J Korean Endocr Soc.
2007 Apr;22(2):130-134. 10.3803/jkes.2007.22.2.130.
A Case of Kallmann's Syndrome Mildly Presenting as Secondary Amenorrhea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, SungKyunKwan University School of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 1523094
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.2.130
Abstract
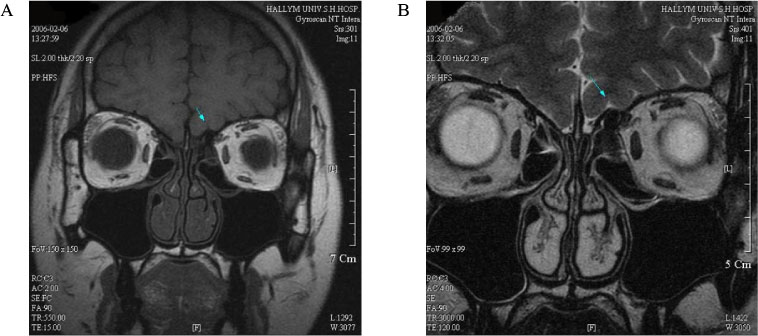
- Kallmann's syndrome is very rare congenital defect in GnRH (gonadotrophin releasing hormone) secretion involving both sexes. The mode of inheritance has not been fully understood. But, including X-linked inheritance, the ratio of incidence between male versus female is 5:1, and there is a few case reports of female Kallmann's syndrome in Korea, especially in internal medicine department. We report a case of 35 year-old female Kallmann's syndrome presenting secondary amenorrhea as a mild presentation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Naftolin F, Harris GW, Bobrow M. Effect of Purified Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Factor of Normal and Hypogonadotrophic Anosmic men. Nature. 1971. 232:496–497.2. WU FCW, Butler GE, Kelnar CJH, Stiring HF, Huhtaniemi I. Patterns of Pulsatile Luteinizing Hormone and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Secretion in Prepubertal Boys and Girls and Patients with Idiopathic Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991. 72:1229–1237.3. Klingmuller D, Dews W, Krecht G, Schweiker HU. Magnetic Resonance imaging of the Brain in Patients with Anosmia and Hypothalamia Hypogonadism (Kallmann's Syndrome). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987. 65:581–584.4. Schwanzel-Fukuda M, Bick D, Pfaff DW. Luteinizing-hormone-releasing-hormone (LHRH) Expressing Cells do not Migrate Normally in an Inherited Hypogonadal Syndrome. Mol Brain Res. 1989. 6:311–326.5. Seminara Stephanie B, France JH, William FC. Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Deficiency in the Human (Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism and Kallmann's syndrome): Pathophysiological and Genetic Considerations. Endocrine Reviews. 1998. 19:521–539.6. Lieblich JM, Rogol AD, White BJ, Rosen SW. Syndrome of Anosmia with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (Kallmann's Syndrome): Clinical and Laboratory Studies in 23 cases. Am J Med. 1982. 73:506–519.7. Santen RJ, Paulsen CA. Hypogonadotropic Eunuchoidism. I. Clinical Study of the Mode of Inheritance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973. 36:47–54.8. Yoo JH, Kim YS, Jung NJ, Lee JI, Kim SW, Choi YK. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with anosmia (Kallmann's syndrome) and responce to luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH). Kor J Intern Med. 1980. 23:253–258.9. Yousem DM, Geckle RJ, Bilker W, McKeown DA, Doty RL. MR Evaluation of Patients with Congenital Hyposmia or Anosmia. AJR. 1996. 166:439–443.10. Hong SC, Yoo YS, Kim ES, Kim SC, Park SH, Kim JK, Kang SH. Development of KVSS Test(Korean Version of Sniffin Sticks Test). Korean J Otolaryngol. 1999. 42:855–860.11. Kallmann FJ, Schoenfeld WA, Barrera SE. The Genetic Aspects of Primary Eunuchoidism. Am J Ment Defic. 1944. 48:203–236.12. Lee EJ, Hong SW, Hong YK, Yoon JS, Mok JO, Kim YJ, Park HK, Lim CH, Lim SJ, Byun DW, Bae WK, Sub KI, Yoo MH. A Case of Kallmann's Syndrome with Unilateral Renal Aplasia and Diabetes Mellitus. J Kor Soc Endocrinol. 2005. 20:96–102.13. Cho YW, Han SW, Oh DY, Whang SG, Kim SJ, Lee HC, Huh KB. Two Cases of Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism with Anosmia (Kallmann's Syndrome). J Kor Soc Endocrinol. 1990. 5:308–313.14. Schwanzel-Fukuda M, Bick D, Pfaff DW. Origin of Luteinizing-hormone-releasing-hormone Neurons. Nature. 1989. 338:161–164.15. Park KH, Mo HJ, Kim JY, Kim JY, Bae SW, Lee BS, Kim Ik, Kim SK, Kim KA, An YH. KAL Gene and GnRH Receptor Gene Analysis in Patients with Kallmann's Syndrome. J Kor Soc Endocrinol. 1999. 14:645–656.16. Quiton R, Duke VM, Zoysa PAD, Platts AD, Valentine A, Kendall B, Pickman S, Kirk JMW, Besser GM, Jacobs HS, Bouloux PMG. The Neuroradiology of Kallmann's Syndrome: A Genotypic and Phenotypic Analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996. 81:3010–3017.17. Nam YS, Lee SH, Lee WS, Park C, Kim JW, Cha KY. A Case of Kallmann Syndrome Inherited in Autosomal Dominant Mode. Korean Journal of Fertility and Sterility. 1999. 26:491–495.18. Nam YS, Kim NK, Jeong CJ, Cha SH, Cha KY. A Case of Kallmann Syndrome Conceived by Administration of Gonadotropin. Korean Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2002. 45:714–717.19. Song ES, Kim SS, Kim SH, Lee JY. A Case of Pregnancy in Patient with Kallmann's Syndrome. Korean Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1993. 36:111–115.20. Han AK, Kim JH, Park CS, Kim BC, Kim HS, Suh SS. A Case of Kallmann Syndrome and A Case of Successful Pregnancy of Kallmann Syndrome Patient. Korean Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2000. 43:1088–1091.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Kallmann Syndrome Inherited in Autosomal Dominant Mode
- Two Cases of Kallmann Syndrome
- A Case of Kallmann Syndrome and A Case of Successful Pregnancy of Kallmann Syndrome Patient
- A Case of Isolated Gonadotropin Deficiency with Negative KALIG-1 Gene
- Clinical Characteristics of Amenorrhea According to the Etiological Classification