J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Jan;24(Suppl 1):S156-S160. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S156.
Comparison between Kidney and Hemoperfusion for Paraquat Elimination
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. syhong@sch.ac.kr
- KMID: 1778156
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S156
Abstract
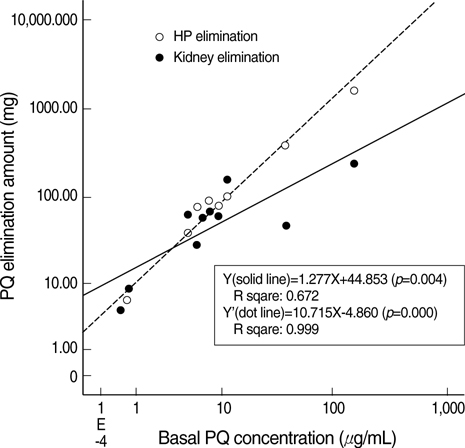
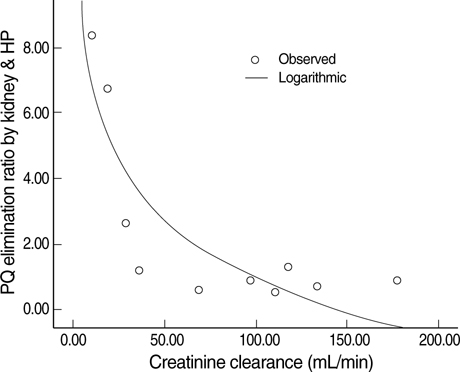
- The mortality rate of acute paraquat (PQ) poisoning depends on the PQ concentration in the blood. It has been shown that the kidneys eliminate PQ effectively. However, early renal function deterioration is frequently observed in acute PQ intoxication. This study is designed to compare the efficacy of PQ elimination with hemoperfusion (HP) and kidneys, taking into account the functional deterioration of the kidneys. The amount of renal and HP excretion of PQ were measured during the procedure of HP in patients with acute PQ intoxication. The PQ clearance and the actual amount of PQ elimination by the HP cartridge during the HP procedure were 111+/-11 mL/min (range; 13.2-162.2 mL/min) and 251.4+/-506.3 mg (range; 4.6- 1,655.7) each. While, the renal clearance and actual amount of renal elimination of PQ was 79.8+/-56.0 mL/min (range; 9.7-177.0) and 75.4+/-73.6 mg (range; 4.9- 245.8). As the creatinine clearance decreased, the PQ elimination by HP was as effective as or more effective than the renal elimination. In conclusion, early HP must be provided for life saving treatment in patients with acute PQ intoxication.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Toxicokinetics of paraquat in Korean patients with acute poisoning
Hak-Jae Kim, Hyung-Ki Kim, Hwayoung Lee, Jun-Seok Bae, Jun-Tack Kown, Hyo-Wook Gil, Sae-Yong Hong
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;20(1):35-39. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.1.35.
Reference
-
1. Smith LL. Mechanism of paraquat toxicity in lung and its relevance to treatment. Hum Toxicol. 1987. 6:31–36.
Article2. Meredith TJ, Vale JA. Treatment of paraquat poisoning in man: methods to prevent absorption. Hum Toxicol. 1987. 6:49–55.
Article3. Okonek S, Hofmann A, Henningsen B. Efficacy of gut lavage, hemodialysis, and hemoperfusion in the therapy of paraquat or diaquat intoxication. Arch Toxicol. 1976. 36:43–51.4. Okonek S. Hemoperfusion in toxicology. Basic considerations of its effectiveness. Clin Toxicol. 1981. 18:1185–1198.
Article5. Hampson EC, Pond SM. Failure of haemoperfusion and haemodialysis to prevent death in paraquat poisoning. A retrospective review of 42 patients. Med Toxicol Adverse Drug Exp. 1988. 3:64–71.6. Lock EA, Smith LL, Rose MS. Inhibition of paraquat accumulation in rat lung slices by a component of rat plasma and a variety of drugs and endogenous amines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976. 25:1769–1772.
Article7. Smith LL. Mechanism of paraquat toxicity in lung and its relevance to treatment. Hum Toxicol. 1987. 6:31–36.
