Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2009 Dec;2(4):203-206. 10.3342/ceo.2009.2.4.203.
Otogenic Pneumocephalus Associated with a Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. hsue0928@nhimc.or.kr
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, Kangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1466499
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2009.2.4.203
Abstract
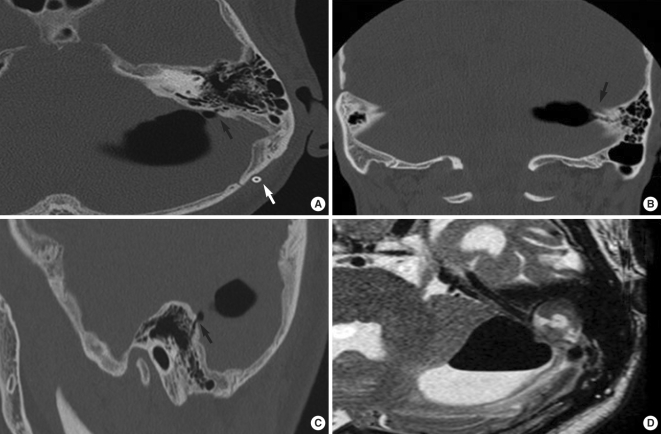
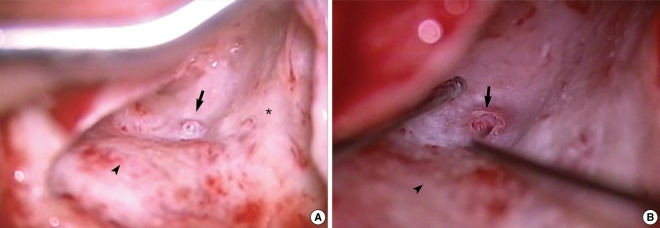
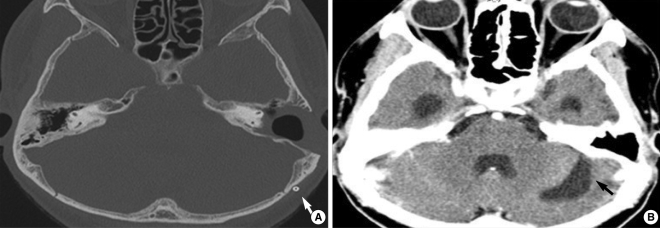
- Otogenic pneumocephalus is a condition of intracranial air originating from the middle ear or mastoid air cells. This communication between the intracranial cavity and the pneumatic cavities is usually associated with trauma after cranial fractures or iatrogenic trauma. We present a rare case of otogenic pneumocephalus arising in the left posterior fossa from wellpneumatized mastoid air cells. The patient complained of roaring tinnitus that developed 29 months after ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion due to brain tumor surgery. High resolution computed tomography scan of the temporal bones revealed a large pneumocephalus below the left tentorium, and a bony dehiscent route was clearly identified in a sagittal view. A left mastoidectomy with preservation of the posterior wall of the external auditory canal was performed, and the expected bony dehiscent site was identified in the posterior fossa dura plate, just posterior to the posterior semicircular canal, below the Donaldson's line. This communication was sealed with a temporalis muscle plug from the deep temporalis muscle fascia and bone dust. Pneumocephalus may be caused by negative intracranial pressure in a patient with very well-pneumatized mastoid bone, and it can be a possible cause of 'wind-like' sound in the ear.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vallejo LA, Gil-Carcedo LM, Borras JM, De Campos JM. Spontaneous pneumocephalus of an otogenic origin. Otolayrngol Head Neck Surg. 1999; 11. 121(5):662–665.
Article2. Andrews JC, Canalis RF. Otogenic pneumocephalus. Laryngoscope. 1986; 5. 96(5):521–528. PMID: 3702568.
Article3. Anorbe E, Aisa P, Saenz de Ormijana J. Spontaneous pneumatocele and pneumocephalus associated with mastoid hyperpneumatization. Eur J Radiol. 2000; 12. 36(3):158–160. PMID: 11091017.4. Krayenbuhl N, Alkadhi H, Jung HH, Yonekawa Y. Spontaneous otogenic intracerebral pneumocephalus: case report and review of the literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; 2. 262(2):135–138. PMID: 15004711.
Article5. Honeybul S, Bala A. Delayed pneumocephalus following shunting for hydrocephalus. J Clin Neurosci. 2006; 11. 13(9):939–942. PMID: 17049242.
Article6. Ruge JR, Cerullo LJ, McLone DG. Pneumocephalus in patients with CSF shunts. J Neurosurg. 1985; 10. 63(4):532–536. PMID: 4032017.
Article7. Nagai H, Moritake K. Otogenic tension pneumocephalus complicated by eustachian tube insufflation in a patient with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt: case report. J Neurosurg. 2007; 6. 106(6):1098–1101. PMID: 17564188.8. Kanner AA, Nageris BI, Chaimoff M, Rappaport ZH. Spontaneous pneumocephalus in the posterior fossa in a patient with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt: case report. Neurosurgery. 2000; 4. 46(4):1002–1004. PMID: 10764280.