Infect Chemother.
2008 Feb;40(1):24-31. 10.3947/ic.2008.40.1.24.
Discriminative PCR of Bordetella pertussis from closely related Bordetella species using 16S rDNA Gene
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Bacterial Respiratory Infections, Centers for Infectious Disease, National Institute of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Seoul, Korea. mryu59@nih.go.kr
- KMID: 1483473
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2008.40.1.24
Abstract
-
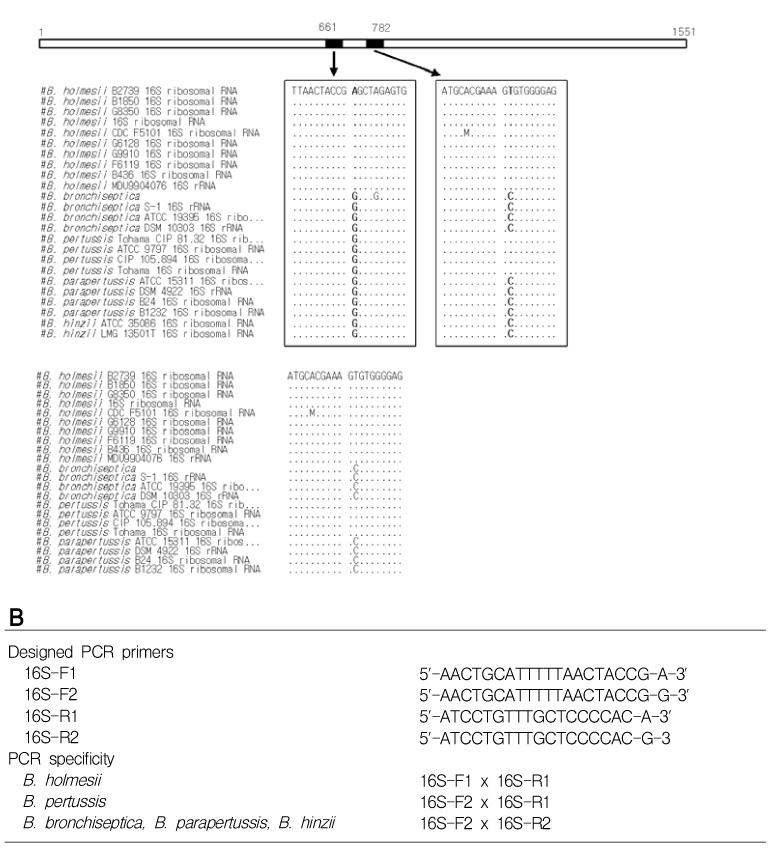
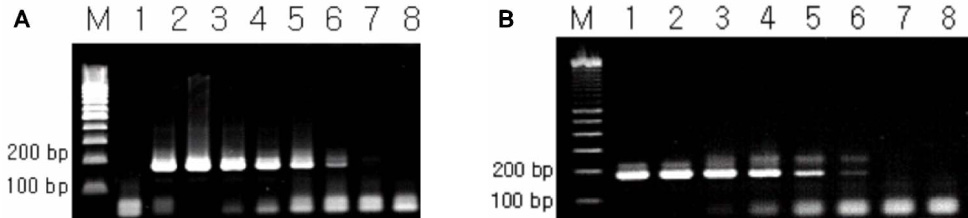
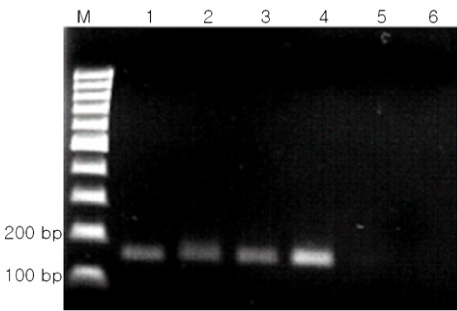
BACKGROUND: Polymerase-chain reaction (PCR) detection is useful to diagnosis of pertussis at initial stage because the growth rate of Bordetella pertussis (B. pertussis) is relatively slow. Currently, the primer set for the insertion sequence IS481 (BP primer) is used widely for PCR detection of B. pertussis. However, the cross-reactivity of BP primer set with Bordetella holmesii (B. holmesii) was reported recently. Therefore, discrimination of B. pertussis and B. holmesii is needed in PCR step. For this reason, we developed new primer sets based on 16S rDNA sequence for diagnostic use and estimated the efficiency of these new primer sets. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The specific PCR primers were designed from the aligned sequence matrix of 16S rDNA genes of various Bordetella species. The specificity of designed primers were estimated using clinically important 4 Bordetella species, B. pertussis, B. holmesii, Bordetella parapertussis (B. parapertussis) and Bordetella bronchiseptica (B. bronchiseptica). The sensitivity to B. pertussis of designed primers was also estimated and compared with BP primer set.
RESULTS
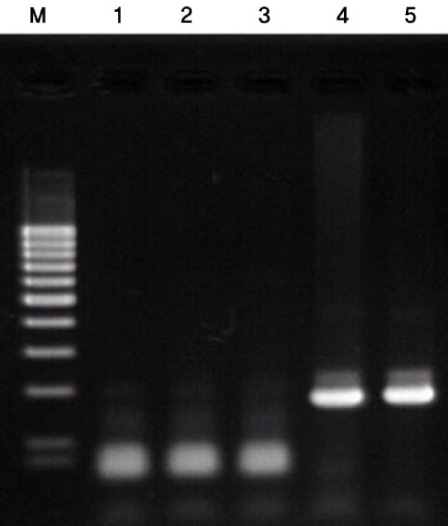
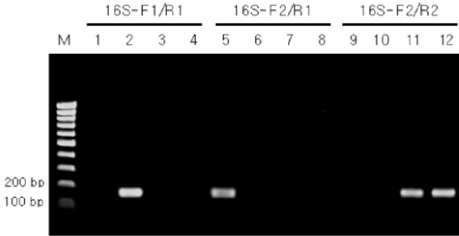
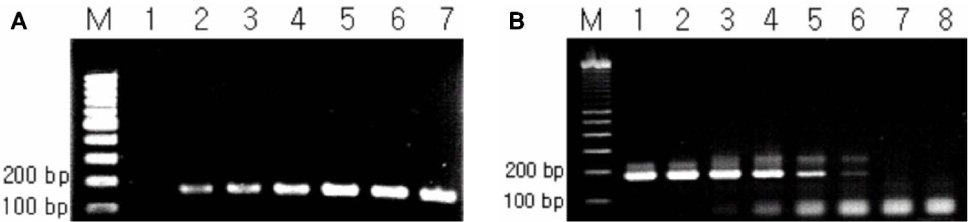
As the results, the developed new primer set successfully distinguished B. pertussis and other Bordetella species containing B. holmesii. In the sensitivity assay, the detectable limits of 16S-F2/16S-R1 primer set for B. pertussis were revealed as 5 pg of genomic DNA and 105 cells/mL of cell suspension. In addition to these, identical results between BP with primer and new primer were obtained in clinical samples. CONCLUSION: In this study, the specific primer set for B. pertussis was developed based on 16S rDNA sequence and this primer set did not show cross-reactivity to B. holmesii. In addition to these, the applicability of this primer set to the clinical specimens was also confirmed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. WHO. WHO/IVB/04.14. Laboratory manual for the diagnosis of whooping cough caused by Bordetella pertussis/Bordetella parapertussis. 2004.2. de Melker HE, Conyn-van Spaendonck MA, Rumke HC, van Wijngaarden JK, Mooi FR, Schellekens JF. Pertussis in the netherlands: an outbreak despite high levels of immunization with whole-cell vaccine. Emerg Infect Dis. 1997. 3:175–178.
Article3. de Melker HE, Schellekens JFP, Neppelenbroek SE, Mooi FR, Rumke HC, Conyn-van Spaendonck MAE. Reemergence of pertussis in the highly vaccinated population of the Netherlands: Observations on surveillance data. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000. 6:348–357.
Article4. Mooi FR, van Loo IH, King AJ. Adaptation of Bordetella pertussis to vaccination: A cause for its reemergence? Emerg Infect Dis. 2001. 7:suppl 3. 526–528.
Article5. Fry NK, Tzivra O, Li YT, McNiff A, Doshi N, Maple PA, Crowcroft NS, Miller E, George RC, Harrison TG. Laboratory diagnosis of pertussis infections: the role of PCR and serology. J Med Microbiol. 2004. 53:519–525.
Article6. van der Zee A, Agterberg C, Peeters M, Schellekens J, Mooi FR. Polymerase chain reaction assay for pertussis: simultaneous detection and discrimination of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993. 31:2134–2140.
Article7. Birkebaek NH, Heron I, Skjodt K. Bordetella pertussis diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction. APMIS. 1994. 102:291–294.8. Houard S, Hackel C, Herzog A, Bollen A. Specific identification of Bordetella pertussis by the polymerase chain reaction. Res Microbiol. 1989. 140:477–487.
Article9. Li Z, Jansen DL, Finn TM, Halperin SA, Kasina A, OConnor SP, Aoyama T, Manclark CR, Brennan MJ. Identification of Bordetella pertussis infection by shared-primer PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1994. 32:783–789.
Article10. Loeffelholz MJ, Thompson CJ, Long KS, Gilchrist MJ. Detection of Bordetella holmesii using Bordetella pertussis IS481 PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:467.
