Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2013 Sep;12(3):61-71. 10.12779/dnd.2013.12.3.61.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Changes Correlate with Clinical Progression in Vascular Mild Cognitive Impairment and Vascular Dementia of Subcortical Type
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. seonghye@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1488582
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2013.12.3.61
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) induces vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) such as subcortical vascular dementia (SVaD) and subcortical vascular mild cognitive impairment (svMCI). We compared MRI parameters between SVaD and svMCI and determined which MRI parameters best correlated with cognitive function and disability on cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses within them.
METHODS
Twenty-four patients with SVaD and twelve with svMCI were recruited. They underwent multimodal MRIs including fluid-attenuated inversion recovery lesion load, lacunar infarct number, and fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), neuropsychological testing, Sum of Boxes of Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR-SB), Barthel Index, and the Korean version of a Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-K). Seventeen patients were retested after 20 months for a brain MRI and clinical evaluation.
RESULTS
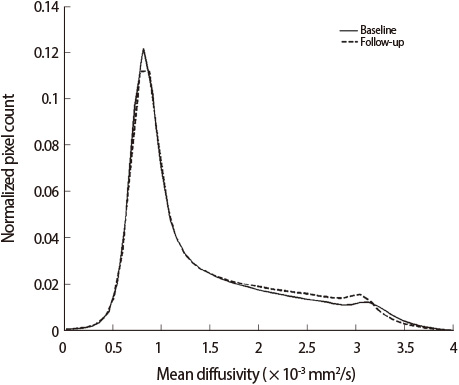
There were significant differences in average MD and peak height of MD histograms within normal-appearing brain tissue (NABT) between SVaD and svMCI patients. In the cross-sectional analysis, average MD within NABT significantly correlated with the composite neuropsychology score (r=-0.80, p<0.001), the composite executive function score (r=-0.67, p< 0.001), and the CDR-SB (r=0.54, p=0.001), and the Barthel Index correlated with peak heights of the MD histograms (r=0.37, p=0.03) in NABT. Changes of CDR-SB was associated with changes of average MD within WMH (r=0.57, p=0.02), and changes of GDS-K was associated with changes of WMH volume (r=0.51, p=0.04) on a longitudinal scale.
CONCLUSIONS
DTI parameters in NABT correlated with cognitive impairment and disability in VCI associated with SVD. Clinical progression of SVD was associated with some increment of WML volume and ultrastructural changes in WMH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Comparison Study of Cilostazol and Aspirin on Changes in Volume of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease White Matter Changes: Protocol of a Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Trial
Hyun Jeong Han, Byeong C. Kim, Young Chul Youn, Jee Hyang Jeong, Jong Hun Kim, Jae-Hong Lee, Kee Hyung Park, Kyung Won Park, Eun-Joo Kim, Mi Sun Oh, Yong S. Shim, Hyun Young Park, Bora Yoon, Soo Jin Yoon, Soo-Jin Cho, Key Chung Park, Duk L. Na, Sun Ah Park, Jong-Min Lee, Seong Hye Choi
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2019;18(4):138-148. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2019.18.4.138.
Reference
-
1. Staekenborg SS, van Straaten EC, van der Flier WM, Lane R, Barkhof F, Scheltens P. Small vessel versus large vessel vascular dementia: risk factors and MRI findings. J Neurol. 2008; 255:1644–1651.2. Yanagihara T. Vascular dementia in Japan. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002; 977:24–28.
Article3. Erkinjuntti T, Inzitari D, Pantoni L, Wallin A, Scheltens P, Rockwood K, et al. Research criteria for subcortical vascular dementia in clinical trials. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2000; 59:23–30.
Article4. Frisoni GB, Galluzzi S, Bresciani L, Zanetti O, Geroldi C. Mild cognitive impairment with subcortical features: clinical characteristics and outcome. J Neurol. 2002; 249:1423–1432.5. Seo SW, Ahn J, Yoon U, Im K, Lee JM, Tae Kim S, et al. Cortical thinning in vascular mild cognitive impairment and vascular dementia of subcortical type. J Neuroimaging. 2010; 20:37–45.
Article6. The LADIS Study Group. 2001-2011: a decade of the LADIS (Leukoaraiosis And Disability) Study: what have we learned about white matter changes and small-vessel disease? Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011; 32:577–588.7. Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010; 9:689–701.
Article8. Junqué C, Pujol J, Vendrell P, Bruna O, Jódar M, Ribas JC, et al. Leukoaraiosis on magnetic resonance imaging and speed of mental processing. Arch Neurol. 1990; 47:151–156.
Article9. Sabri O, Ringelstein EB, Hellwig D, Schneider R, Schreckenberger M, Kaiser HJ, et al. Neuropsychological impairment correlates with hypoperfusion and hypometabolism but not with severity of white matter lesions on MRI in patients with cerebral microangiopathy. Stroke. 1999; 30:556–566.
