Prog Med Phys.
2023 Dec;34(4):48-54. 10.14316/pmp.2023.34.4.48.
Dosimetric Analysis of Lung Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Using Halcyon Linear Accelerator
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2550125
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2023.34.4.48
Abstract
- Purpose
In this study, the dosimetric characteristics of lung stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) plans using the new Halcyon system were analyzed to assess its suitability.
Methods
We compared the key dosimetric parameters calculated for the Halcyon SBRT plans with those of a conventional C-arm linear accelerator (LINAC) equipped with a high-definition multileaf collimator (HD-MLC)—Trilogy Tx. A total of 10 patients with non-small-cell lung cancer were selected, and all SBRT plans were generated using the RapidArc technique.
Results
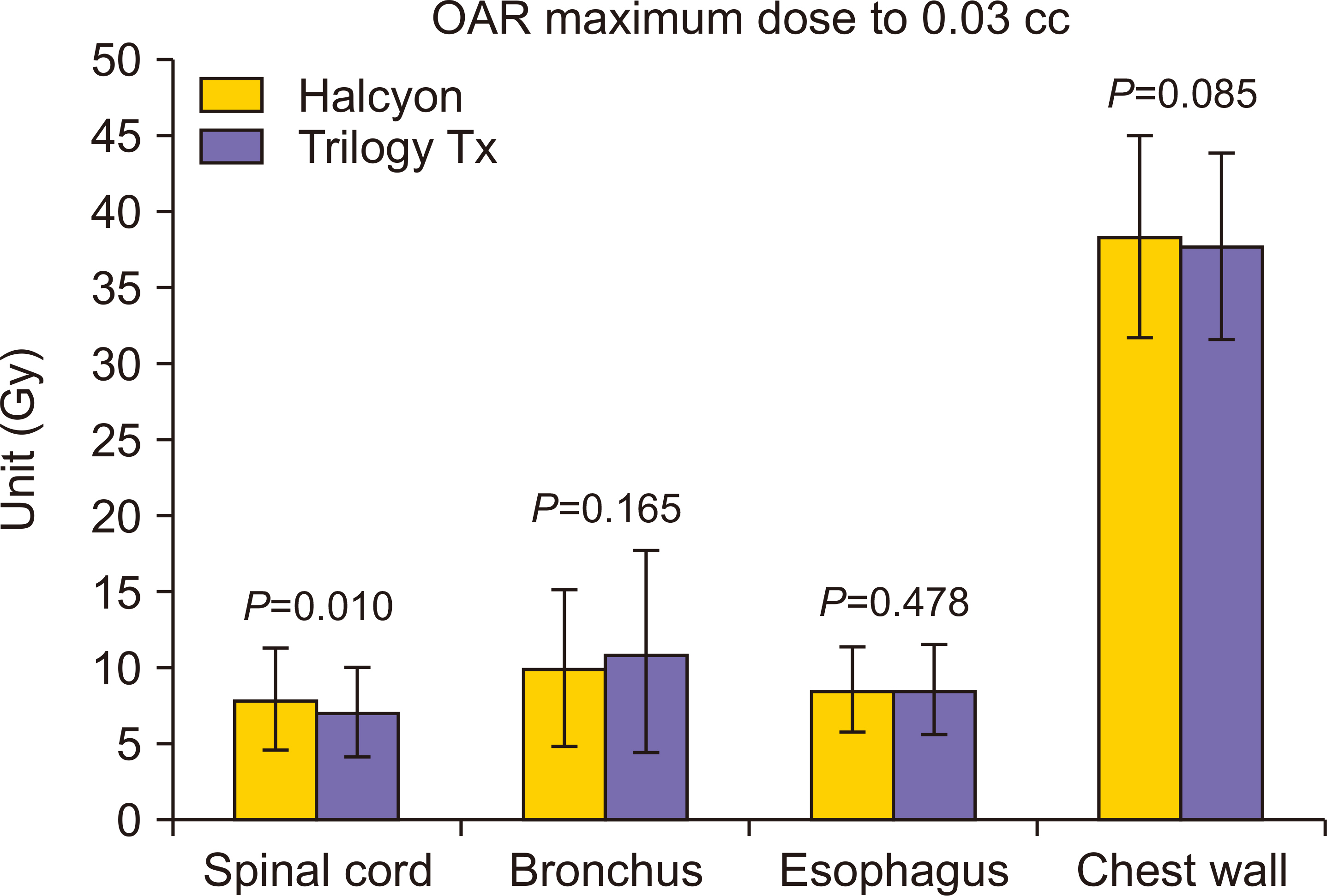
Trilogy Tx exhibited significant superiority over Halcyon in terms of target dose coverage (conformity index, homogeneity index, D0.1 cc, and D95%) and dose spillage (gradient). Trilogy Tx was more efficient than Halcyon in the lung SBRT beam delivery process in terms of the total number of monitor units, modulation factor, and beam-on time. However, it was feasible to achieve a dose distribution that met SBRT plan requirements using Halcyon, with no significant differences in satisfying organs at risk dose constraints between both plans.
