Prog Med Phys.
2014 Jun;25(2):110-115. 10.14316/pmp.2014.25.2.110.
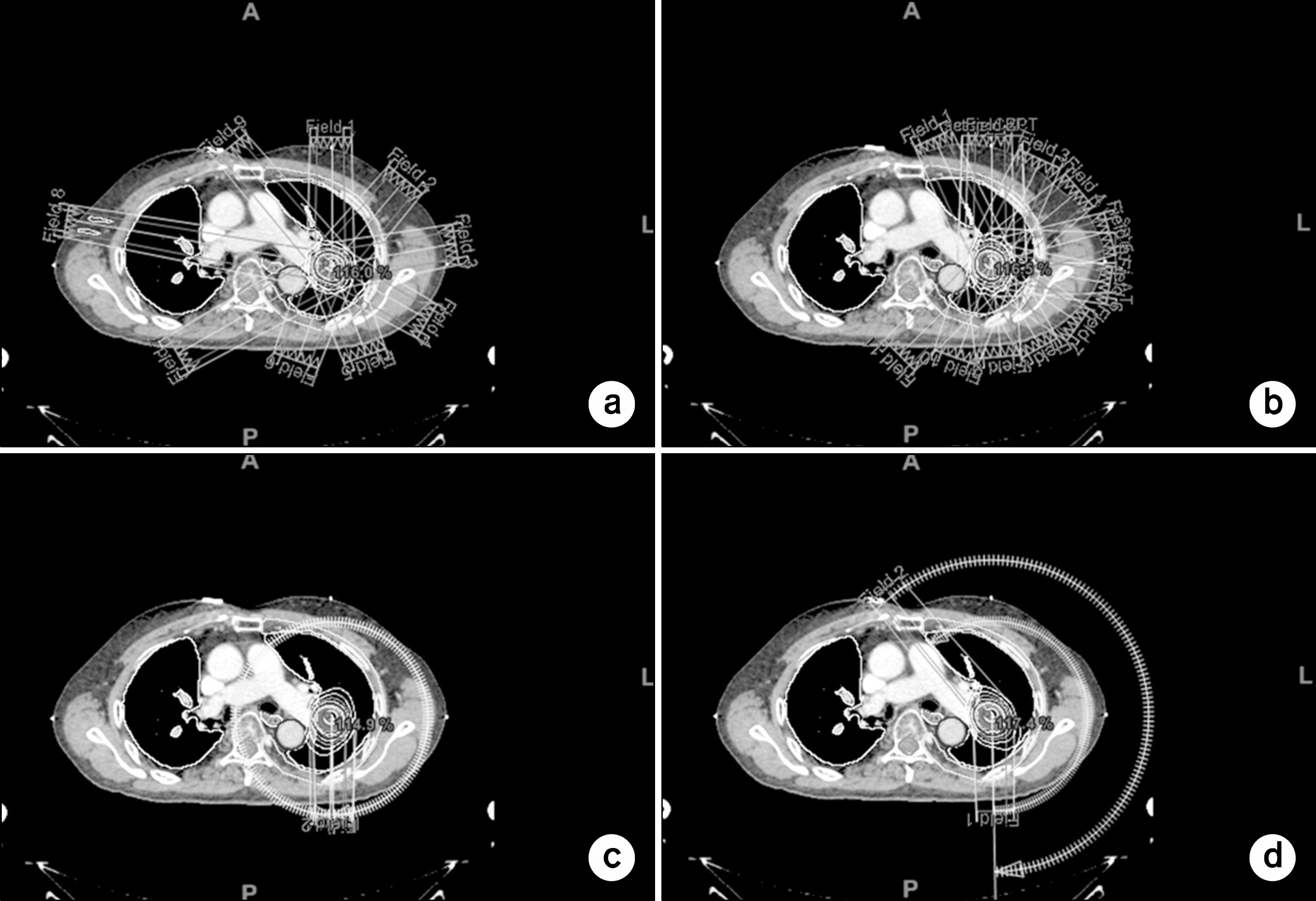
Comparison of the Dose Distributions with Beam Arrangements in the Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Primary Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. yjw1160@ynu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1708178
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2014.25.2.110
Abstract
- To compare 2 beam arrangements, circumferential equally angles (EA) beams or partially angles (PA) beams for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) of primary lung cancer for intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) delivery techniques with respect to target, ipsilateral lung, contralateral lung, and organs-at-risk (OAR) dose-volume metrics, as well as treatment delivery efficiency. Data from 12 patients, four treatment plans were generated per data sets (IMRT(EA), IMRT(PA), VMAT(EA), VMAT(PA)). The prescribed dose (PD) was 60 Gy in 4 fractions to 95% of the planning target volume (PTV) for a 6-MV photon beam. When compared with the IMRT and VMAT treatment plan for 2 beams, conformity index, homogeneity index, high dose spillage, D2 cm (Dmax at a distance > or =2 cm beyond the PTV), R50 (ratio of volume circumscribed by the 50% isodose line and the PTV), resulted in similar. But Dmax of the Organ at risk (OAR), spinal cord, trachea, resulted in differ between four treatment plans. Especially HDS(location) showed big difference in 21.63% vs. 26.46%.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Robert D, Timmerman MD, Brain D, et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Multiple Organ Sites. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 25:947–52. 2007.2. Oh SA, Kang MK, Kim SK, Yea JW. Comparison of IMRT and VMAT techniques in spine stereotactic radiosurgery with international spine radiosurgery consortium consensus guidelines. Prog Med Phys. 24(3):145–153. 2013.
Article3. Lim DH, YI BY, Mirmiran A, et al. Optimal beam arrangement for stereotactic body radiation therapy delivery in lung tumors. Acta Oncologica. 49:219–224. 2010.
Article4. Mara WR, Catherine MK, Kelly MPC, et al. Circumferential or sectored beam arrangements for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) of primary lung tumors: Effect on target and normal-structure dose-volume metrics. Med Dos. 38:407–412. 2013.5. Robert T, Rebecca P, James G, et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Inoperable Early Stage Lung Cancer, JAMA. 303(11):1070–1076. (201).6. Nagata Y, Takayama K, Matsuo Y, et al. Clinical outcomes of a phase I/II study of 48 Gy of stereotactic body radiotherapy in 4 fractions for primary lung cancer using a stereotactic body frame. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 63(5):1427–1431. 2005.
