J Korean Fract Soc.
2008 Jan;21(1):24-30. 10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.24.
Two-staged Delayed Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibial Open Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. osksh@wonkwang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1480960
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.24
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate the outcomes of distal tibial open fractures treated by two-staged delayed minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
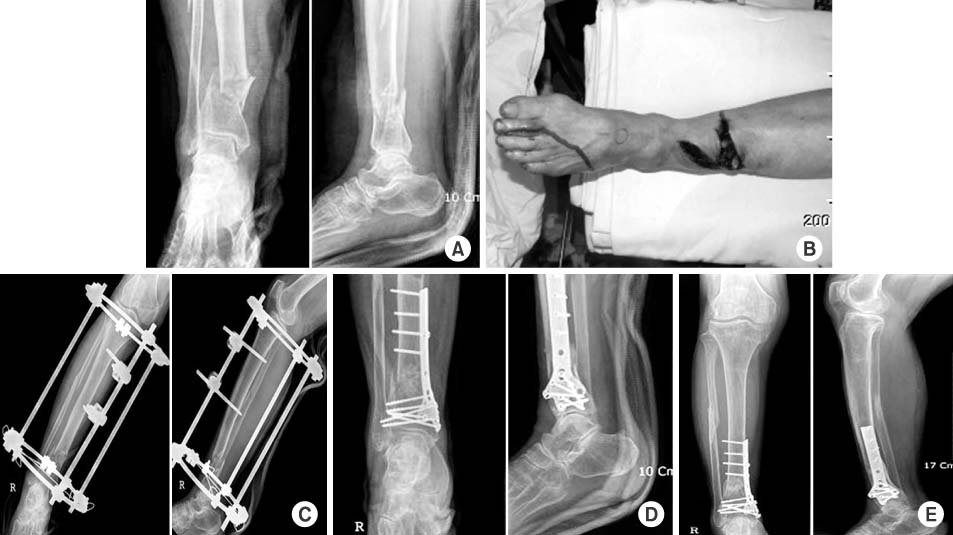
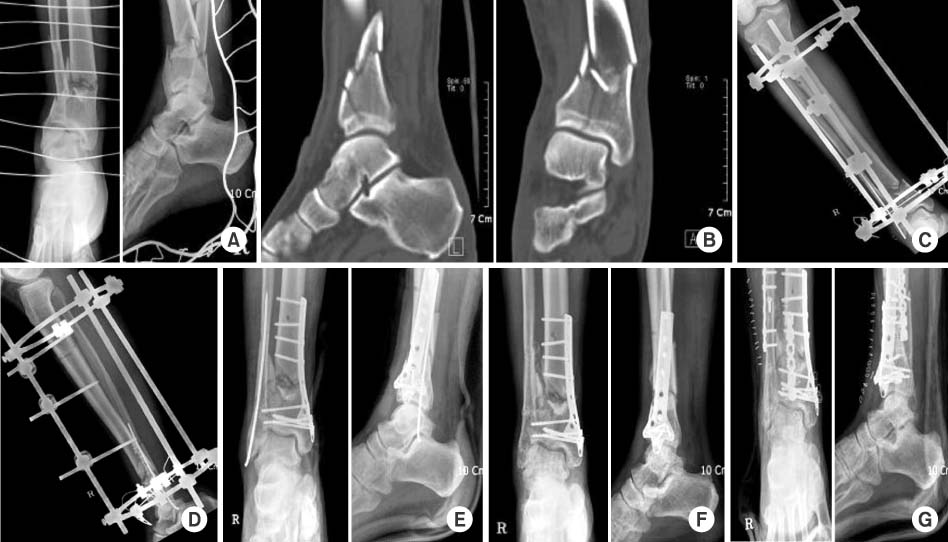
25 cases of distal tibial open fractures were treated with temporary ring fixation and two-staged delayed MIPPO. A mean age was 46 years old, follow-up was 23 months. The type of fracture was evaluated using the AO/OTA classification. The type of open fracture was evaluated using the Gustilo-Anderson classification that revealed 6 cases of type I, 9 cases of type II, 8 cases of type IIIA and 2 cases of type IIIB. We analyzed the radiologic results and postoperative complications. The clinical and functional result were evaluated by using Teeny and Wiss scores.