Article10. O'Sullivan M, Morris RG, Huckstep B, Jones DK, Williams SC, Markus HS. Diffusion tensor MRI correlates with executive dysfunction in patients with ischaemic leukoaraiosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75:441–447.11. Nitkunan A, Barrick TR, Charlton RA, Clark CA, Markus HS. Multimodal MRI in cerebral small vessel disease: its relationship with cognition and sensitivity to change over time. Stroke. 2008; 39:1999–2005.12. Holtmannspötter M, Peters N, Opherk C, Martin D, Herzog J, Brückmann H, et al. Diffusion magnetic resonance histograms as a surrogate marker and predictor of disease progression in CADASIL: a two-year follow-up study. Stroke. 2005; 36:2559–2565.
Article13. Schmidt R, Ropele S, Ferro J, Madureira S, Verdelho A, Petrovic K, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging and cognition in the leukoariosis and disability in the elderly study. Stroke. 2010; 41:e402–e408.
Article14. Jokinen H, Schmidt R, Ropele S, Fazekas F, Gouw AA, Barkhof F, et al. Diffusion changes predict cognitive and functional outcome: The LADIS study. Ann Neurol. 2013; 73:576–583.
Article15. Xu Q, Zhou Y, Li YS, Cao WW, Lin Y, Pan YM, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging changes correlate with cognition better than conventional MRI findings in patients with subcortical ischemic vascular disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2010; 30:317–326.
Article16. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual disorders, 4th ed (DSM-IV). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association;1994. p. 146.17. Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, et al. Mild cognitive impairment-beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Intern Med. 2004; 256:240–246.
Article18. The Guidelines Subcommittee of the World Health Organization - International Society of Hypertension (WHOISH). 1999 World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension. J Hypertens. 1999; 17:151–183.19. The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1997; 20:1183–1197.20. National cholesterol education program. Second report of the expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel II). Circulation. 1994; 89:1333–1445.21. Kang Y. Normative data on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in Korean elderly. Korean J Psychol. 2006; 25:1–12.22. Ahn HJ, Chin J, Park A, Lee BH, Suh MK, Seo SW, et al. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-dementia version (SNSB-D): a useful tool for assessing and monitoring cognitive impairments in dementia patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1071–1076.
Article23. Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993; 43:2412–2414.24. Bae JN, Cho MJ. Development of the Korean version of the Geriatric Depression Scale and its short form among elderly psychiatric patients. J Psychosom Res. 2004; 57:297–305.
Article25. Mahoney FI, Barthel D. "Functional evaluation: the Barthel Index". Md State Med J. 1965; 14:56–61.26. Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC. A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1998; 17:87–97.
Article27. Smith SM. "Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp. 2002; 17:143–155.
Article28. Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC, Riahi F, Sled JG, Chui J, Kollakian M. Automatic quantification of multiple sclerosis lesion volume using stereotaxic space. Lect Note Comput Sci. 1996; 1131:439–448.
Article29. Jeon SU, Yoon UC, Park JS, Seo SW, Kim J, Kim ST, et al. Fully Automated Pipeline for Quantification and Localization of White Matter Hyperintensity in Brain Magnetic Resonance Image. Int J Imaging Syst Technol. 2011; 21:193–200.
Article30. Zhang Y, Brady M, Smith S. Segmentation of brain mr images through a hidden markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2001; 20:45–57.
Article31. Lee JH, Kim SH, Kim GH, Seo SW, Park HK, Oh SJ, et al. Identification of pure subcortical vascular dementia using 11C-Pittsburgh compound B. Neurology. 2011; 77:18–25.
Article32. Scheltens P, Leys D, Barkhof F, et al. Atrophy of medial temporal lobes on MRI in "probable" Alzheimer's disease and normal ageing: diagnostic value and neuropsychological Correlates. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992; 55:967–972.
Article33. Cercignani M, Inglese M, Pagani E, Comi G, Filippi M. Mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy histograms of patients with multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:952–958.34. Zhou Y, Qun-Xu , Qin LD, Qian LJ, Cao WW, Xu JR. A primary study of diffusion tensor imaging-based histogram analysis in vascular cognitive impairment with no dementia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2011; 113:92–97.
Article35. Aharon-Peretz J, Daskovski E, Mashiach T, Tomer R. Natural history of dementia associated with lacunar infarctions. J Neurol Sci. 2002; 203-204:53–55.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subtypes of Vascular Dementia
- Effect of Physical Disability on Instrumental Activities of Daily Living in Alzheimer's Disease, Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), and Vascular Dementia and Vascular MCI of Subcortical Type
- Micro-vascular Diseases of White Matter
- Clinical Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Dementia
- Recent Updates on Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Dementia