Korean J Radiol.
2013 Apr;14(2):202-212. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.202.
Staging of Hepatic Fibrosis: Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Elastography and Shear Wave Elastography in the Same Individuals
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea. jmsh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- KMID: 1482778
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.202
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
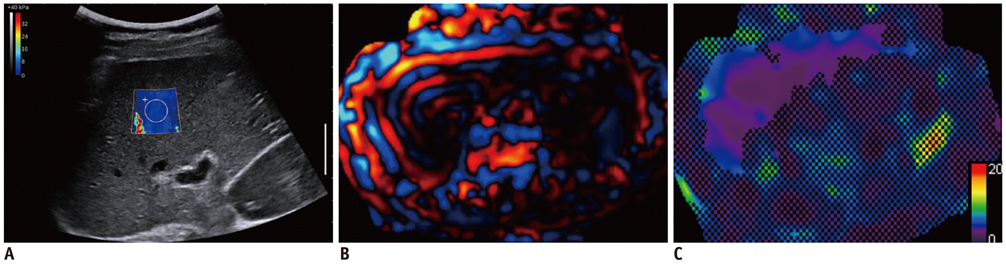
To cross-validate liver stiffness (LS) measured on shear wave elastography (SWE) and on magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) in the same individuals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
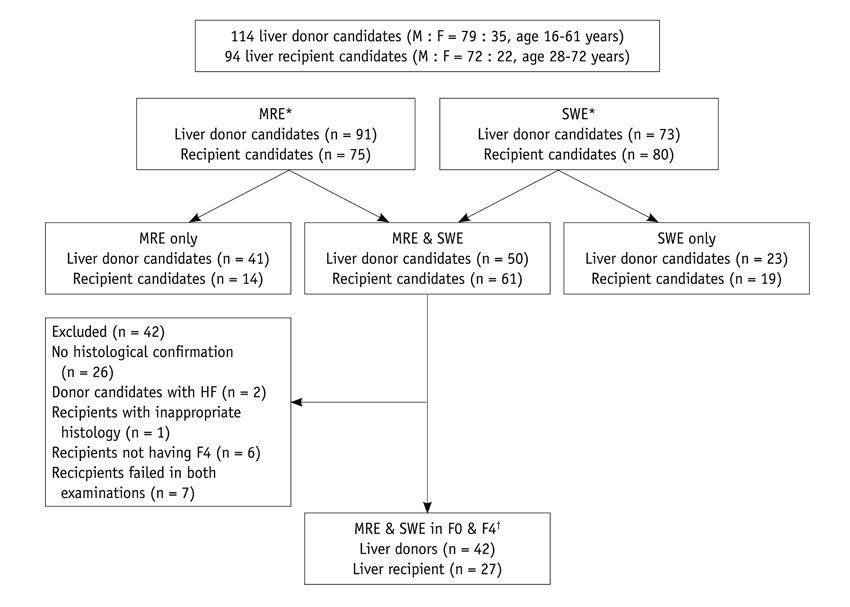
We included 94 liver transplantation (LT) recipients and 114 liver donors who underwent either MRE or SWE before surgery or biopsy. We determined the technical success rates and the incidence of unreliable LS measurements (LSM) of SWE and MRE. Among the 69 patients who underwent both MRE and SWE, the median and coefficient of variation (CV) of the LSM from each examination were compared and correlated. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve in both examinations were calculated in order to exclude the presence of hepatic fibrosis (HF).
RESULTS
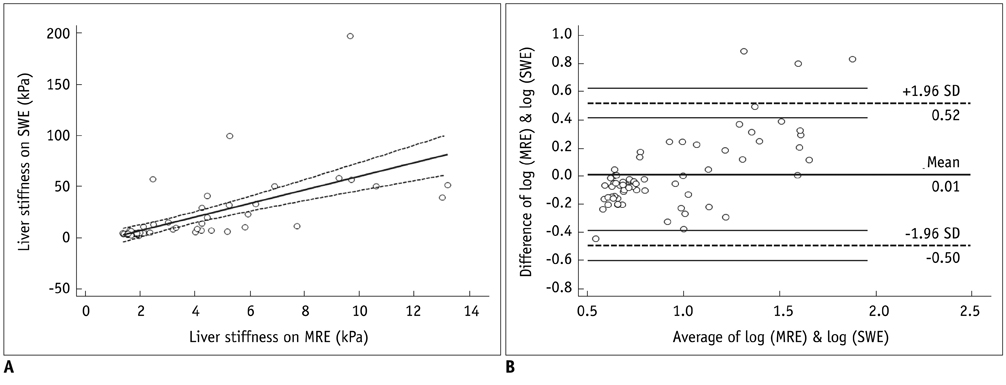
The technical success rates of MRE and SWE were 96.4% and 92.2%, respectively (p = 0.17), and all of the technical failures occurred in LT recipients. SWE showed 13.1% unreliable LSM, whereas MRE showed no such case (p < 0.05). There was moderate correlation in the LSM in both examinations (r = 0.67). SWE showed a significantly larger median LSM and CV than MRE. Both examinations showed similar diagnostic performance for excluding HF (Az; 0.989, 1.000, respectively).
CONCLUSION
MRE and SWE show moderate correlation in their LSMs, although SWE shows higher incidence of unreliable LSMs in cirrhotic liver.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Shear wave elastography: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin A Mo
J Korean Med Assoc. 2016;59(7):529-535. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2016.59.7.529.Segmental Liver Stiffness Evaluated with Magnetic Resonance Elastography Is Responsive to Endovascular Intervention in Patients with Budd-Chiari Syndrome
Peng Xu, Lulu Lyu, Haitao Ge, Muhammad Umair Sami, Panpan Liu, Chunfeng Hu, Kai Xu
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(5):773-780. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0767.
Reference
-
1. Castera L. Invasive and non-invasive methods for the assessment of fibrosis and disease progression in chronic liver disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011. 25:291–303.2. Taouli B, Ehman RL, Reeder SB. Advanced MRI methods for assessment of chronic liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009. 193:14–27.3. Tsochatzis EA, Bosch J, Burroughs AK. New therapeutic paradigm for patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2012. 56:1983–1992.4. Rockey DC. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis and portal hypertension with transient elastography. Gastroenterology. 2008. 134:8–14.5. Han KH, Yoon KT. New diagnostic method for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Intervirology. 2008. 51:Suppl 1. 11–16.6. Castera L. Noninvasive methods to assess liver disease in patients with hepatitis B or C. Gastroenterology. 2012. 142:1293–1302.e4.7. Bravo AA, Sheth SG, Chopra S. Liver biopsy. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:495–500.8. McGill DB, Rakela J, Zinsmeister AR, Ott BJ. A 21-year experience with major hemorrhage after percutaneous liver biopsy. Gastroenterology. 1990. 99:1396–1400.9. Van Thiel DH, Gavaler JS, Wright H, Tzakis A. Liver biopsy. Its safety and complications as seen at a liver transplant center. Transplantation. 1993. 55:1087–1090.10. Friedman SL. Liver fibrosis -- from bench to bedside. J Hepatol. 2003. 38:Suppl 1. S38–S53.11. Kim BH, Lee JM, Lee YJ, Lee KB, Suh KS, Han JK, et al. MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: experience from a tertiary center in Asia. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011. 34:1110–1116.12. Bonekamp S, Torbenson MS, Kamel IR. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011. 45:885–892.13. Faria SC, Ganesan K, Mwangi I, Shiehmorteza M, Viamonte B, Mazhar S, et al. MR imaging of liver fibrosis: current state of the art. Radiographics. 2009. 29:1615–1635.14. Friedrich-Rust M, Nierhoff J, Lupsor M, Sporea I, Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C, Strobel D, et al. Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis: a pooled meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat. 2012. 19:e212–e219.15. Tang A, Kim TK, Heathcote J, Guindi M, Jang HJ, Karshafian R, et al. Does hepatic vein transit time performed with contrast-enhanced ultrasound predict the severity of hepatic fibrosis? Ultrasound Med Biol. 2011. 37:1963–1969.16. Bavu E, Gennisson JL, Couade M, Bercoff J, Mallet V, Fink M, et al. Noninvasive in vivo liver fibrosis evaluation using supersonic shear imaging: a clinical study on 113 hepatitis C virus patients. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2011. 37:1361–1373.17. Huwart L, Sempoux C, Salameh N, Jamart J, Annet L, Sinkus R, et al. Liver fibrosis: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography versus aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index. Radiology. 