Yonsei Med J.
2013 Mar;54(2):445-452. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.445.
Interleukin-10 Down-Regulates Cathepsin B Expression in Fetal Rat Alveolar Type II Cells Exposed to Hyperoxia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. premee@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Medical Sciences, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Medical and Bio-Materials Research Center, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1503909
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.445
Abstract
- PURPOSE
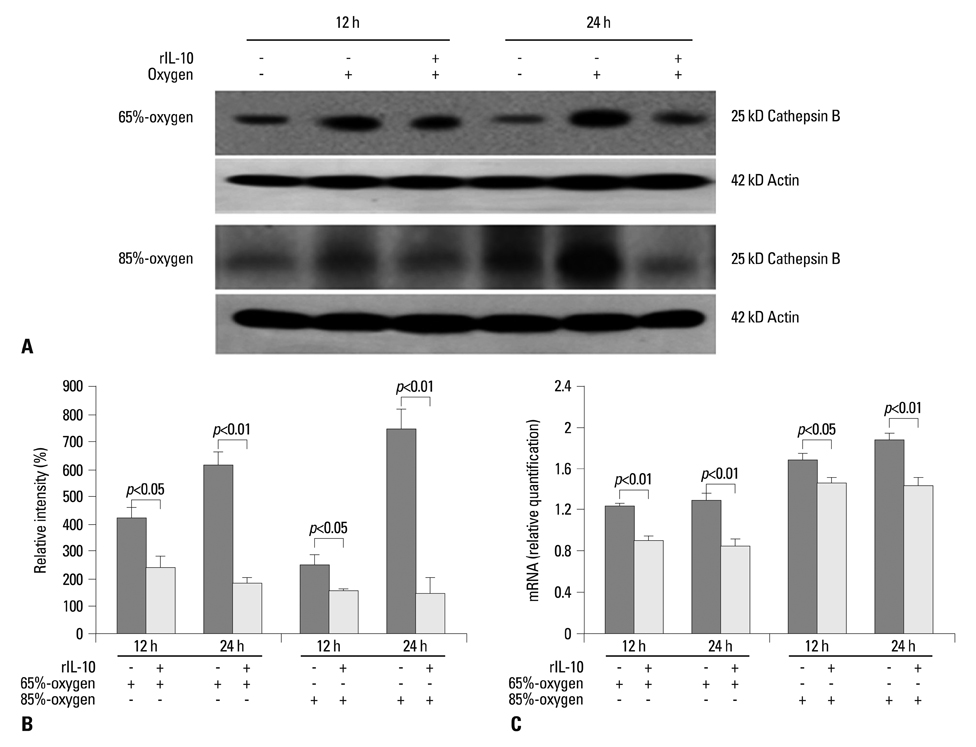
Hyperoxia has the chief biological effect of cell death. We have previously reported that cathepsin B (CB) is related to fetal alveolar type II cell (FATIIC) death and pretreatment of recombinant IL-10 (rIL-10) attenuates type II cell death during 65%-hyperoixa. In this study, we investigated what kinds of changes of CB expression are induced in FATIICs at different concentrations of hyperoxia (65%- and 85%-hyperoxia) and whether pretreatment with rIL-10 reduces the expression of CB in FATIICs during hyperoxia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Isolated embryonic day 19 fetal rat alveolar type II cells were cultured and exposed to 65%- and 85%-hyperoxia for 12 h and 24 h. Cells in room air were used as controls. Cytotoxicity was assessed by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) released into the supernatant. Expression of CB was analyzed by fluorescence-based assay upon cell lysis and western blotting, and LDH-release was re-analyzed after preincubation of cathepsin B-inhibitor (CBI). IL-10 production was analyzed by ELISA, and LDH-release was re-assessed after preincubation with rIL-10 and CB expression was re-analyzed by western blotting and real-time PCR.