Article7. Timmerman R, Galvin J, Michalski J, et al. Accreditation and quality assurance for Radiation Therapy Oncology Group: multicenter clinical trials using stereotactic body radiation therapy in lung cancer. Acta Oncol. 45(7):779–786. 2006.
Article8. Dirk De R, Corinne FF, Ursula N, et al. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Recommendations for Planning and Delivery of High-Dose. High-Precision Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer. 28(36):5301–5310. 2010.9. RTOG 0813: Seamless Phase I/II Study of Stereotactic Lung Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Early Stage, Centrally Located, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) in Medically Inoperable Patients. http://www.rtog.org/ClinicalTrials/ProtocolTable/StudyDetails. aspx?study=0813.10. RTOG 0915: A randomized phase II study comparing 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) schedules for medically inoperable patients with stage I peripheral non-small cell lung cancer. http://www.rtog.org/ClinicalTrials/ProtocolTable/StudyDetails. aspx?study=0915.11. Benedict SH, Yenice KM, Followill D, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: The report of AAPM task group 101.Med Phys. 37:4078–101. 2010.12. Oh SA, Kang MK, Yea JW, Kim SH, Kim KH, Kim SK. Comparison of intensity modulated radiation therapy dose calculations with a PBC and AAA algorithms in the lung cancer. Korea J Med Phys. 23:48–53. 2012.13. Feuvret L, Noel G, Mazeron JJ, Bey P. Conformity index: a review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 64:333–342. 2006.
Article14. Ong CL, Verbakel WF, Cuijpers JP, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy for peripheral lung tumors: A comparison of volumetric modulated arc therapy with 3 other delivery techniques Radiother Oncol. 97:437–42. 2010.15. Holt A, van Vliet-Vroegindeweij C, Mans A, et al. Volumetric-Modulated Arc Therapy for Stereotactic body radiotherapy of lung tumors: A comparison with intensitymodulated radiotherapy techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:1560–7. 2011.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- Dosimetric Analysis of Lung Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Using Halcyon Linear Accelerator
- Stereotactic radiotherapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer
- Feasibility and Efficacy of Adaptive Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy Planning according to Tumor Volume Change in Early Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy