J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2005 Dec;12(4):324-330.
Comparison of the Results of the Decompression Methods for Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Comparison of Posterior Element Saving Procedures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. hmsohn@chosun.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gwangju Veteran's Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: This is a prospective study.
OBJECTIVES
We wanted to analyze the radiographic and clinical results of the three posterior element saving decompression techniques for treating lumbar degenerative spinal stenosis. SUMMARY OF THE LITERATURE REVIEW: Minimal invasive decompression reduces patient morbidity and the hospital stay.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
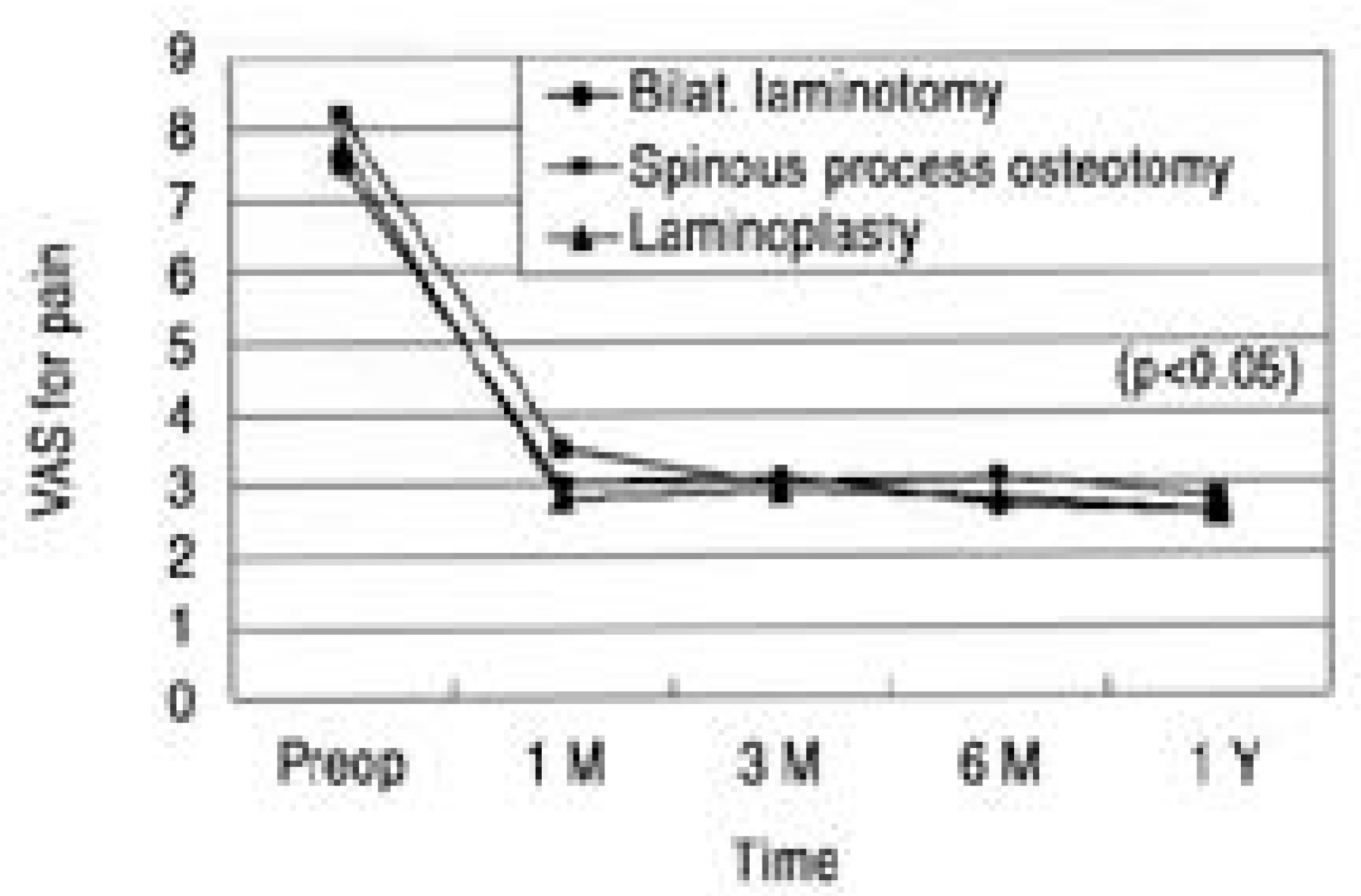
We evaluated 30 patients, who were treated with posterior element saving microscopic decompression for their lumbar spinal stenosis (without instability), during the period from March, 2002 and February, 2004. The procedures were bilateral laminotomy (10 cases), spinous process osteotomy (8 cases) and laminoplasty (12 cases). We evaluated the estimated blood loss, the amount of transfusion, the complications and the radiographic instability at the last follow-up. The clinical results were evaluated with using the Oswestry disability index (ODI) and the visual analogue scale (VAS) for buttock and leg pain both preoperatively and at postoperative 1, 3, 6 and 12 months, respectively.
RESULTS
There was no radiographic instability noted for any of the patients at the last follow up. The mean ODI and VAS scores were substantially improved at postoperative 1 month and then they were marginally improved afterwards. However, there were no statistically significant differences among three procedures (p>0.05). The mean blood loss and the amount of transfusion for each spinal level were 290 ml and 0.5 U for bilateral laminotomy, 370 ml and 0.9 U for spinous process osteotomy and 180 ml and 0.1 U for laminoplasty, respectively.
CONCLUSION
There were no significant differences in the radiograhic and clinical results among bilateral laminotomy, spinous process osteotomy and laminoplasty. Yet in terms of blood loss and transfusion, laminoplasty was better than the other techniques. We believe that laminoplasty is a useful and safe technique for treating degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Goel VK, Fromknecht SJ, Nishiyama K, Weinstein J, Liu YK. The role of lumbar spinal elements in flexion. Spine. 1985; 10:516–523.
Article2). Weiner BK, Fraser RD, Peterson M. Spinous process osteotomies to facilitate lumbar decompressive surgery. Spine. 1999; 24:62–66.
Article3). Abumi K, Panjabi MM, Kramer KM, Duranceau J, Oxland T, Crisco JJ. Biomechanical evaluation of lum - bar spinal stability after graded facetectomies. Spine. 1990; 15:1142–1147.4). Delamarter RB, McCulloch JA. Microdiscectomy and microsurgical spinal laminotomies. Frymoyer JW, editor. The adult spine. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;p. 1961–1988. 1997.5). Bae HW, Fribourg DM, Delamarter RB. Decom pression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Frymoyer JW, Wiesel SW, editors. The adult and pediatric spine. 3rd ed.Philadelphia: LippincottWilliams&Wilkins;p. 1107–1121. 2004.6). McCulloch JA, Snook D, Kruse CF. Advantages of the operating microscope in lumbar spine surgery. Instr Course Lect. 2002; 51:243–245.7). Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Naujokat C, von Keyser-lingk DG, Gilsbach JM. Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part I: Anatomical and surgical considerations. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1997; 139(5):392–396.8). Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Reinges MH, Gilsbach JM. Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part II: Clinical experiences. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1997; 139(5):397–403.
Article9). Aryanpur J, Ducker T. Multilevel lumbar laminotomies: an alternative to laminectomy in the treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery. 1990; 26:429–433.
Article10). Lee CS, Chung SS, Chung KH, Oh SK. Bilateral microscopic laminotomy for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Kor Spine Surg. 2004; 11:99–103.
Article11). Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The Oswestry Disability Index. Spine. 2000; 25:2940–2953.
Article12). Getty CJ. Lumbar spinal stenosis: the clinical spectrum and the results of operation. J Bone Joint Surg. 1980; 62-B:481–485.
Article13). Niggemeyer O, Strauss JM, Schulitz KP. Comparison of surgical procedures for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a metaanalysis of the literature from 1975 to 1995. Eur Spine J. 1997; 6:423–429.
Article14). Deyo RA, Ciol MA, Cherkin DC, Loeser JD, Bigos SJ. Lumbar spinal fusion. A cohort study of complications, reoperations, and resource use in the Medicare population. Spine. 1993; 18:1463–1470.15). Turner JA, Ersek M, Herron L, et al. Patient outcomes after lumbar spinal fusions. JAMA. 1992; 19(268):907–911.
Article16). Jaikumar S, Kim DH, Kam AC. History of minimally invasive spine surgery. Neurosurgery. 2002; 51:S1–14.
Article17). Khoo LT, Fessler RG. Microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for the treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery. 2002; 51:S146–154.
Article18). Palmer S, Turner R, Palmer R. Bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis involving a unilateral approach with microscope and tubular retractor system. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:213–217.
Article19). Johnsson KE, Willner S, Johnsson K. P ostoperat iv e instability after decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine. 1986; 11:107–110.20). Cho KJ, Moon KH, Kim MK, et al. Changes of clinical outcomes after decompression and fusion for spinal stenosis during 2-year follow-up periods. J Kor Spine Surg. 2003; 10:113–118.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Result of Pedicle Screw Fixation in Lumbar Stenosis with: A Comparison of Degenerative Type Lumbar Stenosis with Spondylolisthetic type Lumbar Stenosis
- Clinical Comparison between Decompression and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Chronic Lower Back Pain Involving Degenerative Disc Disease and Spinal Stenosis
- A Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Decompressive Lumbar Laminectomy Alone and with Arthrodesis in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- A Clinical Study on the Causes of the Nerve Entrapment in the Degenerative Spondylolisthesis
- Cotrel - Dubousset Pedicle Screw Fixation After Posterior Decompression of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis