Korean J Gastroenterol.
2013 Dec;62(6):365-369. 10.4166/kjg.2013.62.6.365.
A Case of Ileal Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Accompanied by Luminal Stricture and Arterial Spurting
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. L85210@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1711293
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2013.62.6.365
Abstract
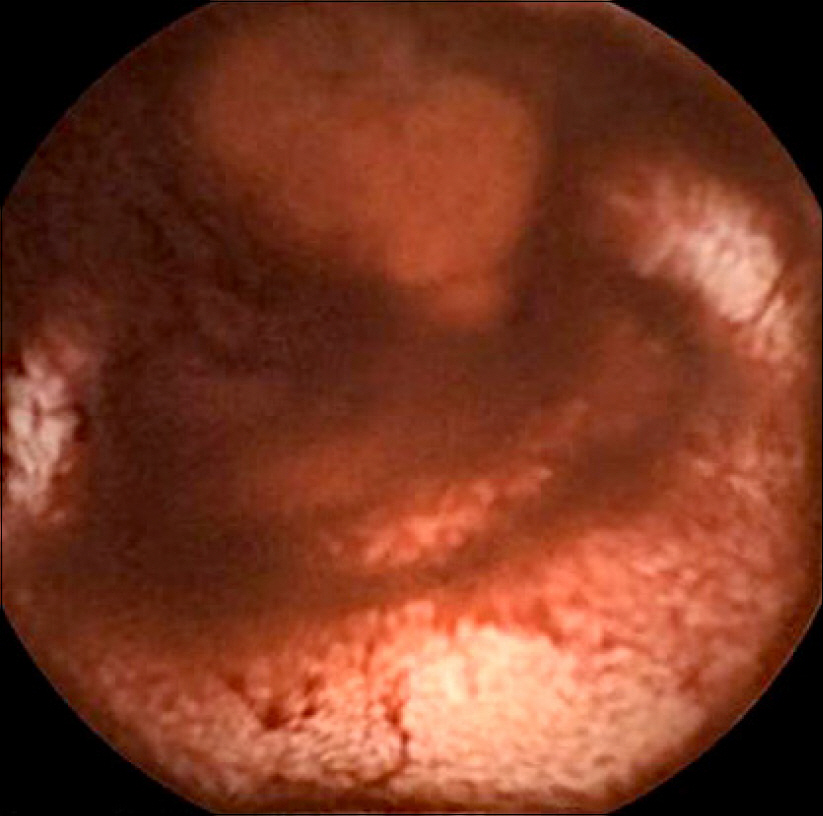
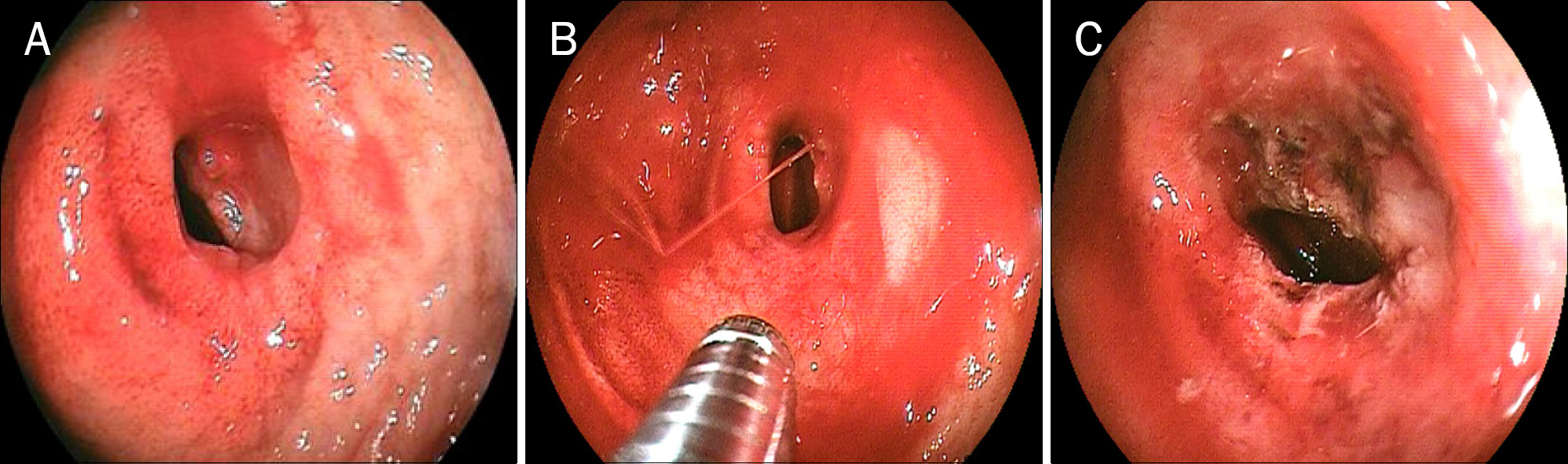
- Primary small intestinal lymphoma is relatively uncommon. Small bowel tumors are difficult to diagnose, because they are usually asymptomatic in the initial phase, and they are not easily detected by traditional methods of investigating the small intestine. This case shows a successfully detected and treated gastrointestinal bleeding from rare ileal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma, using double balloon endoscopy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Darling RC, Welch CE. Tumors of the small intestine. N Engl J Med. 1959; 260:397–408.