Article8. Kitazawa Y, Matsubara M, Takeyama N, Tanaka T. The role of xanthine oxidase in paraquat intoxication. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991. 288:220–224.
Article9. Suntres ZE. Role of antioxidants in paraquat toxicity. Toxicology. 2002. 180:65–77.
Article10. Lin JL, Leu ML, Liu YC, Chen GH. A prospective clinical trial of pulse therapy with glucocorticoid and cyclophosphamide in moderate to severe paraquat-poisoned patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 159:357–360.
Article11. Webb DB, Williams MV, Davies BH, James KW. Resolution after radiotherapy of severe pulmonary damage due to paraquat poisoning. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1984. 288:1259–1260.
Article12. Proudfoot AT, Stewart MS, Levitt T, Widdop B. Paraquat poisoning: significance of plasma-paraquat concentrations. Lancet. 1979. 2:330–332.
Article13. Bismuth C, Garnier R, Dally S, Fournier PE, Scherrmann JM. Prognosis and treatment of paraquat poisoning: a review of 28 cases. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1982. 19:461–474.
Article14. Hart TB, Nevitt A, Whitehead A. A new statistical approach to the prognostic significance of plasma paraquat concentrations. Lancet. 1984. 2:1222–1223.
Article15. Scherrmann JM, Houze P, bismuth C, Bourdon R. Prognostic value of plasma and urine paraquat concentration. Hum Toxicol. 1987. 6:91–93.
Article16. Hong SY, Yang JO, Lee EY, Kim SH. Effect of haemoperfusion on plasma paraquat concentration in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Ind Health. 2003. 19:17–23.
Article17. Mascie-Taylor BH, Thompson J, Davison AM. Haemoperfusion ineffective for paraquat removal in life-threatening poisoning. Lancet. 1983. 1:1376–1377.
Article18. Van de Vyver FL, Giuliano RA, Paulus GJ, Verpooten GA, Franke JP, De Zeeuw RA, Van Gaal LF, De Broe ME. Hemoperfusion-hemodialysis ineffective for paraquat removal in life-threatening poisoning? J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1985. 23:117–131.
Article19. Pond SM, Johnston SC, Schoof DD, Hampson EC, Bowles M, Wright DM, Petrie JJ. Repeated hemoperfusion and continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration in a paraquat poisoned patient. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1987. 25:305–316.
Article20. Koo JR, Kim JC, Yoon JW, Kim GH, Jeon RW, Kim HJ, Chae DW, Noh JW. Failure of continuous venovenous hemofiltration to prevent death in paraquat poisoning. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002. 39:55–59.
Article21. Houzé P, Baud FJ, Mouy R, Bismuth C, Bourdon R, Scherrmann JM. Toxicokinetics of paraquat in humans. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1990. 9:5–12.
Article22. Hawksworth GH, Bennett PN, Davies DS. Kinetics of paraquat elimination in the dog. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981. 57:139–145.
Article23. Pond SM, Rivory LP, Hampson EC, Roberts MS. Kinetics of toxic doses of paraquat and the effects of hemoperfusion in the dog. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1993. 31:229–246.
Article24. Bismuth C, Scherrmann JM, Garnier R, Baud FJ, Pontal PG. Elimination of paraquat. Hum Toxicol. 1987. 6:63–67.
Article25. Bennett PN, Davies DS, Hawkesworth GM. In vivo absorption studies with paraquat and diquat in the dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1976. 58:284.26. Murray RE, Gibson JE. Paraquat disposition in rats, guinea pig and monkeys. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1974. 27:283–291.27. Chan BS, Lazzaro VA, Seale JP, Duggin GG. The renal excretory mechanisms and the role of organic cations in modulating the renal handling of paraquat. Pharmacol Ther. 1998. 79:193–203.
Article28. Van Vleet TR, Schnellmann RG. Toxic nephropathy: environmental chemicals. Semin Nephrol. 2003. 23:500–508.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hemoperfusion and continuous hemodiafiltration in a paraquat poisoned patient
- Efficacy of Extracorporeal Extraction Treatment in Paraquat Poisoning
- Hemoperfusion and continuous veno-venous hemofiltration for treatment of paraquat poisoning
- Usefulness of Hemoperfusion in Paraquat Poisoning
- Clinical experience of hemoperfusion treatment in children with paraquat poisoning