2007. 245:458–466.18. Stebbing J, Farouk L, Panos G, Anderson M, Jiao LR, Mandalia S, et al. A meta-analysis of transient elastography for the detection of hepatic fibrosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010. 44:214–219.19. Tsochatzis EA, Gurusamy KS, Ntaoula S, Cholongitas E, Davidson BR, Burroughs AK. Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Hepatol. 2011. 54:650–659.20. Castéra L, Foucher J, Bernard PH, Carvalho F, Allaix D, Merrouche W, et al. Pitfalls of liver stiffness measurement: a 5-year prospective study of 13,369 examinations. Hepatology. 2010. 51:828–835.21. Lalitha P, Reddy MCh, Reddy KJ. Musculoskeletal applications of elastography: a pictorial essay of our initial experience. Korean J Radiol. 2011. 12:365–375.22. Cho N, Moon WK, Park JS, Cha JH, Jang M, Seong MH. Nonpalpable breast masses: evaluation by US elastography. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:111–118.23. Lee TH, Cha SW, Cho YD. EUS elastography: advances in diagnostic EUS of the pancreas. Korean J Radiol. 2012. 13:Suppl 1. S12–S16.24. Rouvière O, Yin M, Dresner MA, Rossman PJ, Burgart LJ, Fidler JL, et al. MR elastography of the liver: preliminary results. Radiology. 2006. 240:440–448.25. Rustogi R, Horowitz J, Harmath C, Wang Y, Chalian H, Ganger DR, et al. Accuracy of MR elastography and anatomic MR imaging features in the diagnosis of severe hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012. 35:1356–1364.26. Myers RP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Kirsch R, Pollett A, Beaton M, Levstik M, et al. Discordance in fibrosis staging between liver biopsy and transient elastography using the FibroScan XL probe. J Hepatol. 2012. 56:564–570.27. Bercoff J, Tanter M, Fink M. Supersonic shear imaging: a new technique for soft tissue elasticity mapping. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2004. 51:396–409.28. Tanter M, Bercoff J, Athanasiou A, Deffieux T, Gennisson JL, Montaldo G, et al. Quantitative assessment of breast lesion viscoelasticity: initial clinical results using supersonic shear imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008. 34:1373–1386.29. Myers RP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Kirsch R, Pollett A, Duarte-Rojo A, Wong D, et al. Feasibility and diagnostic performance of the FibroScan XL probe for liver stiffness measurement in overweight and obese patients. Hepatology. 2012. 55:199–208.30. Venkatesh SK, Yin M, Glockner JF, Takahashi N, Araoz PA, Talwalkar JA, et al. MR elastography of liver tumors: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 190:1534–1540.31. Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Grimm RC, Rossman PJ, et al. Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 5:1207–1213.e2.32. Manduca A, Oliphant TE, Dresner MA, Mahowald JL, Kruse SA, Amromin E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography: non-invasive mapping of tissue elasticity. Med Image Anal. 2001. 5:237–254.33. Hines CD, Bley TA, Lindstrom MJ, Reeder SB. Repeatability of magnetic resonance elastography for quantification of hepatic stiffness. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010. 31:725–731.34. Bedossa P, Poynard T. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1996. 24:289–293.35. The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1994. 20(1 Pt 1):15–20.36. De Groote J, Desmet VJ, Gedigk P, Korb G, Popper H, Poulsen H, et al. A classification of chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1968. 2:626–628.37. Euser AM, Dekker FW, le Cessie S. A practical approach to Bland-Altman plots and variation coefficients for log transformed variables. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008. 61:978–982.38. Bland JM, Altman DG. Comparing methods of measurement: why plotting difference against standard method is misleading. Lancet. 1995. 346:1085–1087.39. Bland JM, Altman DG. Agreed statistics: measurement method comparison. Anesthesiology. 2012. 116:182–185.40. Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Amemiya F, Sou H, Sano K, Muhi A, et al. Cross-validation of MR elastography and ultrasound transient elastography in liver stiffness measurement: discrepancy in the results of cirrhotic liver. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012. 35:607–610.41. Oudry J, Chen J, Glaser KJ, Miette V, Sandrin L, Ehman RL. Cross-validation of magnetic resonance elastography and ultrasound-based transient elastography: a preliminary phantom study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009. 30:1145–1150.42. Ferraioli G, Tinelli C, Dal Bello B, Zicchetti M, Filice G, Filice C. on behalf of the Liver Fibrosis Study Group. Accuracy of real-time shear wave elastography for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: A pilot study. Hepatology. 2012. 56:2125–2133.43. Ferraioli G, Tinelli C, Zicchetti M, Above E, Poma G, Di Gregorio M, et al. Reproducibility of real-time shear wave elastography in the evaluation of liver elasticity. Eur J Radiol. 2012. 81:3102–3106.44. Rzymski P, Skórzewska A, Skibińska-Zielińska M, Opala T. Factors influencing breast elasticity measured by the ultrasound Shear Wave elastography - preliminary results. Arch Med Sci. 2011. 7:127–133.45. Foucher J, Chanteloup E, Vergniol J, Castéra L, Le Bail B, Adhoute X, et al. Diagnosis of cirrhosis by transient elastography (FibroScan): a prospective study. Gut. 2006. 55:403–408.46. Asbach P, Klatt D, Schlosser B, Biermer M, Muche M, Rieger A, et al. Viscoelasticity-based staging of hepatic fibrosis with multifrequency MR elastography. Radiology. 2010. 257:80–86.47. Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, Salameh N, Annet L, Danse E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008. 135:32–40.48. Mariappan YK, Glaser KJ, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance elastography: a review. Clin Anat. 2010. 23:497–511.49. Bensamoun SF, Wang L, Robert L, Charleux F, Latrive JP, Ho Ba Tho MC. Measurement of liver stiffness with two imaging techniques: magnetic resonance elastography and ultrasound elastometry. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008. 28:1287–1292.50. Carrión JA, Torres F, Crespo G, Miquel R, García-Valdecasas JC, Navasa M, et al. Liver stiffness identifies two different patterns of fibrosis progression in patients with hepatitis C virus recurrence after liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2010. 51:23–34.51. Huwart L, Peeters F, Sinkus R, Annet L, Salameh N, ter Beek LC, et al. Liver fibrosis: non-invasive assessment with MR elastography. NMR Biomed. 2006. 19:173–179.52. Lee DH, Lee JM, Han JK, Choi BI. MR elastography of healthy liver parenchyma: Normal value and reliability of the liver stiffness value measurement. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012. [Epub ahead of print].53. Masuzaki R, Tateishi R, Yoshida H, Goto E, Sato T, Ohki T, et al. Prospective risk assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis C by transient elastography. Hepatology. 2009. 49:1954–1961.54. Robic MA, Procopet B, Métivier S, Péron JM, Selves J, Vinel JP, et al. Liver stiffness accurately predicts portal hypertension related complications in patients with chronic liver disease: a prospective study. J Hepatol. 2011. 55:1017–1024.55. Chon YE, Jung ES, Park JY, Kim do Y, Ahn SH, Han KH, et al. The accuracy of noninvasive methods in predicting the development of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012. 46:518–525.56. Fung J, Lai CL, Seto WK, Wong DK, Yuen MF. Prognostic significance of liver stiffness for hepatocellular carcinoma and mortality in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 2011. 18:738–744.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound Elastography for Liver Disease with Focus on Hepatic Fibrosis
- Diagnostic Performance of Quantitative Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography for Thyroid Cancer
- Future of breast elastography
- Non-Invasive Liver Fibrosis Test Using Shear Wave Elastography
- What we need to know when performing and interpreting US elastography