Korean J Clin Microbiol.
2009 Mar;12(1):48-52. 10.5145/KJCM.2009.12.1.48.
A Case of Emetic Toxin Producing Bacillus cereusStrains Isolated from Outbreak
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Enteric Bacterial Infections, Center for Infectious Diseases, National Institute of Health, Seoul, Korea. bokrates@nih.go.kr
- 2Microbe Division, Ulsan Institute of Health and Environment, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 1469970
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/KJCM.2009.12.1.48
Abstract
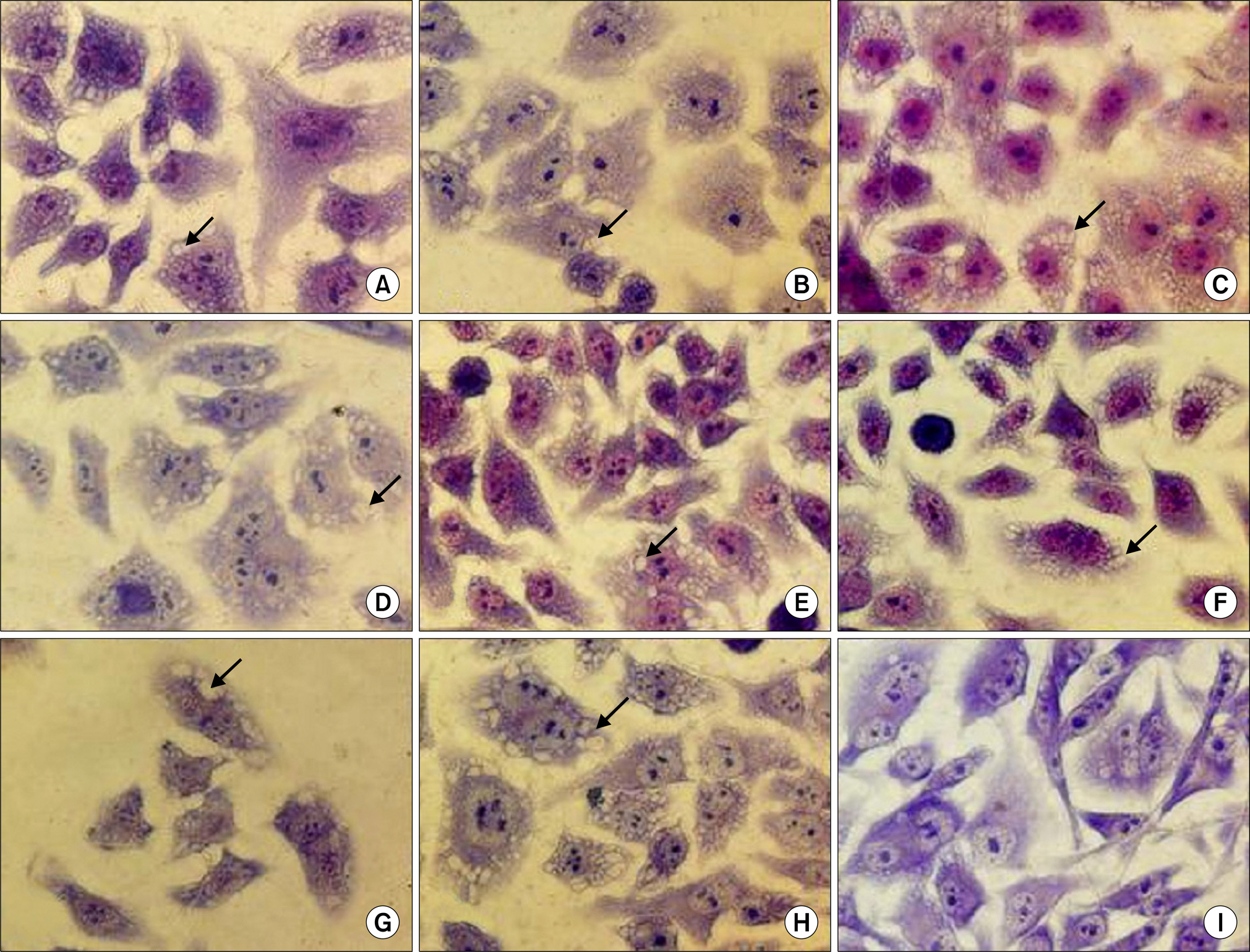
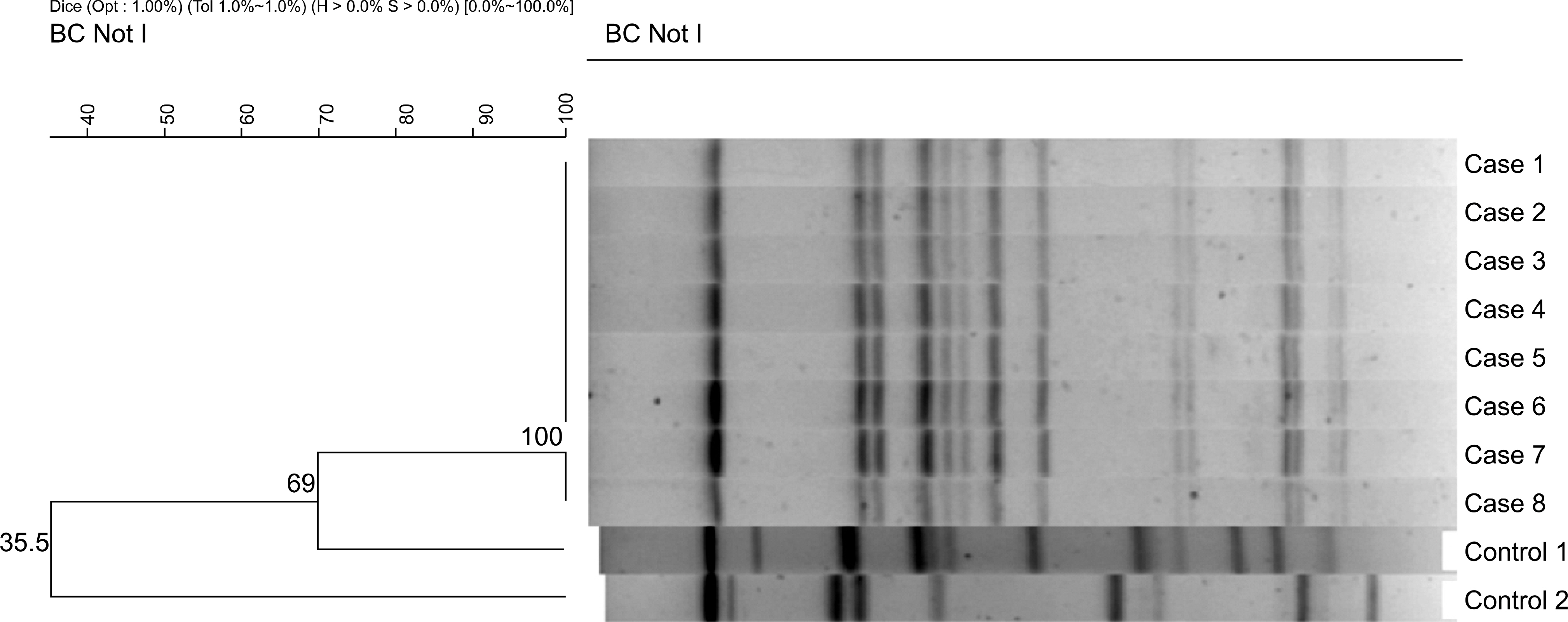
- Bacillus cereus causes two types of gastrointestinal diseases: emesis and diarrhea. It produces one emetic toxin and nine different enterotoxins. In March 2008, eight of a family became sick after eating slices of raw fish. We isolated emetic toxin producing B. cereus from the stools of 6 patients and 2 subclincal humans. In this study, the presence of enterotoxin genes, such as those of haemolysin BL (Hbl), nonhemolytic enterotoxin (Nhe), B. cereus enterotoxin T (BceT), enterotoxin FM (EntFM), cytotoxin K (cytK) and cereulide were assayed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods. Their enterotoxin activities were assayed using the BCET- RPLA, Tecra ELISA kit and Hep-2 vacuole activity. Bacterial isolates were subtyped by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). This study demonstrates the emetic toxin-producing stains of B. cereus in clinical specimens, for the first time in the Republic of Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Agata N, Ohta M, Mori M, Isobe M. A novel dodecadepsipeptide, cereulide, is an emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995; 129:17–20.2. Mahler H, Pasi A, Kramer JM, Schulte P, Scoging AC, Bär W, et al. Fulminant liver failure in association with the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. New Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1142–8.3. Ehling-Schulz M, Vukov N, Schulz A, Shaheen R, Andersson M, Märtlbauer E, et al. Identification and partial characterization of the nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene responsible for cereulide production in emetic Bacillus cereus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005; 71:105–13.4. Yang IC, Shih