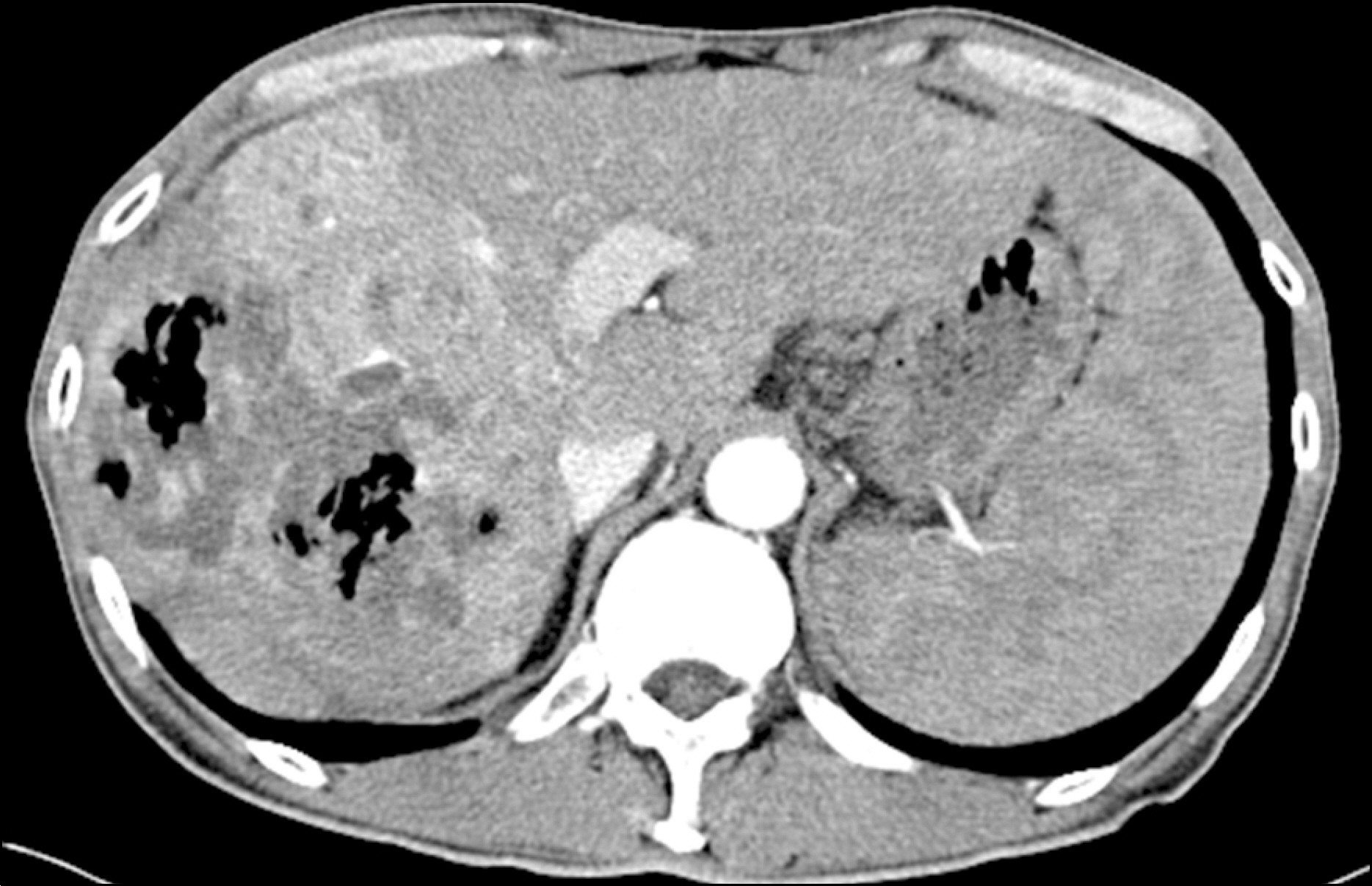
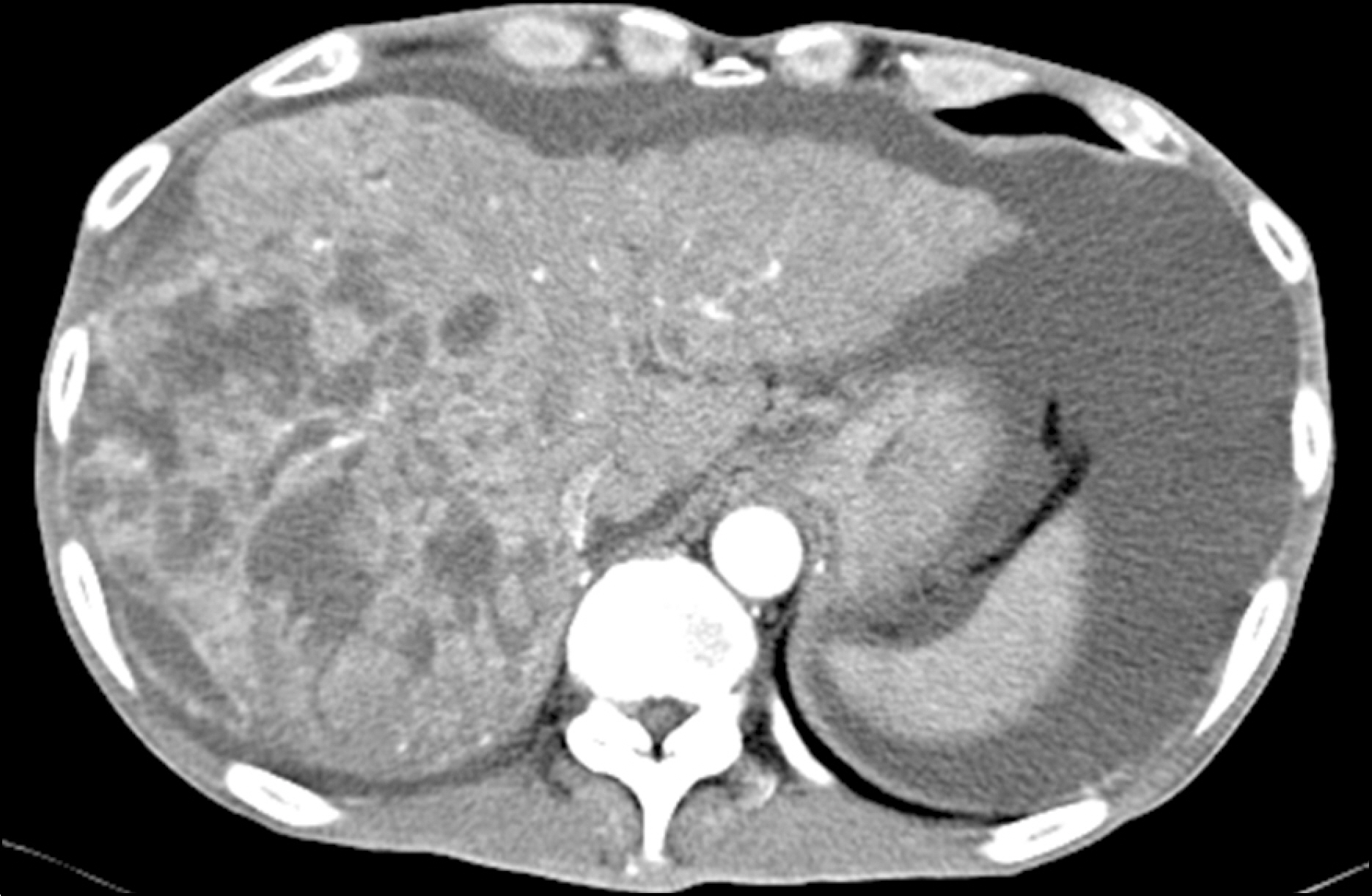
Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Jan;63(1):47-50. 10.4166/kjg.2014.63.1.47.
Liver Abscess in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Sorafenib Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. jhkim@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 1711306
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.63.1.47
Abstract
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a critical global health issue and the third most common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The majority of patients who present HCC are already at an advanced stage and their tumors are unresectable. Sorafenib is a multi-kinase inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway and was recently introduced as a therapy for advanced HCC. Furthermore, studies have shown that oral sorafenib has beneficial effects on survival. However, many patients experience diverse side effects, and some of these are severe. Liver abscess development has not been previously documented to be associated with sorafenib administration in HCC. Here, we report the case of a HCC patient that developed a liver abscess while being treated with sorafenib.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Antineoplastic Agents/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/*drug therapy/radiography
Clostridium/isolation & purification
Clostridium Infections/drug therapy/microbiology
Humans
Liver Abscess/etiology/*microbiology
Liver Neoplasms/*drug therapy/radiography
Male
Middle Aged
Niacinamide/adverse effects/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Phenylurea Compounds/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Antineoplastic Agents
Niacinamide
Phenylurea Compounds
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Miura H, Miyazaki T, Kuroda M, et al. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 1997; 27:854–861.
Article2. Torimura T, Sata M, Ueno T, et al. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1998; 29:986–991.
Article3. Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al. BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:7099–7109.
Article4. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. SHARP Investigators Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:378–390.
Article5. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:25–34.