Conclusions
Results confirm that Halcyon is a viable alternative for performing lung SBRT in the absence of a LINAC equipped with HD-MLC. However, extra consideration should be taken in determining whether to use Halcyon when the planning target volume setting is enormous, as in the case of significant tumor motions.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Zimmermann FB, Geinitz H, Schill S, Grosu A, Schratzenstaller U, Molls M, et al. 2005; Stereotactic hypofractionated radiation therapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 48:107–114. DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.10.015. PMID: 15777977.
Article2. McGarry RC, Papiez L, Williams M, Whitford T, Timmerman RD. 2005; Stereotactic body radiation therapy of early-stage non-small-cell lung carcinoma: phase I study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 63:1010–1015. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.03.073. PMID: 16115740.
Article3. Fakiris AJ, McGarry RC, Yiannoutsos CT, Papiez L, Williams M, Henderson MA, et al. 2009; Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung carcinoma: four-year results of a prospective phase II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 75:677–682. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.11.042. PMID: 19251380.
Article4. Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, Gomi K, et al. 2011; Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:1352–1358. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1751. PMID: 20638194.
Article5. Ong CL, Verbakel WF, Cuijpers JP, Slotman BJ, Lagerwaard FJ, Senan S. 2010; Stereotactic radiotherapy for peripheral lung tumors: a comparison of volumetric modulated arc therapy with 3 other delivery techniques. Radiother Oncol. 97:437–442. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.09.027. PMID: 21074878.
Article6. McGrath SD, Matuszak MM, Yan D, Kestin LL, Martinez AA, Grills IS. 2010; Volumetric modulated arc therapy for delivery of hypofractionated stereotactic lung radiotherapy: a dosimetric and treatment efficiency analysis. Radiother Oncol. 95:153–157. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2009.12.039. PMID: 20116115.
Article7. Holt A, van Vliet-Vroegindeweij C, Mans A, Belderbos JS, Damen EM. 2011; Volumetric-modulated arc therapy for stereotactic body radiotherapy of lung tumors: a comparison with intensity-modulated radiotherapy techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:1560–1567. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.09.014. PMID: 21300461.
Article8. Xiao Y, Kry SF, Popple R, Yorke E, Papanikolaou N, Stathakis S, et al. 2015; Flattening filter-free accelerators: a report from the AAPM Therapy Emerging Technology Assessment Work Group. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 16:5219. DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i3.5219. PMID: 26103482. PMCID: PMC5690108.
Article9. Tanyi JA, Summers PA, McCracken CL, Chen Y, Ku LC, Fuss M. 2009; Implications of a high-definition multileaf collimator (HD-MLC) on treatment planning techniques for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): a planning study. Radiat Oncol. 4:22. DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-4-22. PMID: 19591687. PMCID: PMC2716348.
