J Korean Acad Nurs.
2012 Oct;42(5):699-708. 10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.699.
Structural Equation Modeling on Quality of Life in Pre-dialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Seoul National University / Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul, Korea. smi@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1499497
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.699
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was designed to test structural equation modeling of the quality of life of pre-dialysis patients, in order to provide guidelines for the development of interventions and strategies to improve the quality of life of patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD).
METHODS
Participants were patients who visited the nephrology outpatient department of a tertiary hospital located in Seoul. Data on demographic factors, social support, nutritional status, physical factors and biobehavioral factors and quality of life were collected between March 4 and March 31, 2011.
RESULTS
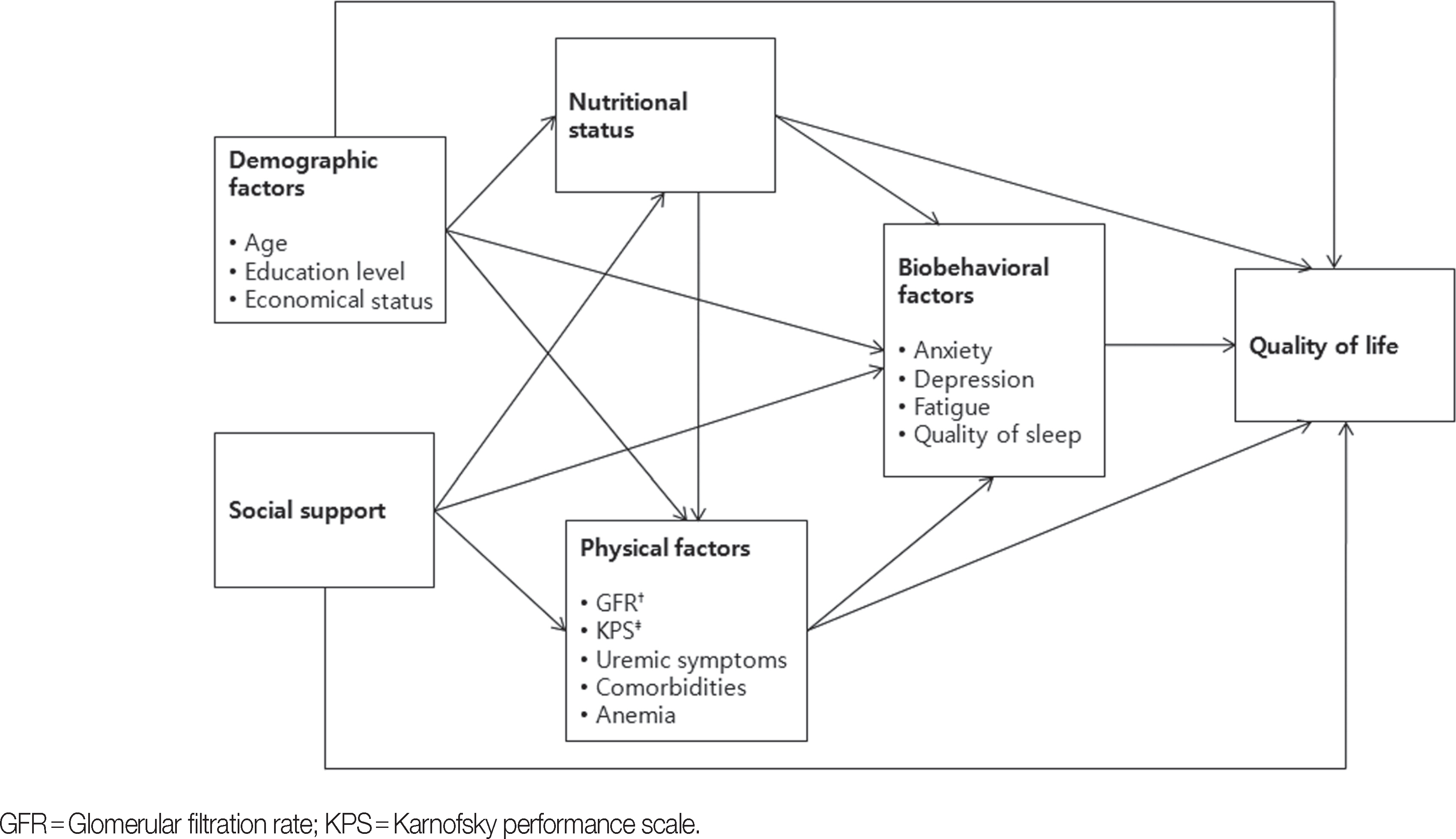
In the final analysis 208 patients were included. Of the patients 42% were in a malnourished state. Anxious or depressed patients accounted for 62.0%, 72.6%, respectively. Model fit indices for the hypothetical model were in good agreement with the recommended levels (GFI=.94 and CFI=.99). Quality of life in pre-dialysis patients with CKD was significantly affected by demographic factors, social support, nutritional status, physical factors and biobehavioral factors. Biobehavioral factors had the strongest and most direct influence on quality of life of patients with CKD.
