J Vet Sci.
2013 Dec;14(4):395-403. 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.395.
Effect of chronic lead intoxication on the distribution and elimination of amoxicillin in goats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Pharmacology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, Giza 12316, Egypt.
- 2Department of Veterinary Basic Medical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid 22110, Jordan.
- 3Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, College of Veterinary Medicine, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50011, USA.
- 4Department of Clinical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS 66506, USA.
- 5Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50011, USA. whsu@iastate.edu
- KMID: 1712305
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.395
Abstract
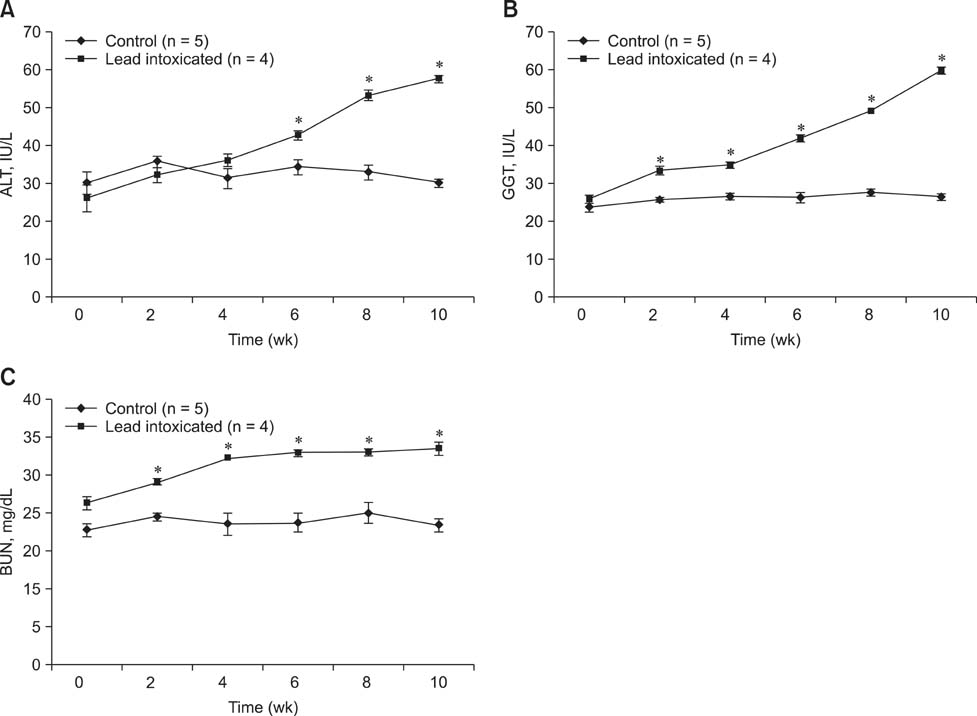
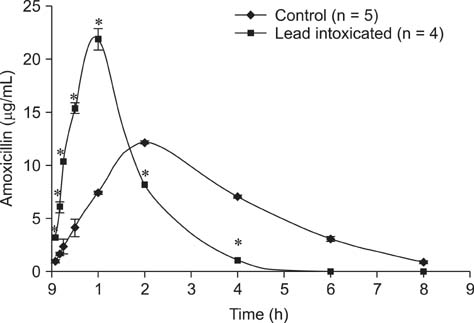
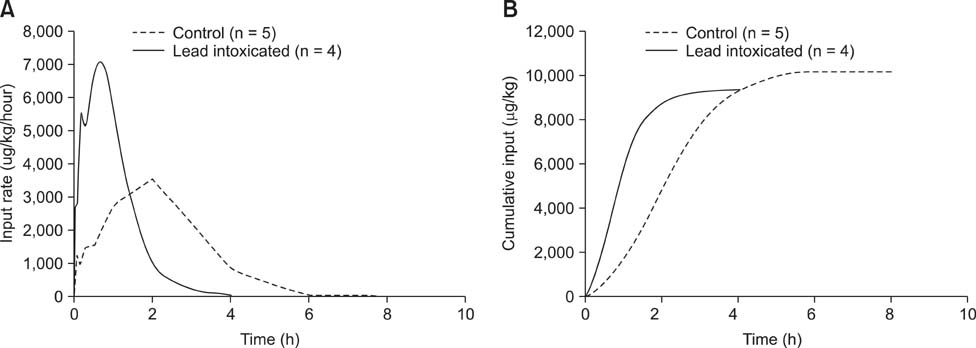
- A study of amoxicillin pharmacokinetics was conducted in healthy goats and goats with chronic lead intoxication. The intoxicated goats had increased serum concentrations of liver enzymes (alanine aminotransferase and gamma-glutamyl transferase), blood urea nitrogen, and reactivated delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase compared to the controls. Following intravenous amoxicillin (10 mg/kg bw) in control and lead-intoxicated goats, elimination half-lives were 4.14 and 1.26 h, respectively. The volumes of distribution based on the terminal phase were 1.19 and 0.38 L/kg, respectively, and those at steady-state were 0.54 and 0.18 L/kg, respectively. After intramuscular (IM) amoxicillin (10 mg/kg bw) in lead-intoxicated goats and control animals, the absorption, distribution, and elimination of the drug were more rapid in lead-intoxicated goats than the controls. Peak serum concentrations of 21.89 and 12.19 microg/mL were achieved at 1 h and 2 h, respectively, in lead-intoxicated and control goats. Amoxicillin bioavailability in the lead-intoxicated goats decreased 20% compared to the controls. After amoxicillin, more of the drug was excreted in the urine from lead-intoxicated goats than the controls. Our results suggested that lead intoxication in goats increases the rate of amoxicillin absorption after IM administration and distribution and elimination. Thus, lead intoxication may impair the therapeutic effectiveness of amoxicillin.
