J Korean Surg Soc.
2009 Dec;77(6):378-384. 10.4174/jkss.2009.77.6.378.
Implications of Isolated Tumor Cells in Sentinel Lymph Nodes of Breast Cancer Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drjh.yang@samsung.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1464816
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2009.77.6.378
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced unnecessary axillary dissection in breast cancer surgery except when the nodes are positive for macrometastasis. But guidelines for isolated tumor cells (ITCs) found in SLNs has not yet been established and further study is ongoing. The goal of this study was to consider the implication of the isolated tumor cells found in the SLNs of Korean breast cancer patients.
METHODS
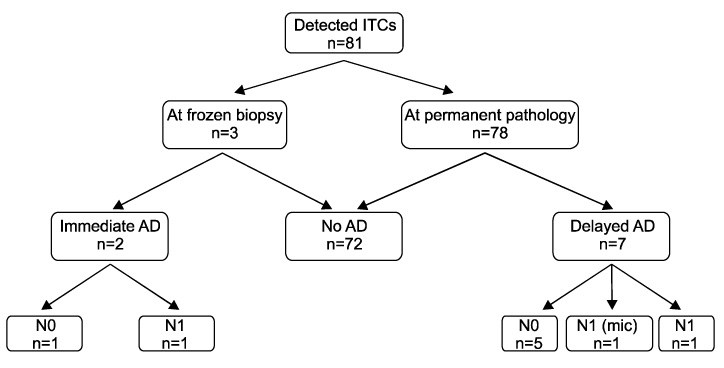
Between September 2003 and March 2008, 985 primary breast cancer patients underwent SLN biopsy. On reviewing the medical records, 81 patients were found to have ITCs in SLNs without macrometastasis or micrometastasis. ITCs were detected by serial sectioning and immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
The mean number of detected SLNs was 3.5+/-1.7. Thirty three patients had multifocally distributed ITCs and 9 had ITCs in multiple SLNs whose N stage was N0 (i+). Completion axillary dissection has been performed in 9 patients and 3 of them (33.3%) finally were found to be N1 or N1mi.
CONCLUSION
The characteristics of ITCs are not clear yet and their prognostic value is still under investigation. Until the significance of ITCs found in SLNs become definite, axillary dissection should be more aggressively considered.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Giuliano AE, Kirgan DM, Guenther JM, Morton DL. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 1994. 220:391–401.2. Schrenk P, Hatzl-Griesenhofer M, Shamiyeh A, Waynad W. Follow-up of sentinel node negative breast cancer patients without axillary lymph node dissection. J Surg Oncol. 2001. 77:165–170.3. Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Viale G, Luini A, Zurrida S, Galimberti V, et al. A randomized comparison of sentinel-node biopsy with routine axillary dissection in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:546–553.4. Veronesi U, Boyle P, Goldhirsch A, Orecchia R, Viale G. Breast cancer. Lancet. 2005. 365:1727–1741.5. Noguchi M. Avoidance of axillary lymph node dissection in selected patients with node-positive breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008. 34:129–134.6. Giuliano AE, Haigh PI, Brennan MB, Hansen NM, Kelley MC, Ye W, et al. Prospective observational study of sentinel lymphadenectomy without further axillary dissection in patients with sentinel node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000. 18:2553–2559.7. Cserni G, Gregori D, Merletti F, Sapino A, Mano MP, Ponti A, et al. Meta-analysis of non-sentinel node metastases associated with micrometastatic sentinel nodes in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2004. 91:1245–1252.8. Sobin LH, Wittekind C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 2002. 6th ed. New York: Wiley-Liss.9. Schwartz GF, Giuliano AE, Veronesi U. Proceedings of the consensus conference on the role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in carcinoma of the breast April 19 to 22, 2001, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Hum Pathol. 2002. 33:579–589.10. Chen SL, Hoehne FM, Giuliano AE. The prognostic significance of micrometastases in breast cancer: a SEER population-based analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. 14:3378–3384.11. Viale G, Maiorano E, Mazzarol G, Zurrida S, Galimberti V, Luini A, et al. Histologic detection and clinical implications of micrometastases in axillary sentinel lymph nodes for patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2001. 92:1378–1384.12. Kuijt GP, Voogd AC, van de Poll-Franse LV, Scheijmans LJ, van Beek MW, Roumen RM. The prognostic significance of axillary lymph-node micrometastases in breast cancer patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2005. 31:500–505.13. Yoo KE, Choi YJ, Choi YL, Kim JH, Nam SJ, Yang JH. Analysis of the clinicopathological features in the micrometastasis and the macrometastasis in sentinel lymph node of primary breast cancer. J Korean Surg Soc. 2006. 70:419–424.14. Querzoli P, Pedriali M, Rinaldi R, Lombardi AR, Biganzoli E, Boracchi P, et al. Axillary lymph node nanometastases are prognostic factors for disease-free survival and metastatic relapse in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12:6696–6701.15. Herbert GS, Sohn VY, Brown TA. The impact of nodal isolated tumor cells on survival of breast cancer patients. Am J Surg. 2007. 193:571–574.16. Hulvat M, Rajan P, Rajan E, Sarker S, Schermer C, Aranha G, et al. Histopathologic characteristics of the primary tumor in breast cancer patients with isolated tumor cells of the sentinel node. Surgery. 2008. 144:518–524.17. Viale G, Maiorano E, Pruneri G, Mastropasqua MG, Valentini S, Galimberti V, et al. Predicting the risk for additional axillary metastases in patients with breast carcinoma and positive sentinel lymph node biopsy. Ann Surg. 2005. 241:319–325.18. de Mascarel I, MacGrogan G, Debled M, Brouste V, Mauriac L. Distinction between isolated tumor cells and micrometastases in breast cancer: is it reliable and useful? Cancer. 2008. 112:1672–1678.19. Katz A, Niemierko A, Gage I, Evans S, Shaffer M, Fleury T, et al. Can axillary dissection be avoided in patients with sentinel lymph node metastasis? J Surg Oncol. 2006. 93:550–558.20. de Widt-Levert L, Tjan-Heijnen V, Bult P, Ruers T, Wobbes T. Stage migration in breast cancer: surgical decisions concerning isolated tumour cells and micro-metastases in the sentinel lymph node. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2003. 29:216–220.21. Swenson KK, Mahipal A, Nissen MJ, Tuttle TM, Heaton K, Lally RM, et al. Axillary disease recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection for breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2005. 104:1834–1839.22. Calhoun KE, Hansen NM, Turner RR, Giuliano AE. Nonsentinel node metastases in breast cancer patients with isolated tumor cells in the sentinel node: implications for completion axillary node dissection. Am J Surg. 2005. 190:588–591.23. Greene FL. AJCC Cancer Staging Handbook: from the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 2002. 6th ed. New York: Springer.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Number of Removed Lymph Nodes for an Acceptable False Negative Rate in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer
- Sentinel Lymph Node in Breast Cancer: Review Article from a Pathologist's Point of View
- Sentinel Lymph Node Imaging in Breast Cancer
- Optimized Criteria for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Patients with Clinically Node Negative Breast Cancer
- Ex-vivo Sentinel Lymph-node Mapping in Colorectal Cancer