RESULTS
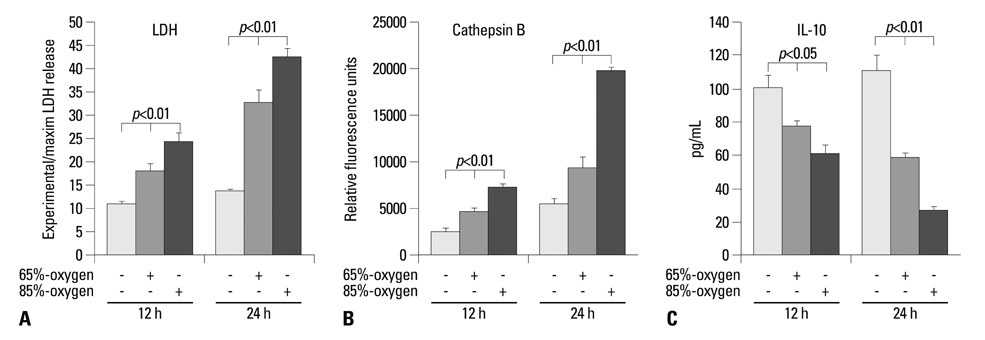
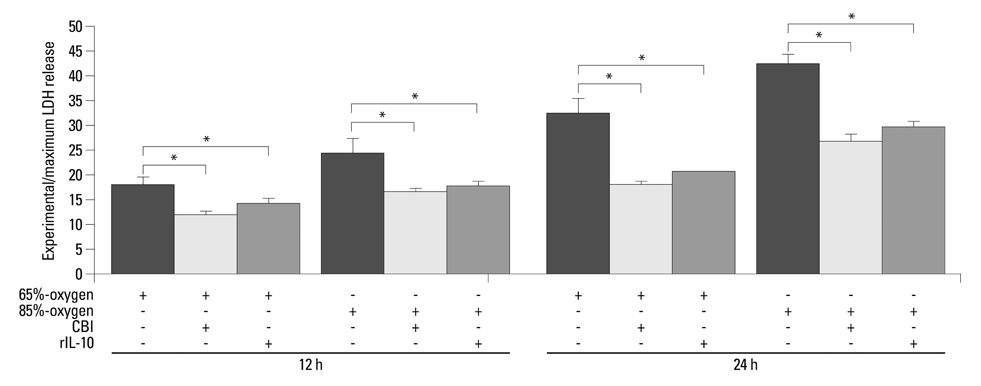
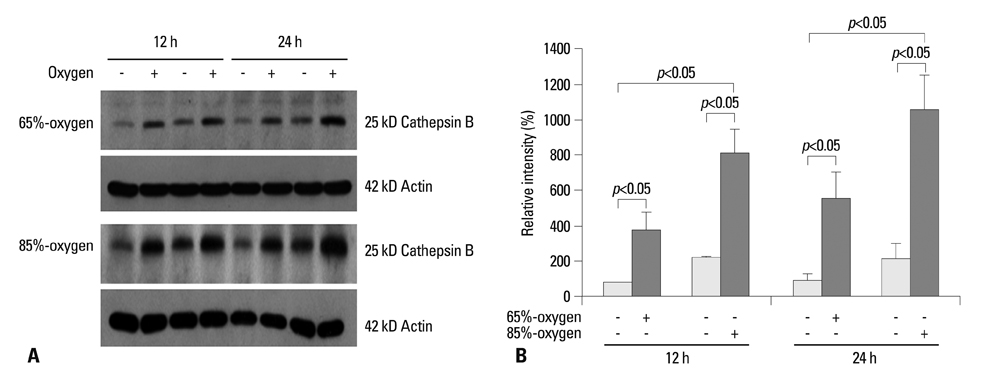
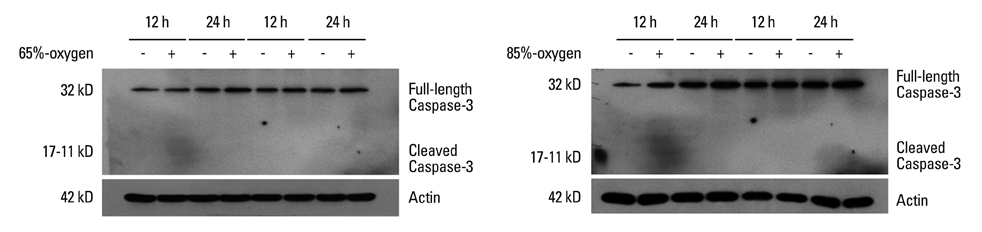
LDH-release and CB expression in FATIICs were enhanced significantly in an oxygen-concentration-dependent manner during hyperoxia, whereas caspase-3 was not activated. Preincubation of FATIICs with CBI significantly reduced LDH-release during hyperoxia. IL-10-release decreased in an oxygen-concentration-dependent fashion, and preincubation of the cells with rIL-10 significantly reduced cellular necrosis and expression of CB in FATIICs which were exposed to 65%- and 85%-hyperoxia.
CONCLUSION
Our study suggests that CB is enhanced in an oxygen-concentration-dependent manner, and IL-10 has an inhibitory effect on CB expression in FATIICs during hyperoxia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee PJ, Choi AM. Pathways of cell signaling in hyperoxia. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003. 35:341–350.
Article2. Li W, Yuan X, Nordgren G, Dalen H, Dubowchik GM, Firestone RA, et al. Induction of cell death by the lysosomotropic detergent MSDH. FEBS Lett. 2000. 470:35–39.
Article3. Bröker LE, Huisman C, Span SW, Rodriguez JA, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G. Cathepsin B mediates caspase-independent cell death induced by microtubule stabilizing agents in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004. 64:27–30.
Article4. Layton GT, Harris SJ, Bland FA, Lee SR, Fearn S, Kaleta J, et al. Therapeutic effects of cysteine protease inhibition in allergic lung inflammation: inhibition of allergen-specific T lymphocyte migration. Inflamm Res. 2001. 50:400–408.