MeSH Terms
-
Amoxicillin/blood/*pharmacokinetics/urine
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents/blood/*pharmacokinetics/urine
Area Under Curve
Chromatography, High Pressure Liquid/veterinary
Goat Diseases/*chemically induced/metabolism
Goats
Half-Life
Injections, Intramuscular/veterinary
Injections, Intravenous/veterinary
Lead Poisoning/etiology/metabolism/*veterinary
Male
Amoxicillin
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abu-Basha EA, Gehring R, Albwa'neh SJ. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of spectinomycin after i.v., i.m., s.c. and oral administration in broiler chickens. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 30:139–144.
Article2. Anttila M, Sotaniemi EA, Pelkonen O, Rautio A. Marked effect of liver and kidney function on the pharmacokinetics of selegiline. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005; 77:54–62.
Article3. Baggot JD. Principles of Drug Disposition in Domestic Animals: The basis of Veterinary Clinical Pharmacology. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1977. p. 168–179.4. Bhar MK, Datta BK, Patra PH, Dash JR, Sar TK, Chakraborty AK, Mandal TK. Disposition kinetics of amoxicillin in healthy, hepatopathic and nephropathic conditions in chicken after single oral administration. Vet Res Forum. 2010; 1:150–156.5. Brander GC, Paugh DM, Bywater RJ, Jenkins WL. Veterinary Applied Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. London: Bailliere Tindall;1991. p. 436–437.6. Dart RC, Hurlbut KM, Maiorino RM, Mayersohn M, Aposhian HV, Hassen LVB. Pharmacokinetics of meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid in patients with lead poisoning and in healthy adults. J Pediatr. 1994; 125:309–316.
Article7. Delis GA, Koutsoviti-Papadopoulou M, Siarkou VI, Kounenis G, Batzias GC. Pharmacodynamics of amoxicillin against Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) correlation in sheep. Res Vet Sci. 2010; 89:418–425.
