J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2008 Mar;15(1):31-37. 10.4184/jkss.2008.15.1.31.
Radiographic Changes of Adjacent Upper Segment Performed Short Segmental Lumbosacral Fusion: Does Total Laminectomy Influence Adjacent Upper Segmental Instability?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National Medical center, Seoul, Korea. iscectomy@empal.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1482841
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2008.15.1.31
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to compare factors that influence degenerative changes in patients undergoing total laminectomy and patients undergoing partial laminectomy. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Lumbar or lumbosacral fusion with total or partial laminectomy may result in adjacent segment problems of the upper segment. However, the differences between the two procedures that may influence adjacent segment instability are still controversial.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
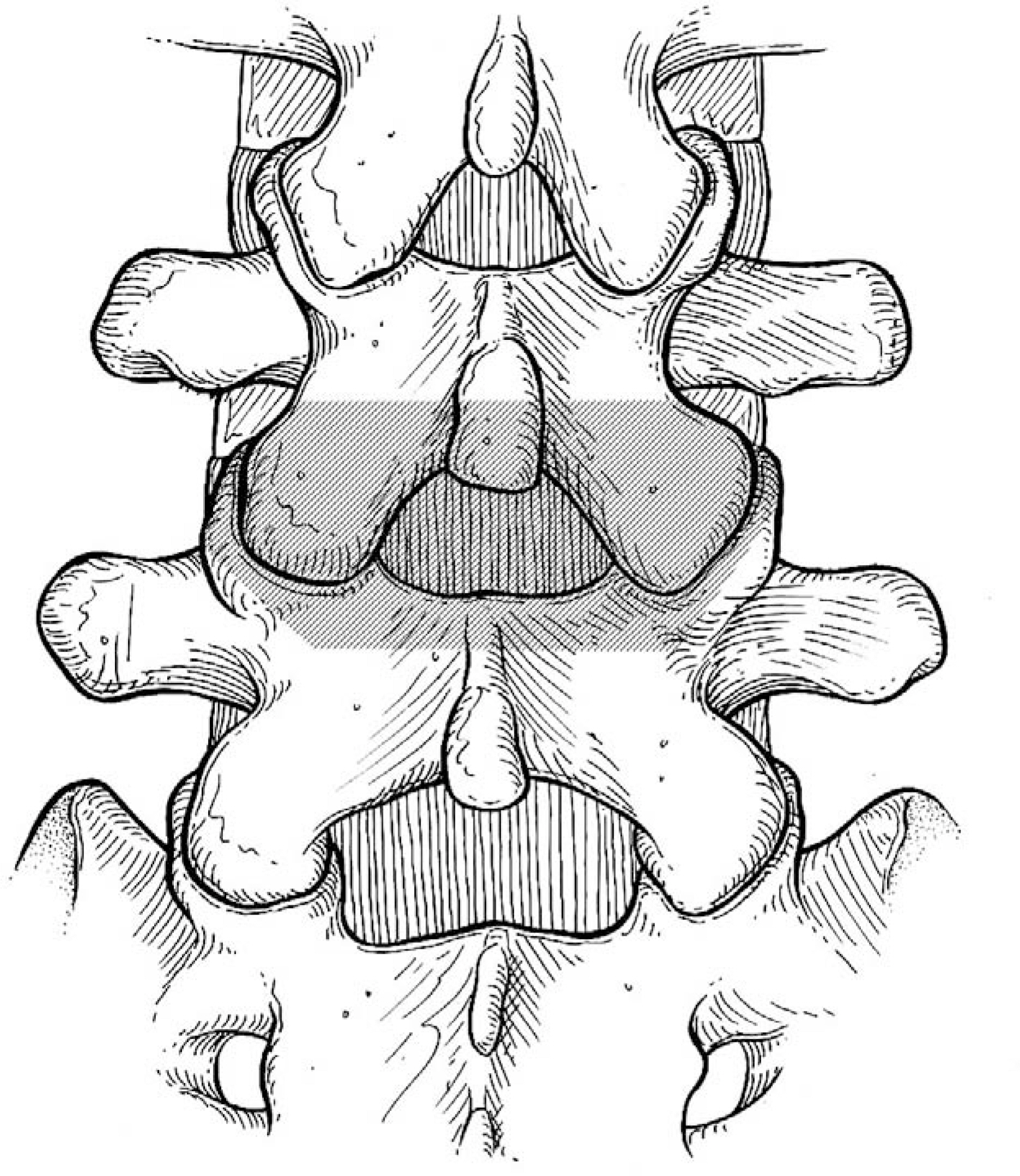
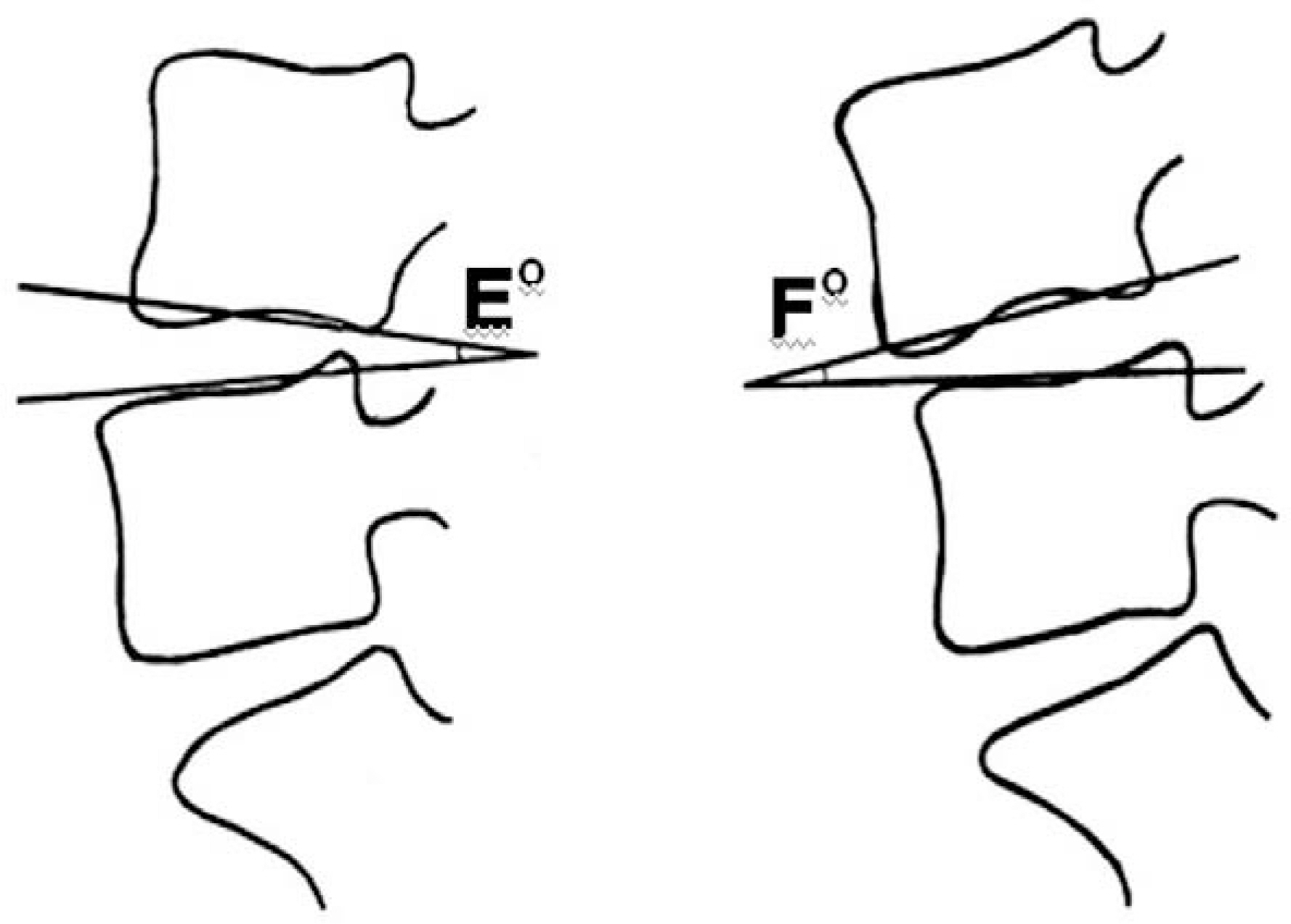
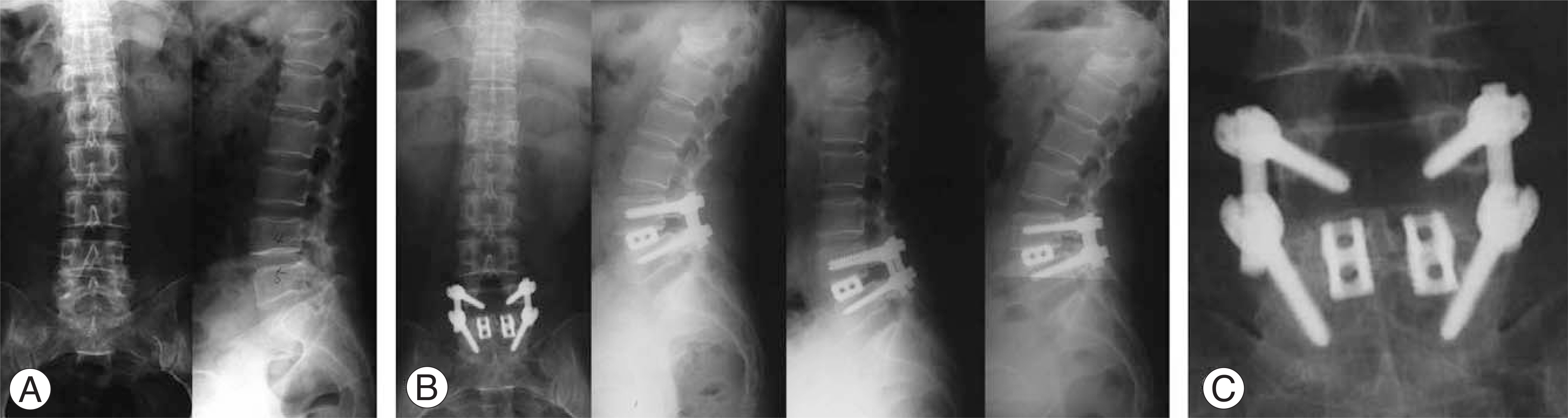
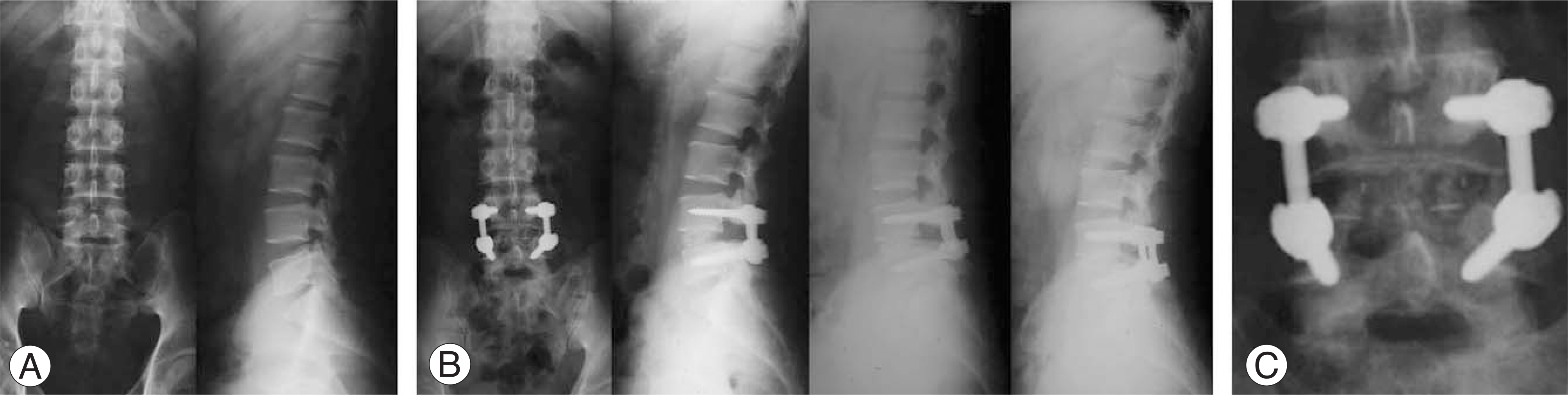
We evaluated 95 patients, followed up for at least 2 years, who had been treated with short level (at most 2 levels) posterior lumbar interbody fusion with pedicle fixation, secondary to spinal stenosis. Treatment procedures included total laminectomy (42 cases) and partial laminectomy (53 cases). We analyzed the preoperative status of the intervertebral discs (Thompson grade), difference of disc height, and difference between preoperative segmental sagittal angle and last follow-up sagittal angle. We excluded cases that required revision secondary to infection, nonunion, or hematoma formation. However, we included cases that required revision due to adjacent segmental problems during the follow-up period.
RESULTS
The mean age of the patients treated with total laminectomy was 59.0+/-10.9 years, and of the patients treated with partial laminectomy was 58.8+/-10.2 years. The preoperative Thompson grade showed no statistical difference. The difference in disc height and segmental sagittal angle between the preoperative and last follow-up examinations showed no statistical difference between the two groups.
CONCLUSIONS
There was no significant difference in the radiographic or clinical outcomes based on removal or preservation of posterior structures. Nevertheless, we need further follow-up to evaluate adjacent segment degeneration.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73:802–808.
Article2). Mardjetko SM, Connolly PJ, Shott S. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. A metaanalysis of literature 1970-1993. Spine. 1994; 19:2256–2265.3). Cho JL, Park YS, Han JH, Lee CH, Roh WI. The changes of adjacent segments after spinal fusion. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998; 5:239–246.4). Ha KY, Kim KW, Park SJ, Lee YH. Changes of the adjacent-unfused mobile segment after instrumental lumbar fusion. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998; 5:205–214.5). Shahin E, David WC. Risk factors for adjacent-segment failure following lumbar fixation with rigid instrumentation for degenerative instability. J Neurosurg. 1999; (Spine 2):90:163–169.6). Weinhofter SL, Guyer RD, Hebert M, Griffith SL. Intradiscal pressure measurement above an instrumented fusion: a cadaveric study. Spine. 1995; 20:526–531.7). Thompson JP, Pearce RH, Schechter MT, Adams ME, Tsang IK, Bishop PB. Preliminary evaluation of a scheme for grading the gross morphology of the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 1990; 15:411–415.
Article8). Hazlett JW, Kinnard P. Lumbar apophyseal process excision and spinal instability. Spine. 1982; 7:171–176.
Article9). Lehmann TR, Spratt KF, Tozzi JE, et al. Long-term follow-up of lower lumbar fusion patients. Spine. 1987; 12:97–104.
Article10). Aota Y, Kumano K, Hirabayashi S. Postfusion instability at the adjacent segments after rigid pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. J Spinal Disord. 1995; 8:464–473.
Article11). Brodsky AE. Post-laminectomy and post-fusion stenosis of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; 115:130–139.
Article12). Brodsky AE, Hendricks RL, Khalil MA, Darden BV, Brotzman TT. Segmental(“floating”) lumbar spine fusions. Spine. 1989; 14:447–450.13). Harris RI, Wiley JJ. Acquired spondylolysis as a sequel to spine fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1963; 45:1159–1170.
Article14). Schlegel JD, Smith JA, Schleusener RL. Lumbar motion segment pathology adjacent to thoracolumbar, lumbar and lumbosacral fusion. Spine. 1996; 21:970–981.15). Lee CK, Langrana NA. Lumbosacral spinal fusion. A biomechanical study. Spine. 1984; 9:574–581.
Article16). Luk KD, Chow DH, Evans JH, Leong JC. Lumbar spine mobility after short anterior interbody fusion. Spine. 1995; 20:813–818.17). Rahm MD, Hall BB. Adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion with instrumentation: A retrospective study. J Spinal Disord. 1996; 9:392–400.18). Gardner VO, Amstrong GW. Long-term lumbar facet joint changes in spinal fracture patients treated with Harrington rods. Spine. 1990; 15:479–484.
Article19). Nagata H, Schendel MJ, Transfeldt EE, Lewis JL. The effects of immobilization of long segments of the spine on the adjacent and distal facet force and lumbosacral motion. Spine. 1993; 18:2471–2479.
Article20). Lai PL, Chen LH, Niu CC, Fu TS, Chen WJ. Relation between laminectomy and development of adjacent segment instability after lumbar fusion with pedicle fixation. Spine. 2004; 29:2527–2532.
Article21). Ahn DK, Lee S, Jeong KW, Park JS, Cha SK, Park HS. Adjacent segment failure after lumbar spine fusion. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2004; 40:203–208.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Preliminary Report on Usefulness of Adjacent Interspinous Stabilization using Interspinous Spacer Combined with Posterior Lumbosacral Spinal Fusion in Degenerative Lumbar Disease
- Change of Segmental Motion After Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion
- Segmental Instability in Posterolateral Lumbar Spinal Fusion
- Risk Factors for “Adjacent-Level Ossification Development” Other Than Short Plate-to-Disc Distance and Clinical Implications for Adjacent-Segment Pathology
- The Revision Operation Rate for Adjacent Segmental Degeneration by Survival Analysis in Mono-segment Lumbar Fusion