Article10. Petroccia HM, Malajovich I, Barsky AR, Ghiam AF, Jones J, Wang C, et al. 2019; Spine SBRT with HalcyonTM: plan quality, modulation complexity, delivery accuracy, and speed. Front Oncol. 9:319. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00319. PMID: 31106151. PMCID: PMC6498946.11. Kim H, Huq MS, Lalonde R, Houser CJ, Beriwal S, Heron DE. 2019; Early clinical experience with Varian Halcyon V2 linear accelerator: dual-isocenter IMRT planning and delivery with portal dosimetry for gynecological cancer treatments. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 20:111–120. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12747. PMID: 31660682. PMCID: PMC6839386.
Article12. Ju E, Heo EJ, Park CG, Kim M, Kim KH, Shim JB, et al. 2021; Dosimetric comparison of VitalBeam® and HalcyonTM 2.0 for hypofractionated VMAT with simultaneous integrated boost treatment of early-stage left-sided breast cancer. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 22:232–238. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13428. PMID: 34554605. PMCID: PMC8504599.
Article13. Visak J, Webster A, Bernard ME, Kudrimoti M, Randall ME, McGarry RC, et al. 2021; Fast generation of lung SBRT plans with a knowledge-based planning model on ring-mounted Halcyon Linac. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 22:54–63. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13427. PMID: 34562308. PMCID: PMC8598154.
Article14. Lim TY, Dragojević I, Hoffman D, Flores-Martinez E, Kim GY. 2019; Characterization of the HalcyonTM multileaf collimator system. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 20:106–114. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12568. PMID: 30889312. PMCID: PMC6448159.15. Pokhrel D, Tackett T, Stephen J, Visak J, Amin-Zimmerman F, McGregor A, et al. 2021; Prostate SBRT using O-Ring Halcyon Linac - plan quality, delivery efficiency, and accuracy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 22:68–75. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13105. PMID: 33340388. PMCID: PMC7856496.
Article16. Li F, Park J, Lalonde R, Jang SY, diMayorca MS, Flickinger JC, et al. 2022; Is Halcyon feasible for single thoracic or lumbar vertebral segment SBRT? J Appl Clin Med Phys. 23:e13458. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13458. PMID: 34845817. PMCID: PMC8803290.
Article17. Wu QJ, Wang Z, Kirkpatrick JP, Chang Z, Meyer JJ, Lu M, et al. 2009; Impact of collimator leaf width and treatment technique on stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy plans for intra- and extracranial lesions. Radiat Oncol. 4:3. DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-4-3. PMID: 19159471. PMCID: PMC2637285.
Article18. Bortfeld T, Oelfke U, Nill S. 2000; What is the optimum leaf width of a multileaf collimator? Med Phys. 27:2494–2502. DOI: 10.1118/1.1319524. PMID: 11128300.
Article19. Shaw E, Kline R, Gillin M, Souhami L, Hirschfeld A, Dinapoli R, et al. 1993; Radiation Therapy Oncology Group: radiosurgery quality assurance guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 27:1231–1239. DOI: 10.1016/0360-3016(93)90548-A. PMID: 8262852.
Article20. Pokhrel D, Visak J, Critchfield LC, Stephen J, Bernard ME, Randall M, et al. 2021; Clinical validation of ring-mounted Halcyon Linac for lung SBRT: comparison to SBRT-dedicated C-arm Linac treatments. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 22:261–270. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13146. PMID: 33342070. PMCID: PMC7856490.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- Analysis of the Multi-Leaf Collimator Quality Assurance for the HalcyonTM Linear Accelerator
- Evaluation of Dosimetric Characteristics of a Double-focused Dynamic Micro-Multileaf Collimator (DMLC)
- A case report of a patient with squamous cell carcinoma of the face irradiated using a stereotactic technique
- LINAC-based High-precision Radiotherapy: Radiosurgery, Image-guided Radiotherapy, and Respiratory-gated Radiotherapy