J Vet Sci.
2013 Dec;14(4):491-494. 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.491.
Development of a real-time SYBR Green PCR assay for the rapid detection of Dermatophilus congolensis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departamento de Sanidad Animal, Facultad de Veterinaria de Caceres, Universidad de Extremadura, 10003 Caceres, Spain. alfrgcia@unex.es
- KMID: 1712318
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.491
Abstract
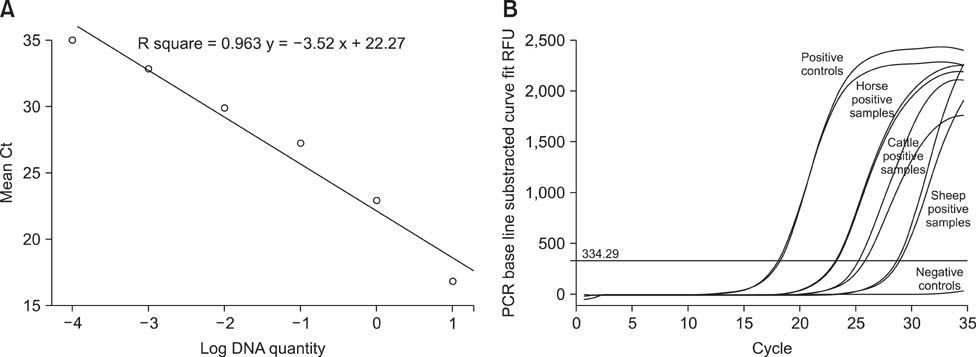
- Methods such as real time (RT)-PCR have not been developed for the rapid detection and diagnosis of Dermatophilus (D.) congolensis infection. In the present study, a D. congolensis-specific SYBR Green RT-PCR assay was evaluated. The detection limit of the RT-PCR assay was 1 pg of DNA per PCR reaction. No cross-reaction with nucleic acids extracted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Staphylococcus aureus, or Austwickia chelonae was observed. Finally, the RT-PCR assay was used to evaluate clinical samples collected from naturally infected animals with D. congolensis. The results showed that this assay is a fast and reliable method for diagnosing dermatophilosis.
MeSH Terms
-
Actinomycetales/*isolation & purification
Actinomycetales Infections/diagnosis/microbiology/*veterinary
Animals
Cattle
Cattle Diseases/*diagnosis/microbiology
Fluorescent Dyes/*diagnostic use
Horse Diseases/*diagnosis/microbiology
Horses
Limit of Detection
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction/*methods/veterinary
Reproducibility of Results
Sheep
Sheep Diseases/*diagnosis/microbiology
Fluorescent Dyes
Figure
Reference
-
1. Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990; 215:403–410.
Article2. Awad WS, Nadra-Elwgoud MIA, El-Sayed AA. Diagnosis and treatment of bovine, ovine and equine dermatophilosis. J Appl Sci Res. 2008; 4:367–374.3. Dalis JS, Kazeem HM, Makinde AA, Fatihu MY. Bacteria associated with bovine dermatophilosis in Zaria, Nigeria. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2010; 4:1475–1479.4. García-Sánchez A, Cerrato R, Larrasa J, Ambrose NC, Parra A, Alonso JM, Hermoso-de-Mendoza M, Rey JM, Hermoso-de-Mendoza J. Identification of an alkaline ceramidase gene from Dermatophilus congolensis. Vet Microbiol. 2004; 99:67–74.5. Gibson JA, Thomas RJ, Domjahn RL. Subcutaneous and lymph node granulomas due to Dermatophilus congolensis in a steer. Vet Pathol. 1983; 20:120–122.
Article6. Hamada M, Iino T, Iwami T, Harayama S, Tamura T, Suzuki K. Mobilicoccus pelagius gen. nov., sp. nov. and Piscicoccus intestinalis gen. nov., sp. nov., two new members of the family Dermatophilaceae, and reclassification of Dermatophilus chelonae (Masters et al. 1995) as Austwickia chelonae gen. nov., comb. nov. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2010; 56:427–436.
Article7. Han W, Chen Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Yan G. Establishment of polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of dermatophilosis in sheep. Chin J Vet Sci. 2009; 29:49–51.8. Larrasa J, Garcia A, Ambrose NC, Alonso JM, Parra A, Hermoso de Mendoza M, Salazar J, Rey J, Hermoso de Mendoza J. A simple random amplified polymorphic DNA genotyping method for field isolates of Dermatophilus congolensis. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2002; 49:135–141.
Article9. Makinde AA. Dermatophilosis in animals and man: recent studies on Dermatophilus congolensis. Vom J Vet Sci. 2004; 1:87–102.10. Niesters HG. Clinical virology in real time. J Clin Virol. 2002; 25:Suppl 3. S3–S12.
Article11. OIE. OIE Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals 2009. 6th ed. Paris: Office International des Epizooties;2010. p. 725–728.12. Ramanathan VS, Jahng AW, Shlopov B, Pham BV. Dermatophilus congolensis infection of the esophagus. Gastroenterology Res. 2010; 3:173–174.13. Rozen S, Skaletsky H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol. 2000; 132:365–386.
Article14. Sebastian MM, Giles RC, Donahu JM, Sells SF, Fallon L, Vickers ML. Dermatophilus congolensis-associated placentitis, funisitis and abortion in a horse. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2008; 55:183–185.
Article15. Seifert HSH. Tropical Animal Health. 1st ed. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers;1996. p. 352–355.16. Shaibu SJ, Kazeem HM, Abdullahi US, Fatihu MY. The use of polimerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of dermatophilosis from cattle, sheep and goat in Nigeria. J Anim Vet Adv. 2010; 9:1034–1036.
Article17. Yeruham I, Elad D, Perl S. Economic aspects of outbreaks of dermatophilosis in first-calving cows in nine herds of dairy cattle in Israel. Vet Rec. 2000; 146:695–698.
Article18. Zaria LT. Dermatophilus congolensis infection (Dermatophilosis) in animals and man! an update. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993; 16:179–222.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Characterization of Chinook head salmon embryo phenotypes of infectious salmon anemia virus by real-time RT-PCR
- Application of SYBR Green real-time PCR assay for the specific detection of Salmonella spp
- Evaluation of the Efficacies of Rapid Antigen Test, Multiplex PCR, and Real-time PCR for the Detection of a Novel Influenza A (H1N1) Virus
- Evaluation of Two Commercial HLA-B27 Real-Time PCR Kits
- Comparison of Rapid Antigen Test and Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR for the Detection of Influenza B Virus