Article6. Rahimian J, Wilson T, Oram V, Holzman RS. Pyogenic liver abscess: recent trends in etiology and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 39:1654–1659.
Article7. Brook I, Frazier EH. Microbiology of liver and spleen abscesses. J Med Microbiol. 1998; 47:1075–1080.
Article8. Lieuw-a-Fa M, Peringa J, Leeksma O, Terpstra W. Sepsis from liver abscesses in metastatic colorectal carcinoma after chemo-immunotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:1381–1382.
Article9. Chen C, Chen PJ, Yang PM, et al. Clinical and microbiological features of liver abscess after transarterial embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92:2257–2259.10. Ong GY, Changchien CS, Lee CM, et al. Liver abscess complicating transcatheter arterial embolization: a rare but serious complication. A retrospective study after 3878 procedures. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 16:737–742.11. Kim MH, Choi MS, Choi YS, et al. Clinical features of liver abscess developed after radiofrequency ablation and transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Hepatol. 2006; 12:55–64.12. Rhim H, Yoon KH, Lee JM, et al. Major complications after radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics. 2003; 23:123–134. discussion 134–136.
Article13. Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, Goldberg SN. Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology. 2003; 226:441–451.
Article14. Kobayashi S, Nakanuma Y, Terada T, Matsui O. Postmortem survey of bile duct necrosis and biloma in hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization therapy: relevance to microvascular damages of peribiliary capillary plexus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993; 88:1410–1415.15. Kim YK, Yu SE, Hong CK, et al. Liver abscess formation in non-tumorous parenchyma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with pneumobilia. Korean J Hepatol. 2001; 7:189–194.16. Everson TC, Cole WH. Spontaneous regression of cancer. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1966. p. 6–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatments Other than Sorafenib for Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Complete Response of Single Nodular Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Pulmonary Metastasis by Sequential Transarterial Chemoembolization and Sorafenib: A Case Report
- Liver resection after sorafenib therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
- Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
- Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy