J Korean Fract Soc.
2008 Jan;21(1):19-23. 10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.19.
Retrograde Nailing for Supracondylar Fracture after Total Knee Replacement: The Compatibility of Femoral Implant with Supracondylar Nail
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kyj1009@hanmir.com
- KMID: 1480959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.19
Abstract
-
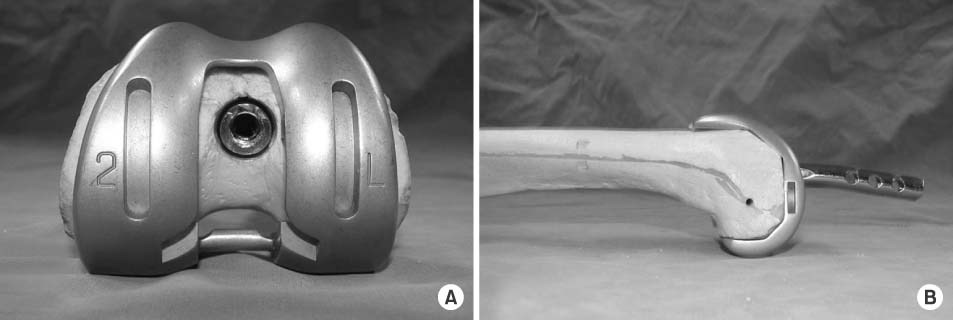
PURPOSE: Retrograde intrameullary nail is one of the treatment of periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fracture after total knee replacement (TKR), but all TKRs will not permit to insert a supracondylar nail. Therefore, we have investigated the compatibility of the TKRs with supracondylar nail.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Using trial femoral component of the 5 used TKRs in Korea and saw bone model, we checked their compatibility and measured the dimensions of the intercondylar notches in both cruciate retaining (CR) and posterior stabilized (PS) type.
RESULTS
Although most CR prostheses had an intercondylar notch large enough to accept a supracondylar nail, in some case, this was not possible due to the notch being situated too far posteriorly. The position of the intercondylar notch is also important factor in the PS prostheses.
CONCLUSION
The notch position, rather than the notch size, was the most important factor in determining nail compatibility with femoral stem.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Althausen PL, Lee MA, Finkemeier CG, Meehan JP, Rodrigo JJ. Operative stabilisation of supracondylar femur fractures above total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of four treatment methods. J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18:834–839.
Article2. Backstein D, Safir O, Gross A. Periprosthetic fracture of the knee. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:4 suppl 1. 45–49.3. Cain PR, Rubash HE, Wissinger HA, McClain EJ. Periprothetic femoral fractures following total knee arthroplsty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; 208:205–214.4. Chen F, Mont MA, Bachner RS. Management of ipsilateral supracondylar femur fractures following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1994; 9:521–526.
Article5. Culp RW, Schmidt RG, Hanks G, Mak A, Esterhai JL Jr, Heppenstall RB. Supracondylar fracture of the femur following prosthetic knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; 222:212–222.
Article6. Cusick RP, Lucas GL, McQueen DA, Graber CD. Construct stiffness of different fixation methods for supracondylar femoral fractures above total knee prostheses. Am J Orthop. 2000; 29:695–699.7. DiGioia AM 3rd, Rubash HE. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur after total knee arthroplasty: a literature review and treatment algorithm. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (271):135–142.8. Figgie MP, Goldberg VM, Figgie HE 3rd, Sobel M. The results of treatment of supracondylar fracture above total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1990; 5:267–276.
Article9. Gliatis J, Megas P, Panagiotopoulos E, Lambris E. Midterm results of treatment with a retrograde nail for supracondylar periprosthetic fractures of the femur following total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:164–171.
Article10. Healy WL, Siliski JM, Incavo SJ. Operative fixation of distal femoral fractures proximal to total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75:27–34.
Article11. Henry SL. Management of supracondylar fractures proximal to total knee arthroplasty with the GSH supracondylar nail. Contemp Orthop. 1995; 31:231–238.12. Hirsh DM, Bhalla S, Roffman M. Supracondylar fractures of the femur following total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63:162–163.13. Iannacone WM, Bennet BS, Delong WG, Born CT, Dalsey RM. Initial experience with the treatment of supracondylar femoral fractures using the supracondylar intramedullary nail: a preliminary report. J Orthop Trauma. 1994; 8:322–327.
Article14. Kraay MJ, Goldberg VM, Figgie MP, Figgie HE 3rd. Distal femoral replacement with allograft/prosthetic reconstruction for the treatment of supracondylar fractures in patients with total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1992; 7:7–16.
Article15. Kwon JW, Shin SH, Cho WH, et al. Retrograde nailing in femur supracondylar fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 2003; 16:465–473.
Article16. McLaren AC, Dupont JA, Schroeber DC. Open reduction internal fixation of supracondylar fractures above total knee arthroplasties using the intramedullary supracondylar rod. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (302):194–198.
Article17. Merkel KD, Johnson EW Jr. Supracondylar fracture of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:29–43.
Article18. Ritter MA, Fabris PM, Keating EM. Anterior femoral notching and ipsilateral supracondylar femur fracture in toal knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1988; 3:185–187.
Article19. Rolston LR, Christ DJ, Halpern A, O'Connor PL, Ryan TG, Uggen WM. Treatment of supracondylar fractures of the femur proximal to a total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:924–931.
Article20. Sochart DH, Hardinge K. Nonsurgical management of supracondylar fracture above total knee arthroplasty. Still meniscus option. J Arthroplasty. 1997; 12:830–834.
Article21. Su ET, DeWal H, Di Cesare PE. Periprothetic fractures above total knee replacements. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004; 12:12–20.22. Yoo MJ, Kim MH, Park HG, Byun WS, Kim KC. Treatment of the distal femur fracture with retrograde intramedullary nailing. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005; 18:238–243.
Article23. Zehntner MK, Ganz R. Internal fixation of supracondylar fractures after condylar total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 293:219–224.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Supracondylar Intramedullary Nail for Femoral Supracondylar Fracture following TKA: 3 Cases Report
- Treatment of Distal Femoral Fractures with a Retrograde Supracondylar Intramedullary Nail assisted with Arthroscopy
- Arthroscopieally Assisted Insertion of a Supracondylar Intramedullary Nail for Distal and Supracondylar Femoral Fracture: Technique Report
- Treatment of Supracondylar Fracture of the Femur using the Supracondylar intramedullary Nail under the Arthroscopy(Preliminary Report)
- Treatment of Supracondylar-Intercondylar Femoral Fractures with a Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing