Korean J Gastroenterol.
2013 Sep;62(3):174-178. 10.4166/kjg.2013.62.3.174.
A Case of Diaphragmatic Hernia Induced by Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. portalvein@naver.com
- KMID: 1707201
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2013.62.3.174
Abstract
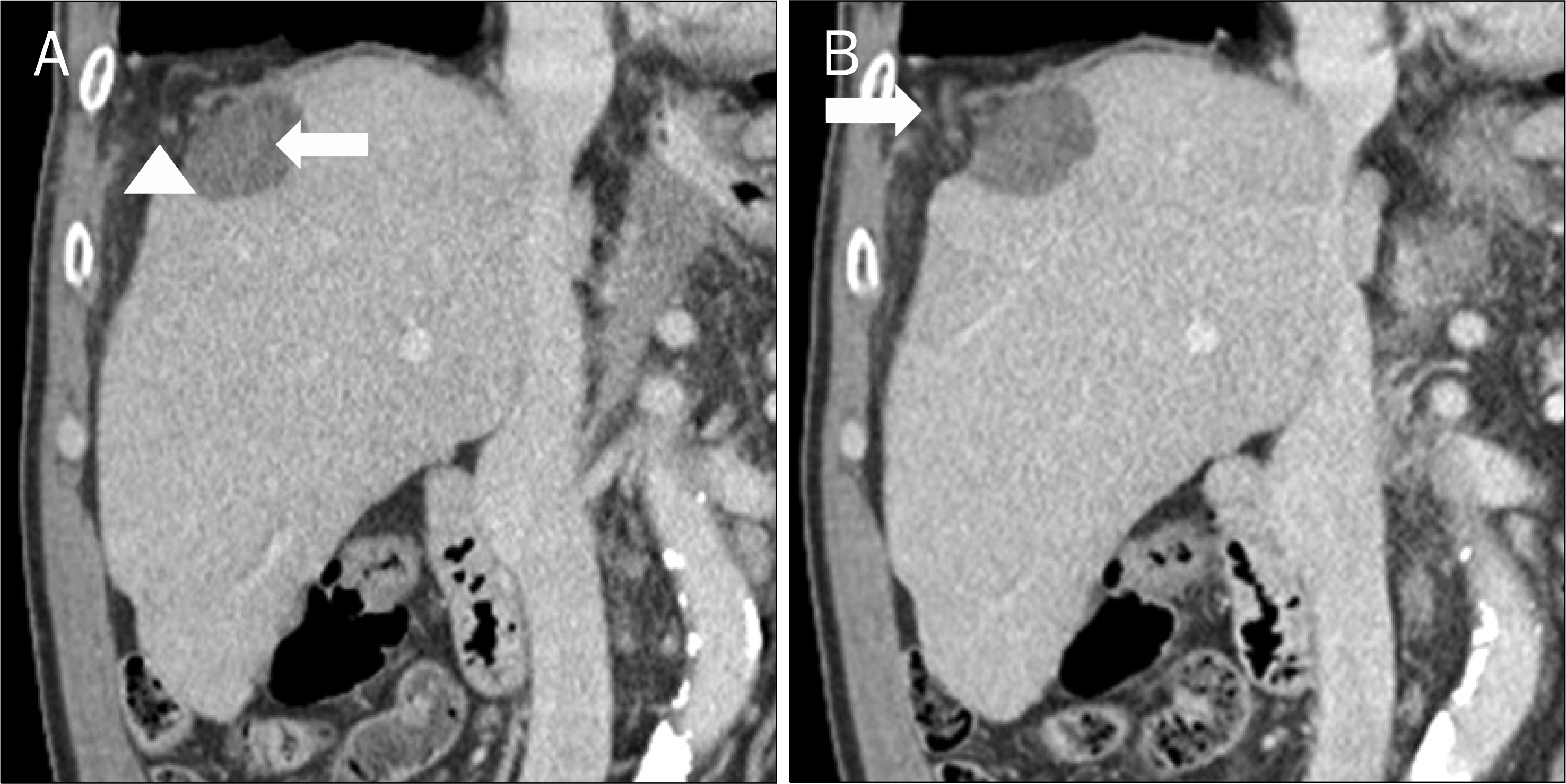
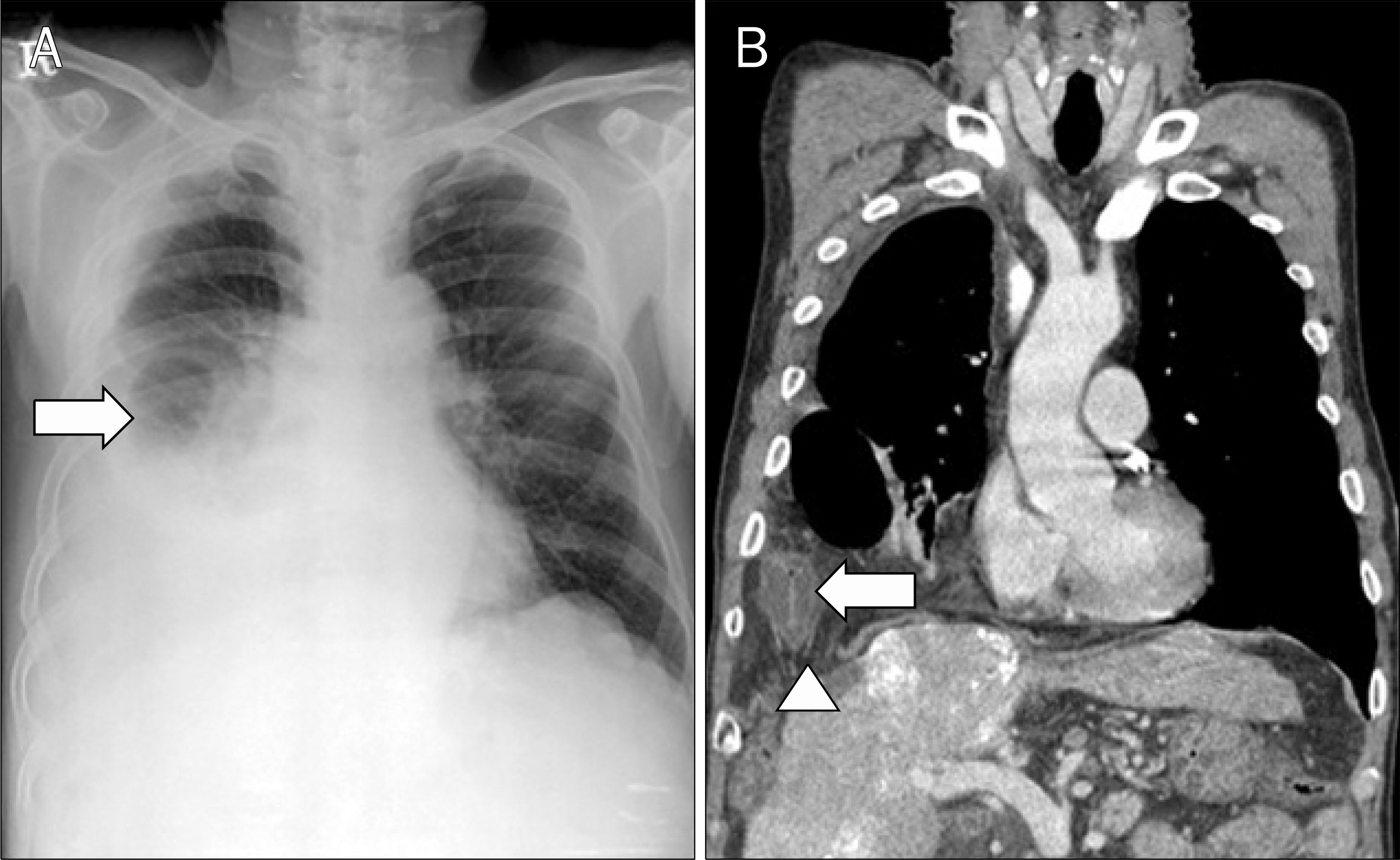
- Because of its safety and treatment effectiveness, the popularity of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has gradually increased. However, some serious complications of RFA such as hepatic infarction, bowel perforation, and tumor seeding have been reported. Recently, we experienced a case of diaphragmatic hernia after RFA for HCC. A 61-year-old man with alcoholic cirrhosis was diagnosed with a 1.0 cm sized HCC in segment (S) 5 and a 1.3 cm sized HCC in S 8 of the liver. He was treated by transarterial chemoembolization and RFA. After RFA, an abdominal CT revealed a diaphragmatic defect with herniating mesentery. Twenty-two months after the RFA, the chest CT showed the diaphragmatic defect with herniating colon and mesentery. Because he had no symptoms, and surgical repair for the diaphragmatic hernia would be a high risk operation for him, we decided to treat the patient conservatively. For its great rarity, we report this case with a review of the literature.
