Korean J Radiol.
2013 Jun;14(3):540-543. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.3.540.
Case of Pulmonary Cryptococcosis Mimicking Hematogeneous Metastases in an Immuocompetent Patient: Value of Absent 18F-Fluorodeoxylucose Uptake on Positron Emission Tomography/CT Scan
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital and National Defense Medical Center, Taipei 114, Taiwan, Republic of China. hsianhe@yahoo.com.tw
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, Tri-Service General Hospital and National Defense Medical Center, Taipei 114, Taiwan, Republic of China.
- 3Department of Pathology, Tri-Service General Hospital and National Defense Medical Center, Taipei 114, Taiwan, Republic of China.
- KMID: 1705472
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.3.540
Abstract
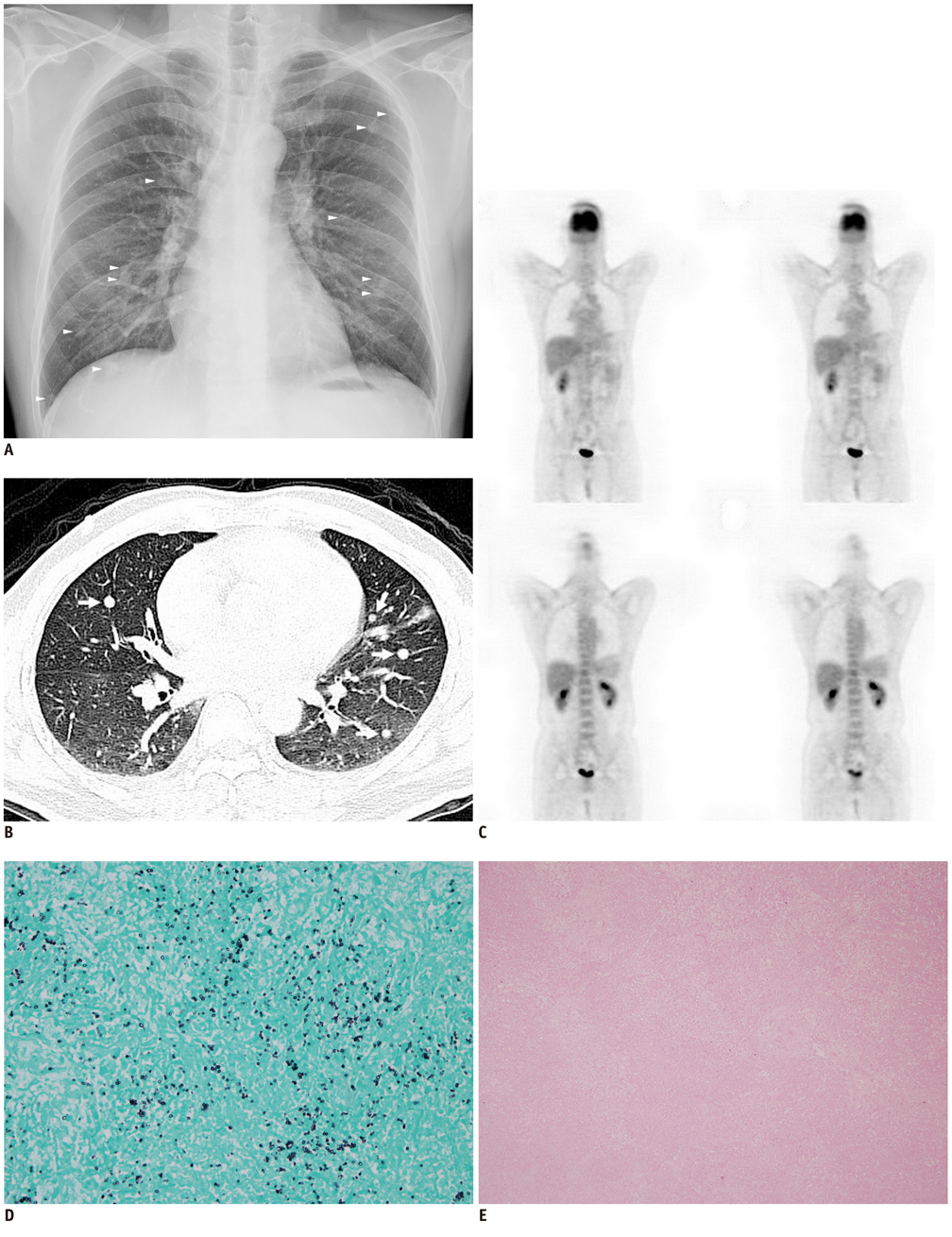
- The radiologic appearance of multiple discrete pulmonary nodules in immunocompetent patients, with cryptococcal infection, has been rarely described. We describe a case of pulmonary cryptococcosis, presenting with bilaterally and randomly distributed nodules on a computed tomography, mimicking hematogeneous metastases. Positron emission tomography does not demonstrate 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake, suggesting a low probability for malignancy, which is a crucial piece of information for clinicians when making a management decision. We find the absence of FDG uptake correlates with the pathologic finding of an infectious nodule, composed of fibrosis and necrosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cryptococcosis/metabolism/*radionuclide imaging
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18/*diagnostic use/pharmacokinetics
Humans
Immunocompetence
Lung Diseases, Fungal/metabolism/*radionuclide imaging
Lung Neoplasms/radionuclide imaging
Male
Middle Aged
Multimodal Imaging/*methods
Multiple Pulmonary Nodules/radionuclide imaging
Positron-Emission Tomography/*methods
Radiopharmaceuticals/*diagnostic use/pharmacokinetics
Tomography, X-Ray Computed/*methods
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18
Radiopharmaceuticals
Figure
Reference
-