RESULTS
The average time of bone union was 18 weeks in 24 cases. There were three delayed union that achieved union twenty weeks after second operation, and 1 case underwent bone graft with additional plate fixation. 6 cases of skin necrosis were treated with skin graft, 2 cases were treated with flap. The clinical and functional assessment showed that 6 cases were excellent, 16 cases were good, 2 cases were fair, and 1 case were poor results.
CONCLUSION
Two-staged MIPPO technique for distal tibia open fractures seems to be a good procedure to obtain bone union.
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures
Sung-Ki Park, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Kyung-Hoon Kim, Woo-Kie Min, Byung-Chul Park, Won-Ju Jeong, Joo-Chul Ihn
J Korean Fract Soc. 2010;23(3):289-295. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.3.289.Management of Open Fracture
Gu-Hee Jung
J Korean Fract Soc. 2010;23(2):236-250. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.236.Staged Protocol in Treatment of Open Distal Tibia Fracture: Using Lateral MIPO
Oog Jin Sohn, Dong Hwa Kang
Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(1):69-76. doi: 10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.69.
Reference
-
1. Barbieri R, Schenk R, Koval K, Aurori B, Aurori K. Hybrid external fixation in the treatment of tibial plafond fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; 332:16–22.
Article2. Bhandari M, Zlowodzki M, Tornetta P 3rd, Schmidt A, Templeman DC. Intramedullary nailing following external fixation in femoral and tibial shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:140–144.
Article3. Blachut PA, Meek RN, O'Brien PJ. External fixation and delayed intramedullary nailing of open fractures of the tibial shaft. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990; 72:729–735.
Article4. Bonar SK, Marsh JL. Unilateral external fixation for severe pilon fractures. Foot Ankle. 1993; 14:57–64.
Article5. Bone LB. Fractures of the tibial plafond: the pilon fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987; 18:95–104.6. Bone L, Stegemann P, McNamara K, Seibel R. External fixation of severely comminuted and open tibial pilon fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 292:101–107.
Article7. Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Macnab J. Intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia: the pilon fracture. J Trauma. 1983; 23:591–596.8. Dillin L, Slabaugh P. Delayed wound healing, infection, and nonunion following open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures. J Trauma. 1986; 26:1116–1119.
Article9. Edwards CC, Simmons SC, Browner BD, Weigel MC. Severe open tibial fractures. Results treating 202 injuries with external fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 230:98–115.10. Griffiths GP, Thordarson DB. Tibial plafond fractures: limited internal fixation and a hybrid external fixator. Foot Ankle Int. 1996; 17:444–448.
Article11. Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58:453–458.
Article12. Helfet DL, Shonnard PY, Levine D, Borrelli J Jr. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal fractures of the tibia. Injury. 1997; 28:A42–A47.
Article13. Marsh JL, Bonar S, Nepola JV, Decoster TA, Hurwits SR. Use of an articulated external fixator for fractures of the tibial plafond. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:1498–1509.
Article14. McFerran MA, Smith SW, Boulas HJ, Schwartz HS. Complications encountered in the treatment of pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1992; 6:195–200.
Article15. McGraw JM, Lim EV. Treatment of open tibial-shaft fractures. External fixation and secondary intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:900–911.
Article16. Muller ME, Allgower M, Schreider R, Willenegger H. The manual of internal fixation. 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;1991.17. Oh CW. Treatment of complex distal tibia fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005; 18:485–490.18. Patterson MJ, Cole JD. Two-staged delayed open reduction and internal fixation of severe pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:85–91.
Article19. Saleh M, Shanahan MD, Fern ED. Intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia: surgical management by limited internal fixation and articulated distraction. Injury. 1993; 24:37–40.
Article20. Sirkin M, Sanders R, DiPasquale T, Herscovici D Jr. A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:78–84.
Article21. Sohn HM, Lee JY, Ha SH, You JW, Lee SH, Lee KC. Treatment of high-energy distal tibia intraarticular fractures with two-staged delayed minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Korean Fract Soc. 2007; 20:19–25.
Article22. Teeny SM, Wiss DA. Open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures. Variables contributing to poor results and complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (292):108–117.23. Tornetta P 3rd, Weiner L, Bergman M, et al. Pilon fractures: treatment with combined internal and external fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 1993; 7:489–496.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note
- Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Proximal Tibial Fracture
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using Periarticular Plate for Distal Tibial Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Periarticular Tibial Fractures