J Korean Fract Soc.
2010 Apr;23(2):227-231. 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.227.
Bursting Fracture of the Proximal Femur during Insertion of Unreamed Femoral Nail for Femur Shaft Fracture: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea. jjkim2@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Samchunpo Seoul Hospital, Samchunpo, Korea.
- KMID: 1461552
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.227
Abstract
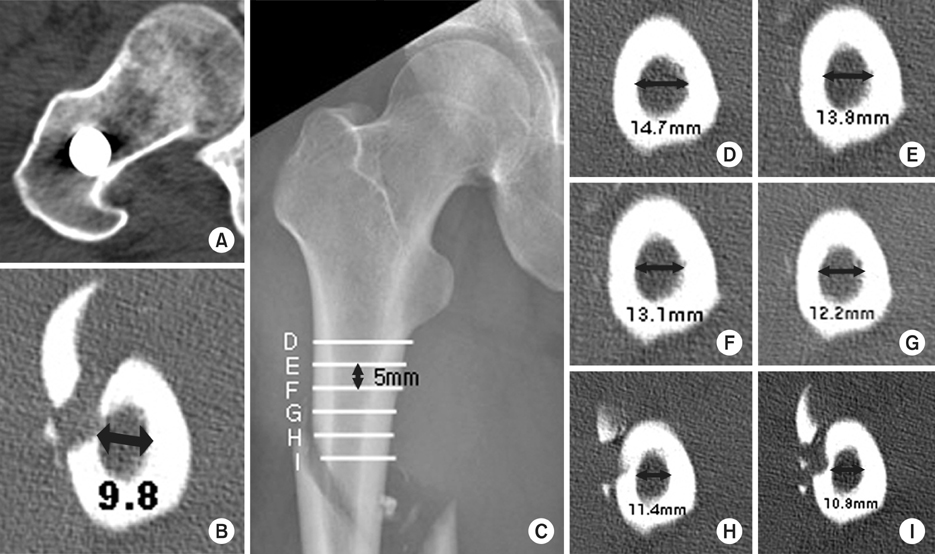
- When treating femur shaft fracture in adults, undreamed nail can be an option in order to avoid systemic complications. To appropriately insert unreamed intramedullary nail, an accurate entry point and sufficient reaming of the entry portal is essential. The intramedullary canal of the proximal femur must be reamed over than the diameter of the proximal end of the nail. If the proximal reaming is not sufficient, complications such as bursting fracture of proximal femur can occur. We present two cases of bursting fracture of proximal femur following insertion of undreamed intramedullary nail as well as a literature review.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Results of Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture - Trochanteric Entry Portal (Sirus Nail) versus Piriformis Entry Portal (M/DN Nail) -
Sang Ho Ha, Woong-Hee Kim, Gwang Chul Lee
J Korean Fract Soc. 2014;27(1):50-57. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.50.
Reference
-
1. Abbas D, Faisal M, Butt MS. Unreamed femoral nailing. Injury. 2000. 31:711–717.
Article2. Alho A, Strømsøe K, Ekeland A. Locked intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures. J Trauma. 1991. 31:49–59.
Article3. Brumback RJ, Virkus WW. Intramedullary nailing of the femur: reamed versus nonreamed. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000. 8:83–90.
Article4. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Reamed versus unreamed intramedullary nailing of the femur: comparison of the rate of ARDS in multiple injured patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2006. 20:384–387.5. Forster MC, Aster AS, Ahmed S. Reaming during anterograde femoral nailing: is it worth it? Injury. 2005. 36:445–449.
Article6. Johnson KD, Tencer AF, Sherman MC. Biomechanical factors affecting fracture stability and femoral bursting in closed intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures, with illustrative case presentations. J Orthop Trauma. 1987. 1:1–11.
Article7. Papadakis SA, Zalavras C, Mirzayan R, Shepherd L. Undetected iatrogenic lesions of the anterior femoral shaft during intramedullary nailing: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2008. 3:30.
Article8. Shepherd LE, Shean CJ, Gelalis ID, Lee J, Carter VS. Prospective randomized study of reamed versus unreamed femoral intramedullary nailing: an assessment of procedures. J Orthop Trauma. 2001. 15:28–32.
Article9. Tencer AF, Sherman MC, Johnson KD. Biomechanical factors affecting fracture stability and femoral bursting in closed intramedullary rod fixation of femur fractures. J Biomech Eng. 1985. 107:104–111.
Article10. Yoon HK, Jeon KP, Kang KH, Kim JI, Kim DS, Koh YK. A Clinical Comparative Study of Reamed and Unreamed Nail of Femoral Shaft Fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1998. 11:495–500.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intramedullary pressure changes in reamed and unreamed nailing systems: an experimental study in cadaveric femoral bones
- The Distraction Effect of the Fracture Site on Insertion of the Distal Screw in Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing
- A Comparative Study of Reamed and Unreamed Nail for Femoral Shaft Fracture's Treatment
- Femur Shaft Fracture with Ipsilateral Neck Fracture: Report of Two Cases
- Excessive Sliding of the Helical Blade and the Femoral Neck Fracture after Insertion of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation for Type A2 Intertrochanteric Fractures - A Case Report -