Article5. Tang PS, Tsang ME, Lodyga M, Bai XH, Miller A, Han B, et al. Lipopolysaccharide accelerates caspase-independent but cathepsin B-dependent death of human lung epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006. 209:457–467.
Article6. Guicciardi ME, Leist M, Gores GJ. Lysosomes in cell death. Oncogene. 2004. 23:2881–2890.
Article7. Mantell LL, Lee PJ. Signal transduction pathways in hyperoxia-induced lung cell death. Mol Genet Metab. 2000. 71:359–370.
Article8. Bhandari V, Elias JA. Cytokines in tolerance to hyperoxia-induced injury in the developing and adult lung. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006. 41:4–18.
Article9. Schultz C, Temming P, Bucsky P, Göpel W, Strunk T, Härtel C. Immature anti-inflammatory response in neonates. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004. 135:130–136.
Article10. Coalson JJ. Pathology of new bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Neonatol. 2003. 8:73–81.
Article11. Coalson JJ. Pathology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2006. 30:179–184.
Article12. Lee HS, Kim CK. Cathepsin B is activated as an executive protease in fetal rat alveolar type II cells exposed to hyperoxia. Exp Mol Med. 2011. 43:223–229.
Article13. Lee HS, Kim CK. Effect of recombinant IL-10 on cultured fetal rat alveolar type II cells exposed to 65%-hyperoxia. Respir Res. 2011. 12:68.
Article14. Gerber A, Welte T, Ansorge S, Bühling F. Expression of cathepsins B and L in human lung epithelial cells is regulated by cytokines. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000. 477:287–292.
Article15. Sanchez-Esteban J, Wang Y, Gruppuso PA, Rubin LP. Mechanical stretch induces fetal type II cell differentiation via an epidermal growth factor receptor-extracellular-regulated protein kinase signaling pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004. 30:76–83.
Article16. Lee HS, Wang Y, Maciejewski BS, Esho K, Fulton C, Sharma S, et al. Interleukin-10 protects cultured fetal rat type II epithelial cells from injury induced by mechanical stretch. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. 294:L225–L232.
Article17. Dauger S, Ferkdadji L, Saumon G, Vardon G, Peuchmaur M, Gaultier C, et al. Neonatal exposure to 65% oxygen durably impairs lung architecture and breathing pattern in adult mice. Chest. 2003. 123:530–538.
Article18. Zhu L, Li H, Tang J, Zhu J, Zhang Y. Hyperoxia arrests alveolar development through suppression of histone deacetylases in neonatal rats. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2012. 47:264–274.
Article19. Foghsgaard L, Wissing D, Mauch D, Lademann U, Bastholm L, Boes M, et al. Cathepsin B acts as a dominant execution protease in tumor cell apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor. J Cell Biol. 2001. 153:999–1010.
Article20. Herr I, Debatin KM. Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood. 2001. 98:2603–2614.
Article21. Page TH, Smolinska M, Gillespie J, Urbaniak AM, Foxwell BM. Tyrosine kinases and inflammatory signalling. Curr Mol Med. 2009. 9:69–85.
Article22. Li JJ, Guo YL, Yang YJ. Enhancing anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 may be beneficial for acute coronary syndrome. Med Hypotheses. 2005. 65:103–106.
Article23. Geraghty P, Rogan MP, Greene CM, Boxio RM, Poiriert T, O'Mahony M, et al. Neutrophil elastase up-regulates cathepsin B and matrix metalloprotease-2 expression. J Immunol. 2007. 178:5871–5878.
Article24. Mishiro T, Nakano S, Takahara S, Miki M, Nakamura Y, Yasuoka S, et al. Relationship between cathepsin B and thrombin in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2004. 31:1265–1273.25. Lee CW, Lee IT, Lin CC, Lee HC, Lin WN, Yang CM. Activation and induction of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by IL-1beta in human tracheal smooth muscle cells: role of MAPKs/p300 and NF-kappaB. J Cell Biochem. 2010. 109:1045–1056.26. Yee M, Vitiello PF, Roper JM, Staversky RJ, Wright TW, McGrath-Morrow SA, et al. Type II epithelial cells are critical target for hyperoxia-mediated impairment of postnatal lung development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006. 291:L1101–L1111.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fetal Alveolar Type II Cell Injury Induced by Short-term Exposure to Hyperoxia
- Cathepsin B is activated as an executive protease in fetal rat alveolar type II cells exposed to hyperoxia
- Effect of Short-term Exposure of Different Concentrations of Hyperoxia on Fetal Alveolar Type II Cell Death
- Protective effect of recombinant interleukin-10 on newborn rat lungs exposed to short-term sublethal hyperoxia
- Expression of Peroxiredoxin I and II in Neonatal and Adult Rat Lung Exposed to Hyperoxia