CONCLUSION
In order to improve the quality of life in pre-dialysis patients with CKD, comprehensive interventions are necessary to assess and manage biobehavioral factors, physical factors and nutritional status.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
A Predictive Model of Quality of Life for Stomach Cancer Patients with Gastrectomy
Young Suk Kim, Young Sook Tae
Korean J Adult Nurs. 2015;27(6):613-623. doi: 10.7475/kjan.2015.27.6.613.Factors Affecting Quality of Life in Patients with Radical Prostatectomy
Hyo Jung Park, Yoonju Lee
Korean J Adult Nurs. 2019;31(2):190-201. doi: 10.7475/kjan.2019.31.2.190.Factors Influencing the Quality of Life of Prostate Cancer Patients
Jeonghye Chae, Youngsuk Kim
Asian Oncol Nurs. 2017;17(4):237-245. doi: 10.5388/aon.2017.17.4.237.
Reference
-
References
Al Saran K.., Elsayed S.., Molhem A.., Aldrees A.., Alzara, H. 2011. Nutritional assessment of patients on hemodialysis in a large dialysis center. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation. 22:675–681.Alvarez-Ude Cotera F.., Rebollo Alvarez, P. 2008. Psychological disturbances and deterioration of health-related quality of life of patients with stage 3-5 chronic kidney disease not on dialysis. Nefrologia. 28(3):57–62.Al Saran K.., Elsayed S.., Molhem A.., Aldrees A.., Alzara, H. 2011. Nutritional assessment of patients on hemodialysis in a large dialysis center. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation. 22:675–681.Alvarez-Ude Cotera F.., Rebollo Alvarez, P. 2008. Psychological disturbances and deterioration of health-related quality of life of patients with stage 3-5 chronic kidney disease not on dialysis. Nefrologia. 28(3):57–62.Basok E. K.., Atsu N.., Rifaioglu M. M.., Kantarci G.., Yildirim A.., Tokuc, R. 2009. Assessment of female sexual function and quality of life in predialysis, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, and renal transplant patients. International Urology and Nephrology. 41:473–481. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11255-008-9475-z.
ArticleBae B.R. 2009. Structural Equation Modeling with AMOS 17.0. Seoul: Chungram.Campbell K. L.., Ash S.., Bauer J.D. 2008. The impact of nutrition intervention on quality of life in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients. Clinical Nutrition. 27:537–544. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2008.05.002.
ArticleCohen S. D.., Patel S. S.., Khetpal P.., Peterson R. A.., Kimmel P.L. 2007. Pain, sleep disturbance, and quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clinical Journal of the American Society Nephrology. 2:919–925. http://dx.doi.org/10.2215/CJN.00820207.
ArticleDevins G. M.., Mendelssohn D. C.., Barre P. E.., Binik Y.M. 2003. Pre-dialysis psychoeducational intervention and coping styles influence time to dialysis in chronic kidney disease. American Journal of Kidney Disease. 42:693–703. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0272-6386(03)00835-7.
ArticleDinwiddie L. C.., Burrows-Hudson S.., Peacock E.J. 2006. Stage 4 chronic kidney disease: Preserving kidney function and preparing patients for stage 5 kidney disease. American Journal of Nursing. 106(9):40–51.Frank A.., Auslander G. K.., Weissqarten, J. 2003. Quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease at various stages of the illness. Social Work in Health Care. 38(2):1–27.