Article8. Elsheikh HA, Taha AA, Khalafalla AE, Osman IA, Wasfi IA. Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin trihydrate in Desert sheep and Nubian goats. Vet Res Commun. 1999; 23:507–514.9. Errecalde JO, Carmely D, Mariño EL, Mestorino N. Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin in normal horses and horses with experimental arthritis. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2001; 24:1–6.
Article10. Fiorim J, Ribeiro Júnior RF, Silveira EA, Padilha AS, Vescovi MVA, de Jesus HC, Stefanon I, Salaices M, Vassallo DV. Low-level lead exposure increases systolic arterial pressure and endothelium-derived vasodilator factors in rat aortas. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e17117.
Article11. Foulstone M, Reading C. Assay of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, the components of Augmentin, in biological fluids with high-performance liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982; 22:753–762.
Article12. Haas T, Mache W, Schaller KH, Mache K, Klavis G, Stumpf R. The determination of delta-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase activity and its diagnostic value. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1972; 30:87–104.13. Lashev L, Fink-Gremels J. Changes in amoxicillin pharmacokinetics in white rats with experimentally damaged kidneys and liver. Vet Med Nauki. 1987; 24:57–63.14. Liu ZP. Lead poisoning combined with cadmium in sheep and horses in the vicinity of non-ferrous metal smelters. Sci Total Environ. 2003; 309:117–126.
Article15. McKellar QA, Sanchez Bruni SF, Jones DG. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationships of antimicrobial drugs used in veterinary medicine. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 27:503–514.
Article16. Zaki MS, Mostafa S, Awad I. Some studies on lead toxicity in Marino sheep. J Am Sci. 2010; 6:128–131.17. Pires de Abreu LR, Ortiz RAM, de Castro SC, Pedrazzoli J. HPLC determination of amoxicillin comparative bioavailability in healthy volunteers after a single dose administration. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2003; 6:223–230.18. Plumb DC. Veterinary Drug Handbook. 4th ed. Ames: Iowa State Press;2002. p. 42–45.19. Rahimi E. Lead and cadmium concentrations in goat, cow, sheep, and buffalo milks from different regions of Iran. Food Chem. 2013; 136:389–391.
Article20. Rodríguez-Estival J, Barasona JA, Mateo R. Blood Pb and δ-ALAD inhibition in cattle and sheep from a Pb-polluted mining area. Environ Pollut. 2012; 160:118–124.
Article21. Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall ABA. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere. 2006; 65:725–759.
Article22. Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985; 150:76–85.
Article23. Smith KM, Abrahams PW, Dagleish MP, Steigmajer J. The intake of lead and associated metals by sheep grazing mining-contaminated floodplain pastures in mid-Wales, UK: I. Soil ingestion, soil-metal partitioning and potential availability to pasture herbage and livestock. Sci Total Environ. 2009; 407:3731–3739.
Article24. Smith KM, Dagleish MP, Abrahams PW. The intake of lead and associated metals by sheep grazing mining-contaminated floodplain pastures in mid-Wales, UK: II. Metal concentrations in blood and wool. Sci Total Environ. 2010; 408:1035–1042.
Article25. Turnidge JD. The pharmacodynamics of β-lactams. Clin Infect Dis. 1998; 27:10–22.
Article26. Vaziri ND, Ding Y, Ni Z. Nitric oxide synthase expression in the course of lead-induced hypertension. Hypertension. 1999; 34:558–562.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of trikatu pretreatment on the pharmacokinetics of pefloxacin administered orally in mountain Gaddi goats
- Change of Biogenic Amine Contents in Lead Intoxicated Rat Brain
- Acute Exacerbation of Myasthenia Gravis after Amoxicillin Therapy
- Comparison between Kidney and Hemoperfusion for Paraquat Elimination
- A Study on the Use of 10 MV X-ay with Lead Absorber for Treatment of Hean and Neck Tumors