J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2009 Mar;16(1):30-37. 10.4184/jkss.2009.16.1.30.
Unilateral Undercutting Laminoplasty in the Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Comparison with Conventional Bilateral Partial Laminectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. schsbj@hosp.sch.ac.kr
- KMID: 1473387
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2009.16.1.30
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: A retrospective study
OBJECTIVES
Contralateral undercutting laminoplasty via a unilateral laminotomy has been performed instead of bilateral partial laminectomy in lumbar spinal stenosis. This study compared the radiographic and clinical results of undercutting laminoplasty with bilateral partial laminectomy. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Less invasive surgery has become attractive for minimizing soft tissue injury and reducing the recovery time.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
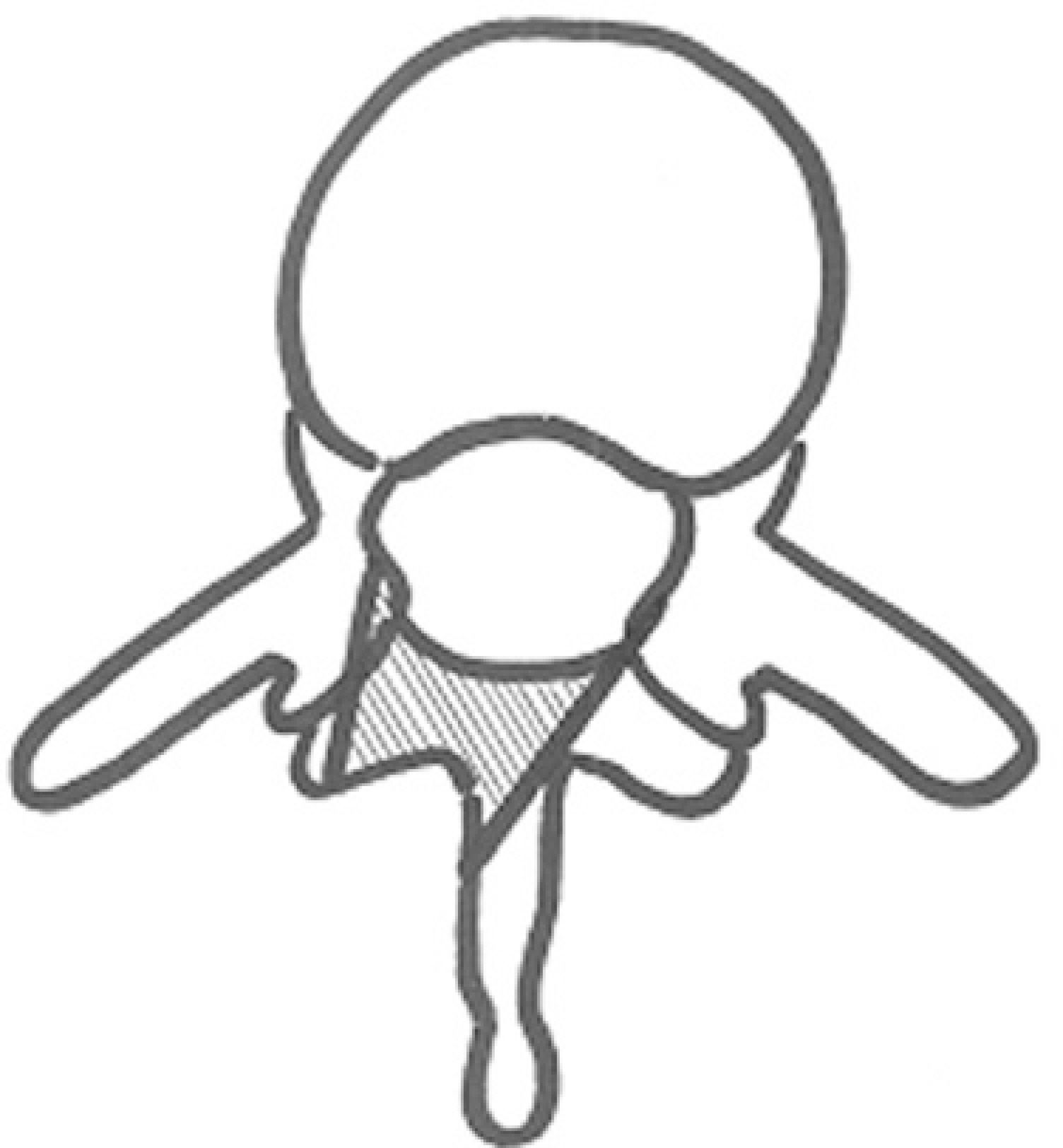
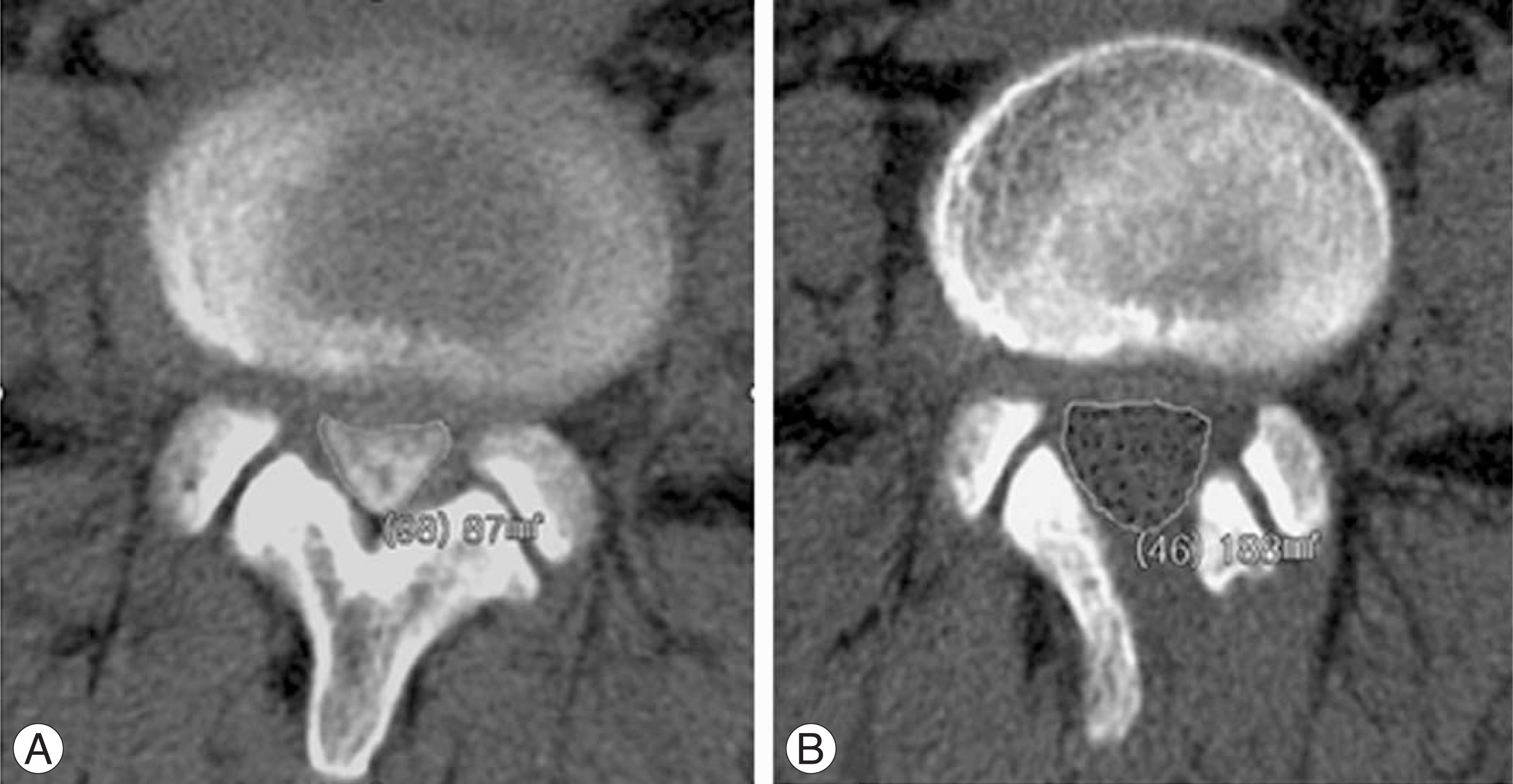
Twenty five patients, who underwent decompressive surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis and were followed-up more than one year, were enrolled in this study. Unilateral undercutting laminoplasty and bilateral partial laminectomy was performed in 13 and 12 cases, respectively. The blood loss was compared and the presence of instability was observed. The increase in dural cross sectional area was measured in the preoperative and postoperative CT scans. In the clinical assessment, the Oswestry disability index (ODI) and visual analogue scale (VAS) to pain was used.
RESULTS
The average blood loss per segment was 273 ml and 436 ml in the laminoplasty and laminectomy group. There was no case of instability after surgery but there was a significant difference in the increase in dural cross sectional area between the two groups: 109.7 mm2 and 78.6 mm2 in the laminoplasty and laminectomy group, respectively. The preoperative and final change in the ODI and VAS scores was similar between the two groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Unilateral undercutting laminoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure with less blood loss than the conventional technique and is equally effective.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
01). Goel VK., Fromknecht SJ., Nishiyama K, et al. The role of lumbar spinal elements in flexion. Spine. 1985. 10:516–523.
Article02). Weiner BK., Fraser RD., Peterson M. Spinous process osteotomies to facilitate lumbar decompressive surgery. Spine. 1999. 24:62–66.
Article03). Jeon CH., Kim DJ., Lee HM, et al. Cross-cultural adaptation of the Korean Version Of the Oswestry Disability Index. J Korean Spine surgery. 2005. 12:146–152.04). Turner JA., Ersek M., Herron L, et al. Surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Attempted meta-analysis of the literature. Spine. 1992. 17:1–8.05). Niggemeyer O., Strauss JM., Schulitz KP. Comparison of surgical procedures for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a meta-analysis of the literature form 1975 to 1995. Eur Spine J. 1997. 6:423–429.06). Caspar W., Papavero L., Sayler MK, et al. Precise and limited decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Acta Neurochir. 1994. 131:130–136.
Article07). Mackay DC., Wheelwright EF. Unilateral fenestration in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. Br J Neurosurg. 1998. 12:556–558.
Article08). Sanderson PL., Getty CJ. Long-term results of partial undercutting facetectomy for lumbar lateral recess steno- sis. Spine. 1996. 21:1352–1356.09). Aryanpur J., Ducker T. Multilevel lumbar laminotomies: an alternative to laminectomy in ther treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery. 1990. 26:429–432.10). Kleeman TJ., Hiscoe AC., Berg EE. Patient outcomes after minimally destabilizing lumbar stenosis decompression: the “Port-Hole” technique. Spine. 2000. 25:865–870.11). Nakai O., Ookawa A., Yamaura I. Long-term roentgenographic and functional changes in patients who were treated with wide fenestration for central lumbarstenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:1184–1191.12). Tsai RY., Yang RS., Bray RS Jr. Microscopic laminotomies for degenerative lumbar spinal stensos. J Spinal Disord. 1998. 11:389–394.13). Yamazaki K., Yoshida S., Ito T, et al. Postoperative outcome of lumbar spinal canal stenosis after fenestration: correlation with changes in intradural and extradural tube on magnetic resonance imaging. J Orthop Surg. 2002. 10:136–143.
Article14). Young S., Veerapen R., O'Laoire SA. Relief of lumbar canal stenosis using multilevel subarticular fenestrations as an alternative to wide laminectomy: preliminary report. Neurosurgery. 1988. 23:628–633.
Article15). Guiot BH., Khoo LT., Fessler RG. A minimally invasive technique for decompression of the lumbar spine. Spine. 2002. 27:432–438.
Article16). Khoo LT., Fessler RG. Microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for ther treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery. 2002. 51:146–154.17). Mariconda M., Fava R., Gatto A, et al. Unilateral laminectomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: a prospective comparative study with conservatively treated patients. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2002. 15:39–46.
Article18). Palmer S., Turner R., Palmer R. Bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis involving a unilateral approach with microscope and tubular retractor system. J Neurosurg. 2002. 97:213–217.
Article19). Poletti CE. Central lumbar stenosis caused by ligamentum flavum: unilateral laminotomy for bilateral ligamentecto-my: preliminary report of two cases. Neurosurgery. 1995. 37:343–347.20). Spetzger U., Bertalanffy H., Naujokat C, et al. Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part Ⅰ: Anatomical and surgical considerations. Acta Neurochir. 1997. 139:392–396.21). Spetzger U., Bertalanffy H., Naujokat C, et al. Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part Ⅱ: Clinical experiences. Acta Neurochir. 1997. 139:397–403.22). Weiner BK., Walker M., Brower RS, et al. Microdecom-pression for lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine. 1999. 24:2268–2272.
Article23). Thome C., Zevgaridis D., Leheta O, et al. Outcome after less-invassive decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: a randomized comparison of unilateral laminotomy, bilateral laminotomy, and laminectomy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005. 3:129–141.24). You JW., Sohn HM., Lee JY, et al. Comparison of the results of the decompression methods for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: Comparison of posterior element saving procedures. J Kor Spine Surg. 2005. 12:324–330.
Article25). Fox MW., Onofrio BM., Hanssen AD. Clinical outcomes and radiological instability following decompressive lumbar laminectomy for degenerative spinal stenosis: a comparison of patients undergoing concomitant arthrodesis versus decompression alone. J Neurosurg. 1996. 85:793–802.
Article26). Johnsson KE., Willner S., Johnsson K. Postoperative instability after decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine. 1986. 11:107–110.
Article27). Mullin BB., Rea GL., Irsik R, et al. The effect of post-laminectomy spinal instability on the outcome of lumbar spinal stenosis patients. J Spinal Disord. 1996. 9:107–116.
Article28). Sienkiewicz PJ., Flatley TJ. Postoperative spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop. 1987. 221:172–180.
Article29). Tuite GF., Doran SE., Stern JD, et al. Outcome after laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis. Part Ⅱ: Radiographic changes and clinical correlations. J Neurosurg. 1994. 81:707–715.30). Yukawa Y., Lenke LG., Tenhula J, et al. A comprehensive study of patients with surgically treated lumbar spinal stenosis with neurogenic claudication. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84:1954–1959.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Spinal Epidural Hematoma Following Unilateral Laminectomy for Bilateral Decompression
- Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Decompression for Thoracic Spinal Stenosis
- Expansive Laminoplasty for Cervical Compression Myelopathy
- Efficacy of Unilateral Laminectomy for Bilateral Decompression in Elderly Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Comparison of the Results of the Decompression Methods for Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Comparison of Posterior Element Saving Procedures