DY, Huang TP, Huang YP, Wang JY, Pan TM. Establishment of a novel multiplex PCR assay and detection of toxigenic strains of the species in the Bacillus cereus group. J Food Prot. 2005; 68:2123–30.5. Taylor JM, Sutherland AD, Aidoo KE, Logan NA. Heat-stable toxin production by strains of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus firmus, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus simplex and Bacillus licheniformis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005; 242:313–7.6. Liu PY, Ke SC, Chen SL. Use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to investigate a pseudo-outbreak of Bacillus cereus in a pediatric unit. J Clin Microbiol. 1997; 35:1533–5.7. Division of Enteric Bacterial Infections, Division of Enteric and Hepatitis viruses, Division of Malaria and Parasitic Diseases. Surveillance Network of Water-borne and Food-borne disease. 1th ed.Seoul: Center for Infectious Diseases, National Institute of Health;2007. p. 7–31.8. Kramer JM, Gilbert RJ. Bacillus cereus and other Bacillus species. Doyle MP, editor. Food Borne Bacterial Pathogens. New York: Marcel Dekker;1989. p. 21–70.9. Rusul G, Yaacob NH. Prevalence of Bacillus cereus in selected foods and detection of enterotoxin using TECRA-VIA and BCET-RPLA. Int J Food Microbiol. 1995; 25:131–9.10. Nishikawa Y, Kramer JM, Hanaoka M, Yasukawa A. Evaluation of serotyping, biotyping, plasmid banding pattern analysis, and HEp-2 vacuolation factor assay in the epidemiological investigation of Bacillus cereus emetic-syndrome food poisoning. Int J Food Microbiol. 1996; 31:149–59.11. Liu PY, Ke SC, Chen SL. Use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to investigate a pseudo-outbreak of Bacillus cereus in a pediatric unit. J Clin Microbiol. 1997; 35:1533–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surveillance of Bacillus cereus Isolates in Korea from 2012 to 2014
- Inhibition of Lethal Toxin Expression in Bacillus anthracis Using Antisense Technology
- Epidemiological Analysis of Shiga Toxin-producing E. coli Isolated in Gwangju, Korea, by Pulse-field Gel Electrophoresis
- Identification of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli by Colony Hybridization with stx-specific Oligonucleotide
- Whole genome sequence analyses of thermotolerant Bacillus sp. isolates from food