a University Hospital in Korea
Jun Seong Son, Mi Suk Lee, So Young Kang, Woo In Lee
Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29(6):551-556. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.6.551.
Reference
-
1. Craig AS, Schaffner W. Prevention of hepatitis A with hepatitis A vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:476–481.2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention of hepatitis A through active or passive immunization: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 1999. 48(RR-12):1–37.3. Willner IR, Uhl MD, Howard SC, Williams EQ, Riely CA, Waters B. Serious hepatitis A: an analysis of patients hospitalized during an urban epidemic in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1998. 128:111–114.
Article4. Wise ME, Sorvillo F. Hepatitis A-related mortality in California, 1989-2000: analysis of multiple cause-coded death data. Am J Public Health. 2005. 95:900–905.
Article5. Keeffe EB. Is hepatitis A more severe in patients with chronic hepatitis B and other chronic liver disease? Am J Gastroenterol. 1995. 90:201–205.6. Lefilliatre P, Villeneuve JP. Fulminant hepatitis A in patients with chronic liver disease. Can J Public Health. 2000. 91:168–170.
Article7. Yao G. Hollinger FB, Lemon SM, Margolis H, editors. Clinical spectrum and natural history of viral hepatitis A in a 1988 Shanghai epidemic. Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease. 1991. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;76–78.8. Vento S, Garofano T, Renzini C, Cainelli F, Casali F, Ghironzi G, Ferraro T, Concia E. Fulminant hepatitis associated with hepatitis A virus superinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 1998. 338:286–290.
Article9. Keeffe EB. Acute hepatitis A and B in patients with chronic liver disease: prevention through vaccination. Am J Med. 2005. 118:Supple 10A. 21S–27S.
Article10. Kim CY, Hong WS. Seroepidemiology of type A and type B hepatitis in Seoul area. Korean J Intern Med. 1982. 25:19–26.11. Choi W, Eom HS, Kim IH, Lee DH, Kim PS, Kim HG, Kwon KS, Cho HG, Shin YW, Kim YS. Patterns of acute hepatitis A and anti-HAV seroprevalence of Kyungin province. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999. 34:69–75.12. Sohn YM, Rho HO, Park MS. The changing epidemiology and hepatitis A in children and the consideration of active immunization in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2000. 41:34–39.13. Kang JH, Lee KY, Kim CH, Sim D. Changing hepatitis A epidemiology and the need for vaccination in Korea. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2004. 22:237–242.14. Song MH, Lim YS, Song TJ, Choi JM, Kim JI, Jun JB, Kim MY, Pyun DK, Lee HC, Jung YH, Lee YS. The etiology of acute viral hepatitis for the last 3 years. Korean J Med. 2005. 68:256–260.15. Lee TH, Kim SM, Lee GS, Im EH, Huh KC, Choi YW, Kang YW. Clinical features of acute hepatitis A in the western part of Daejeon and Chungnam province: single center experience. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006. 47:136–143.16. Han SH, Lee SH, Roh BJ, Shim SC, Cho SC, Sohn JH, Lee DH, Kee CS. An outbreak of hepatitis A in south Korean military personnel: a clinical and epidemiologic study. Korean J Hepatol. 2001. 7:392–400.17. Lee SD. Asian perspectives on viral hepatitis A. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000. 15:Suppl. 94–99.
Article18. Saab S, Lee C, Shapaner A, Ibrahim AB. Seroepidemiology of hepatitis A in patients with chronic liver disease. J Viral Hepat. 2005. 12:101–105.
Article19. Cooksley G. The importance and benefits of hepatitis A prevention in chronic liver disease patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. 19:Suppl. S17–S20.
Article20. Woo YS, Chung SH, Kim SK, Jang UI, Chung WC, Lee KM, Yang JM, Han JY, Lee YS, Chung KW, Seon HS. Fulminant hepatitis A associated with hepatorenal syndrome in asymptomatic chronic hepatitis B virus carrier. Korean J Hepatol. 2002. 8:Suppl 3. 120.21. Reiss G, Keeffe EB. Review article: Hepatitis vaccination in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004. 19:715–727.22. Lau DT, Hewlett AT. Screening for hepatitis A and B antibodies in patients with chronic liver disease. Am J Med. 2005. 118:Suppl 10. 28–33.
Article23. Saab S, Martin P, Yee HF Jr. A simple cost-decision analysis model comparing two strategies for hepatitis A vaccination. Am J Med. 2000. 109:241–244.
Article24. Lemon SM, Shapiro CN. The value of immunization against hepatitis A. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. 3:38–49.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- The Seroconversion Rate of Hepatitis A Virus Vaccination among Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Chronic Liver Disease in Korea
- A Case of Allergic Vasculitis Associated with Chronic Active Hepatitis
- A case of fulminant hepatic failure complicating hepatitis A virus superinfection in a hepatitis B virus carrier
- Management of viral hepatitis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma