J Korean Fract Soc.
2010 Jan;23(1):97-103. 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.97.
The Effect of Adjacent Vertebral Body on Vertebroplasty for Compression Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, School of Medicine, Hallym University, Anyang, Korea. yckim@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 1461579
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.97
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the effect of adjacent vertebral body on local sagittal segment in performing vertebroplasty for thoracolumabr vertebral compression fracture on the terms of radiological results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
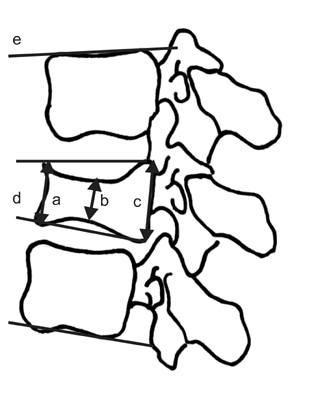
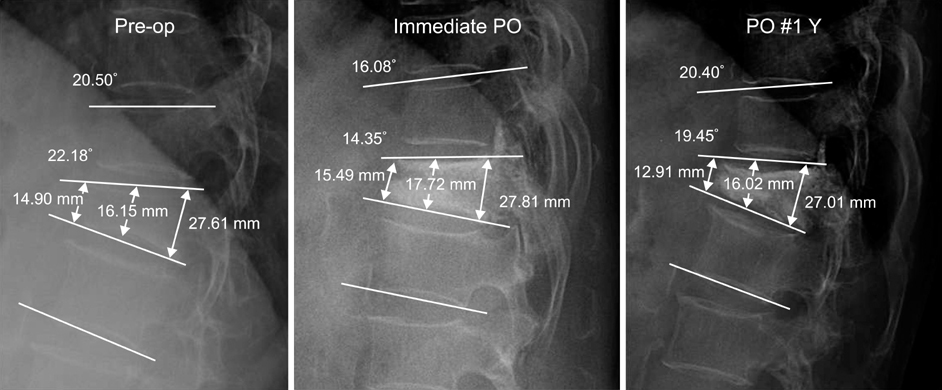
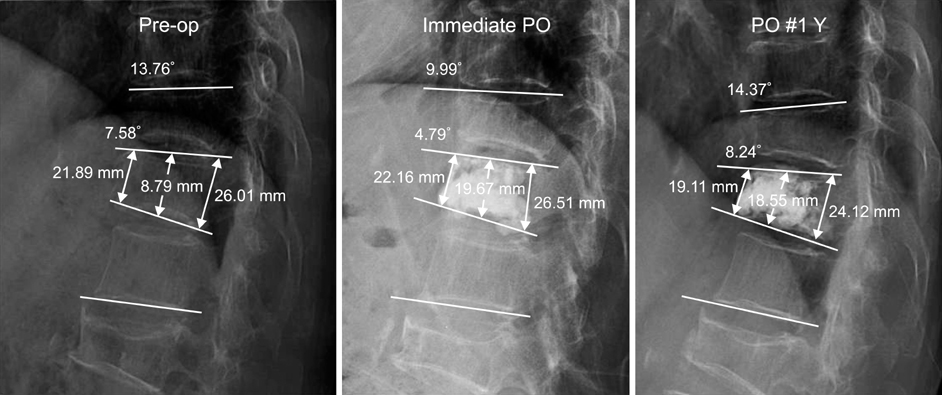
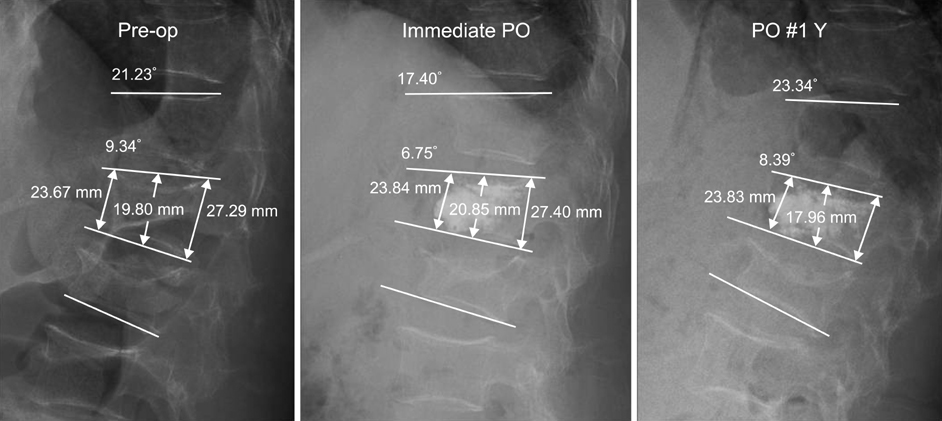
We experienced 61 cases of T12 and L1 Compression fracture between June 2003 and November 2005. We classified with 3 groups; no collapse of adjacent body, collapse of adjacent upper body, and collapse of adjacent lower body. The measuring factors were anterior, middle, posterior vertebral height, wedge angle and local kyphotic angle.
RESULTS
In group I, Increase rate of anterior, middle, posterior vertebral height and restoration rate of wedge angle, and local kyphotic angle were average of 0.41%, 0.31%, 0.16%, 1.47%, ?3.48% respectively. Group II was -3.19%, 0.11%, -3.02%, -1.23%, -4.63%. Group III was -2.28%, 4.72%, -1.01%, -2.41%, -13.12%. There are no significant differences among the groups except local kyphotic angle in Group III statistically.
CONCLUSION
The previous wedged collapse of adjacent vertebral body do not affect local sagittal segment performed vertebroplasty in the thoracolumbar compression fracture. However the previous wedged collapse of adjacent lower body affect significantly local kyphotic angle.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Survival Rate and Risk Factor Analysis in Patients Who Experience a New Fracture after Kyphoplasty
Dong-Hyok Kim, Jung-Hoon Kim
J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2018;25(3):99-107. doi: 10.4184/jkss.2018.25.3.99.
Reference
-
1. Alvarez L, Pérez-Higueras A, Quiñones D, Calvo E, Rossi RE. Vertebroplasty in the treatment of vertebral tumors: postprocedural outcome and quality of life. Eur Spine J. 2003. 12:356–360.
Article2. Baráth K, Martin JB, Fasel HJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: method indications, results. Orv Hetil. 2002. 143:2469–2477.3. Baroud G, Heini P, Nemes J, Bohner M, Ferguson S, Steffen T. Biomechanical explanation of adjacent fractures following vertebroplasty. Radiology. 2003. 229:606–607.
Article4. Baroud G, Nemes J, Heini P, Steffen T. Load shift of the intervertebral disc after a vertebroplasty: a finite-element study. Eur Spine J. 2003. 12:421–426.
Article5. Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, McCann RM. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine. 2000. 25:923–928.
Article6. Berlemann U, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP, Heini PF. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty. A biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002. 84:748–752.7. Cho YS, Cho SD, Kim BS, Park TW, Lew SU, Cho SH. Percutaneous vertebroplasty on osteoporotic compressive fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002. 37:13–18.
Article8. Cotten A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Radiology. 1996. 200:525–530.
Article9. Deramond H, Depriester C, Galibert P, Le Gars D. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate. Technique, indications, and results. Radiol Clin North Am. 1998. 36:533–546.10. Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA. Management of acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy. Am J Med. 2003. 114:257–265.
Article11. Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D. Note preliminaire sur le traitenent des angiomes vertebraux par vertebroplastie acrylique percutanee. Neurochirurgie. 1987. 33:166–168.12. Galibert P, Déramond H. Percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty as a treatment of vertebral angioma as well as painful and debilitating diseases. Chirurgie. 1990. 116:326–334.13. Gangi A, Guth S, Imbert JP, Marin H, Dietmann JL. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: indications, technique, and results. Radiographics. 2003. 23:e10.
Article14. Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA. New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:1511–1515.15. Hiwatashi A, Moritani T, Numaguchi Y, Westesson PL. Increase in vertebral body height after vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. 24:185–189.16. Kaplan FS, Scherl JD, Wisneski R, Cheatle M, Haddad JG. The cluster phenomenon in patients who have multiple vertebral compression fractures. Clin Orthop. 1993. 297:161–167.
Article17. Kim MH, Min SH, Jeon SH. Risk factors of new compression fractures in adjacent vertebra after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Korean Fract Soc. 2007. 20:260–265.
Article18. Kim WJ, Yeom JS, Kang JW, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: short-term results of 38cases. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002. 37:471–477.
Article19. Kim YW. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009. 22:218–223.
Article20. Na HY, Cho HW, Kim SK, Lee SY. Comparison of outcome between percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for osteoporotic painful vertebral compression fracture. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2003. 10:127–136.
Article21. Polikeit A, Nolte LP, Ferguson SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit: finite-element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. 28:991–996.
Article22. Teng MM, Wei CJ, Wei LC. Kyphosis correction and height restoration effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. 24:1893–1900.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
- Comparisons of Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
- Complication of the Augmented Vertebral Body after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients with Osteoporotic Compression Fracture: Hammer Effect: Preliminary Report
- Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
- Long Term Results of Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Compression Fracture