ArticleHoth K. F.., Christensen A. J.., Ehlers S. L.., Raichle K. A.., Lawto W.J. 2007. A longitudinal examination of social support, agreeableness and depressive symptoms in chronic kidney disease. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 30(1):69–76. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10865-006-9083-2.
ArticleKalender B.., Ozdemir A. C.., Dervisoglu E.., Ozdemir, O. 2007. Quality of life in chronic kidney disease: Effects of treatment modality, depression, malnutrition and inflammation. International Journal of Clinical Practice. 61:569–576. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01251.x.
ArticleKim H. W.., Choi-Kwon, S. 2010. Study on knowledge levels of pre-dialysis, chronic renal failure patients at glomerular filtration rates and their educational demands. Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science. 12(2):114–126.Kim J.M. 2009. Comparison quality of life and the factors affecting on QOL between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Unpublished mas-ter's degree dissertation. Seoul National University;Seoul:Kim Y.H. 2000. Clinical nutrition guide for health-provider. Seoul: Gwang-mungag.Kohatsu, W. 2005. Nutrition and depression. Explore. 1:474–476. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.explore.2005.08.017.
ArticleKrupp L. B.., LaRocca N. G.., Muir-Nash J.., Steinberg A.D. 1989. The fatigue severity scale. Application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Archives of Neurology. 46:1121–1123. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1989.00520460115022.Lee H. M.., Ryu S. A.., Kim E. A.., Jang K.S. 2009. Factors influencing sleep disorders in patients on hemodialysis. The Korean Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing. 16(2):190–199.Lee Y.P. 2006. Relationship between depression and quality of sleep in peritoneal dialysis patients. Unpublished master's thesis. Kosin University;Busan:Oliveira C. M.., Kubrusly M.., Mota R. S.., Silva C. A.., Oliveira V.N. 2010. Malnutrition in chronic kidney failure: What is the best diagnostic method to assess? Brazilian Journal of Nephrology. 32(1):55–68. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0101-28002010000100011.Park J.S. 2003. Literature review for biobehavioral nursing research. Journal of Nursing Query. 12(2):41–57.Pugh-Clarke K.., Naish P. F.., Mercer T.M. 2006. Quality of life in chronic kidney disease. Journal of Renal Care. 32:156–159.
ArticleRodrigue J. R.., Mandelbrot D. A.., Hanto D. W.., Johnson S. R.., Karp S. J.., Pavlakis, M. 2011. A cross-sectional study of fatigue and sleep quality before and after kidney transplantation. Clinical Transplant. 25(1):E13–E21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0012.2010.01326.x.
ArticleSnyder-Halpern R.., Verran J.A. 1987. Instrumentation to describe subjective sleep characteristics in healthy subjects. Research in Nursing & Health. 10:155–163. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/nur.4770100307.
ArticleThe Korean Society of Nephrology. 2010. Renal replacement therapy in Korea. The Korean Journal of Nephrology. 25:381–404.Tong A.., Sainsbury P.., Chadban S.., Walker R. G.., Harris D. C.., Carter S. M., et al2009. Patients' experiences and perspectives of living with chronic kidney disease. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 53:689–700. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.10.050.Wood B. L.., Klebba K. B.., Miller B.D. 2000. Evolving the biobehav-ioral family model: The fit of attachment. Family Process. 39:319–344. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1545-5300.2000.39305.x.
ArticleYang H.J. 2001. A model for quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Keimyung University;Daegu:Yoon S. J.., Yang C. K.., Han H.M. 1999. Depression, anxiety and sleep disturbance in patients with hemodialysis. Journal of the Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 38:997–1005.Zigmond A. S.., Snaith R.P. 1983. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 67:361–370. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x.
ArticleZimet G. D.., Dahlem N. W.., Zimet S. G.., Farley G.K. 1988. The multidimensional scale of perceived social support. Journal of Personality Assessment. 52(1):30–41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa5201_2.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Control Effect of Illness Perception on Depression and Quality of Life in Patients with Hemodialysis: Using Structural Equation Modeling
- Structural equation modeling for association between patient satisfaction and quality of life after implant surgery
- Health-related quality of life for older patients with chronic low back pain: A structural equation modeling study
- Structural Equation Model of Health-Related Quality of Life in School Age Children with Asthma
- Association between masticatory ability, oral health-related quality of life and cognitive function in the elderly population using structural equation modeling