Article2. Radaszkiewicz T, Dragosics B, Bauer P. Gastrointestinal malignant lymphomas of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue: factors relevant to prognosis. Gastroenterology. 1992; 102:1628–1638.
Article3. Isaacson P, Wright DH. Malignant lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. A distinctive type of B-cell lymphoma. Cancer. 1983; 52:1410–1416.
Article4. Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994; 84:1361–1392.5. Cogliatti SB, Schmid U, Schumacher U, et al. Primary B-cell gastric lymphoma: a clinicopathological study of 145 patients. Gastroenterology. 1991; 101:1159–1170.
Article6. Lee BI, Choi H, Choi KY, et al. Clinical characteristics of small bowel tumors diagnosed by double-balloon endoscopy: KASID multicenter study. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:2920–2927.
Article7. Dinesen LC, Kaffes AJ, Selby W. Diagnostic and therapeutic benefits of double balloon endoscopy in small bowel neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140(Suppl 1):S118–S119.
Article8. Imaoka H, Higaki N, Kumagi T, et al. Characteristics of small bowel tumors detected by double balloon endoscopy. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:2366–2371.
Article9. Nakamura S, Matsumoto T, Takeshita M, et al. A clinicopathologic study of primary small intestine lymphoma: prognostic significance of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue-derived lymphoma. Cancer. 2000; 88:286–294.10. de Leval L, Gaulard P. Pathology and biology of peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Histopathology. 2011; 58:49–68.
Article11. Ioannidis O, Cheva A, Kakoutis E, et al. Acute adult intussusception caused by primary cecal non Hodgkin lymphoma. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2011; 74:451–453.12. Ferreri AJ, Montalbán C. Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the stomach. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007; 63:65–71.
Article13. Mansoor A, Pittaluga S, Beck PL, Wilson WH, Ferry JA, Jaffe ES. NK-cell enteropathy: a benign NK-cell lymphoproliferative disease mimicking intestinal lymphoma: clinicopathologic features and follow-up in a unique case series. Blood. 2011; 117:1447–1452.
Article14. Yanai S, Nakamura S, Hirahashi M, Ueki T, Matsumoto T, Kitazono T. Education and imaging. Gastrointestinal: MALT lymphoma of the small bowel accompanied by NSAID-induced enteropathy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:1126.15. Schechter NR, Portlock CS, Yahalom J. Treatment of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the stomach with radiation alone. J Clin Oncol. 1998; 16:1916–1921.
Article16. Papa A, Cammarota G, Tursi A, Gasbarrini A, Gasbarrini G. Helicobacter pylori eradication and remission of low-grade gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: a long-term follow-up study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000; 31:169–171.17. Fischbach W, Tacke W, Greiner A, Konrad H, Müller-Hermelink HK. Regression of immunoproliferative small intestinal disease after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1997; 349:31–32.18. Raderer M, Wöhrer S, Streubel B, et al. Assessment of disease dissemination in gastric compared with extragastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma using extensive staging: a single-center experience. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:3136–3141.
Article19. Domizio P, Owen RA, Shepherd NA, Talbot IC, Norton AJ. Primary lymphoma of the small intestine. A clinicopathological study of 119 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993; 17:429–442.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ileal Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma with a Large-Cell Component That Regressed Spontaneously
- Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Esophagus Coexistent with Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Lung
- A case report of the Pulmonary Malignant Lymphomaof the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue(MALT)
- A Polypoid Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Stomach Treated with Endoscopic Polypectomy
- A Case of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of Colon as Multiple Large Polypoid Lesions