1. Patz EF Jr, Goodman PC. Pulmonary cryptococcosis. J Thorac Imaging. 1992. 7:51–55.2. Rozenbaum R, Gonçalves AJ. Clinical epidemiological study of 171 cases of cryptococcosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1994. 18:369–380.3. Chang WC, Tzao C, Hsu HH, Lee SC, Huang KL, Tung HJ, et al. Pulmonary cryptococcosis: comparison of clinical and radiographic characteristics in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Chest. 2006. 129:333–340.4. Yang CJ, Hwang JJ, Wang TH, Cheng MS, Kang WY, Chen TC, et al. Clinical and radiographic presentations of pulmonary cryptococcosis in immunocompetent patients. Scand J Infect Dis. 2006. 38:788–793.5. Lindell RM, Hartman TE, Nadrous HF, Ryu JH. Pulmonary cryptococcosis: CT findings in immunocompetent patients. Radiology. 2005. 236:326–331.6. Fox DL, Müller NL. Pulmonary cryptococcosis in immunocompetent patients: CT findings in 12 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 185:622–626.7. Choe YH, Moon H, Park SJ, Kim SR, Han HJ, Lee KS, et al. Pulmonary cryptococcosis in asymptomatic immunocompetent hosts. Scand J Infect Dis. 2009. 41:602–607.8. Núñez M, Peacock JE Jr, Chin R Jr. Pulmonary cryptococcosis in the immunocompetent host. Therapy with oral fluconazole: a report of four cases and a review of the literature. Chest. 2000. 118:527–534.9. Huang CJ, You DL, Lee PI, Hsu LH, Liu CC, Shih CS, et al. Characteristics of integrated 18F-FDG PET/CT in Pulmonary Cryptococcosis. Acta Radiol. 2009. 50:374–378.10. Hashimoto Y, Tsujikawa T, Kondo C, Maki M, Momose M, Nagai A, et al. Accuracy of PET for diagnosis of solid pulmonary lesions with 18F-FDG uptake below the standardized uptake value of 2.5. J Nucl Med. 2006. 47:426–431.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perirenal 18F-FDG Uptake in a Patient with a Pheochromocytoma
- Non-Malignant 18F-FDG Uptake in the Thorax by Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography Fusion Imaging
- Lymphocytic Thyroiditis Presenting as a Focal Uptake on 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography: A Case Report
- 18F-FDG PET/CT Findings in a Breast Cancer Patient with Concomitant Tuberculous Axillary Lymphadenitis
- Differential Imaging Features of Pulmonary Artery Dissection from Other Intraluminal Diseases of Pulmonary Artery: Two Cases Report