Article11. Poddar SK. Detection and discrimination of B pertussis and B. holmesii by real-time PCR targeting IS481 using a beacon probe and probe-target melting analysis. Mol Cell Probes. 2003. 17:91–98.
Article12. Reischl U, Lehn N, Sanden GN, Loeffelholz MJ. Real-Time PCR assay targeting IS481 of Bordetella pertussis and molecular basis for detecting Bordetella holmesii. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 39:1963–1966.
Article13. Templeton KE, Scheltinga SA, van der Zee A, Diederen BM, van Kruijssen AM, Goossens H, Kuijper E, Claas EC. Evaluation of real-time PCR for detection of and discrimination between Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, and Bordetella holmesii for clinical diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:4121–4126.
Article14. Yih WK, Silva EA, Ida J, Harrington N, Lett SM, George H. Bordetella holmesii-like organisms isolated from Massachusetts patients with pertussis-like symptoms. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999. 5:441–443.
Article15. Mazengia E, Silva EA, Peppe JA, Timperi R, George H. Recovery of Bordetella holmesii from patients with pertussis-like symptoms: use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to characterize circulating strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:2330–2333.
Article16. Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA3: Integrated Software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and Sequence Alignment. Brief Bioinform. 2004. 5:150–163.
Article17. Nei M, Kumar S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics. 2000. New York: Oxford University Press.18. Mattoo S, Cherry JD. Molecular pathogenesis, Epidemiology, and clinical manifestations of respiratory infections due to Bordetella pertussis and other Bordetella subspecies. Clin Microb Rev. 2005. 18:326–382.
Article19. Cummings CA, Brinig MM, Lepp PW, van de Pass , Relman DA. Bordetella species are distinguished by patterns of substantial gene loss and host adaptation. J Bacteriol. 2004. 186:1484–1492.
Article20. Vandamme P, Hommez J, Vancanneyt M, Monsieurs M, Hoste B, Cookson B, Wirsing von Konig CH, Kerster K, Blackall PJ. Bordetella hinzii sp. Nov., isolated from poultry and humans. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1995. 45:37–45.
Article21. Weyant RS, Hollis DG, Weaver RE, Amin MF, Steigerwalt AG, O'Connor SP, Whitney AM, Daneshvar MI, Moss CW, Brenner DJ. Bordetella holmesii sp. Nov., a new gram-negative species associated with septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. 33:1–7.
Article22. Coenye T, Goris J, Spilker T, Vandamme P, LiPuma JJ. Characterization of unusual bacteria isolated from respiratory secretions of cystic fibrosis patients and description of Inquilinus limosus gen. Nov., sp. Nov. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. 40:2062–2069.
Article23. Ko KS, Peck KR, Oh WS, Lee NY, Lee JH, Song JH. New species of Bordetella, Bordetella ansorpii sp. Nov., isolated from the purulent exudate of an epidermal cyst. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:2516–2519.
Article24. Vandamme P, Heyndrickx M, Vancanneyt M, Hoste B, De Vos P, Falsen E, Kersters K, Hinz KH. Bordetella trematum sp. nov., isolated from wounds and ear infections in humans, and reassessment of Alcaligenes denitrificans Ruger and Tan 1983. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996. 46:849–858.
Article25. Shepard CW, Daneshvar MI, Kaiser RM, Ashford DA, Lonsway D, Patel JB, Morey RE, Jordan JG, Weyant RS, Fischer M. Bordetella holmesii Bacteremia: A newly recognized clinical entity among asplenic patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 38:799–804.
Article26. Antila M, He Q, de Jong C, Aarts I, Verbakel H, Bruisten S, Keller S, Haanpera M, Makinen J, Eerola E, Viljanen MK, Mertsola J, van der Zee A. Bordetella holmesii DNA is not detected in nasopharyngeal swabs from Finnish and Dutch patients with suspected pertussis. J Med Microbiol. 2006. 55:1043–1051.
Article27. Glare EM, Paton JC, Premier RR, Lawrence AJ, Nisbet IT. Analysis of a repetitive DNA sequence from Bordetella pertussis and its application to the diagnosis of pertussis using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990. 28:1982–1987.
Article28. Coenye T, Vandamme P. Intragenomic heterogeneity between multiple 16S ribosomal RNA operons in sequenced bacterial genomes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003. 228:45–49.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis of Bordetella Pertussis Infections by Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Update on pertussis and pertussis immunization
- Pertussis as a Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Cough in Adults
- Bordetella bronchiseptica Respiratory Infection in the Immunosuppressed Patient
- Pertussis Accompanying Recent Mycoplasma Infection in a 10-Year-Old Girl