MeSH Terms
-
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/*diagnosis/*radiotherapy/therapy
Catheter Ablation/*adverse effects
Chemoembolization, Therapeutic
Hernia, Diaphragmatic/*etiology/surgery
Humans
Liver Cirrhosis, Alcoholic/complications/*diagnosis
Liver Neoplasms/*diagnosis/*radiotherapy/therapy
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Middle Aged
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Rossi S, Di Stasi M, Buscarini E, et al. Percutaneous RF interstitial thermal ablation in the treatment of hepatic cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 167:759–768.
Article2. Yan K, Chen MH, Yang W, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term outcome and prognostic factors. Eur J Radiol. 2008; 67:336–347.
Article3. Bertot LC, Sato M, Tateishi R, Yoshida H, Koike K. Mortality and complication rates of percutaneous ablative techniques for the treatment of liver tumors: a systematic review. Eur Radiol. 2011; 21:2584–2596.
Article4. Park SG, Park SJ, Koo HS, et al. Biliary-duodenal fistula following radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 51:199–203.5. Kim JY, Kwon YH, Lee SJ, et al. Abscesso-colonic fistula following radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma;a case successfully treated with histoacryl embolization. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 58:270–274.6. Liu JG, Wang YJ, Du Z. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:3450–3456.
Article7. Guglielmi A, Ruzzenente A, Valdegamberi A, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008; 12:192–198.
Article8. Goldberg SN, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD 3rd, et al. International Working Group on Image-Guided Tumor Ablation. Image-guided tumor ablation: proposal for standardization of terms and reporting criteria. Radiology. 2003; 228:335–345.
Article9. Koda M, Ueki M, Maeda N, Murawaki Y. Diaphragmatic perforation and hernia after hepatic radiofrequency ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:1561–1562.
Article10. Shibuya A, Nakazawa T, Saigenji K, Furuta K, Matsunaga K. Diaphragmatic hernia after radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 186(5 Suppl):S241–S243.
Article11. di Francesco F, di Sandro S, Doria C, et al. Diaphragmatic hernia occurring 15 months after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of a hepatocellular cancer. Am Surg. 2008; 74:129–132.12. Yamagami T, Yoshimatsu R, Matsushima S, Tanaka O, Miura H, Nishimura T. Diaphragmatic hernia after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2011; 34(Suppl 2):S175–S177.
Article13. Singh M, Singh G, Pandey A, Cha CH, Kulkarni S. Laparoscopic repair of iatrogenic diaphragmatic hernia following radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 2011; 41:1132–1136.
Article14. Tateishi R, Shiina S, Teratani T, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer. 2005; 103:1201–1209.15. Curley SA, Izzo F, Ellis LM, Nicolas Vauthey J, Vallone P. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 2000; 232:381–391.
Article16. Uehara T, Hirooka M, Ishida K, et al. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma with artificially induced pleural effusion and ascites. J Gastroenterol. 2007; 42:306–311.
Article17. Raman SS, Aziz D, Chang X, Sayre J, Lassman C, Lu D. Minimizing diaphragmatic injury during radiofrequency ablation: efficacy of intraabdominal carbon dioxide insufflation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:197–200.18. Lee SD, Han HS, Cho JY, et al. Safety and efficacy of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for hepatic malignancies. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 83:36–42.
Article19. Iwai S, Sakaguchi H, Fujii H, et al. Benefits of artificially induced pleural effusion and/or ascites for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma located on the liver surface and in the hepatic dome. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012; 59:546–550.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Microwave thermosphere versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we approaching the time to end the debate?
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?
- Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation
- Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas
- Current status and future of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma