J Korean Fract Soc.
2010 Apr;23(2):194-200. 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.194.
Double Parallel Plates Fixation for Distal Humerus Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hsgong@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1461547
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.194
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to review the outcome of fixation of distal humerus fractures using recently-introduced double parallel plate system in sagittal plane.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
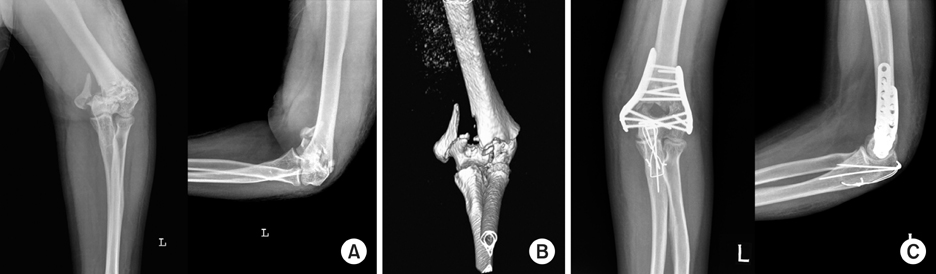
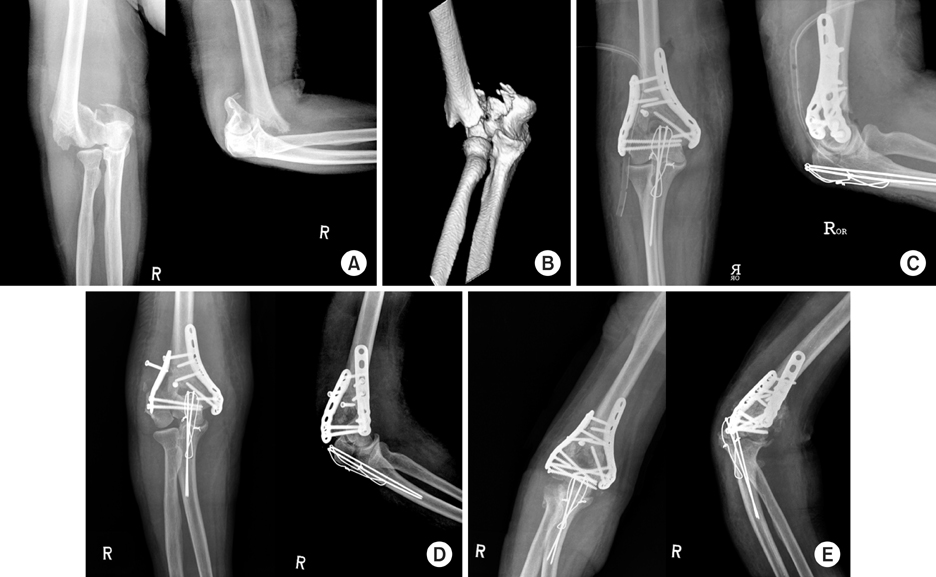
From May 2004 to June 2008, seventeen patients with distal humerus fractures underwent primary open reduction and internal fixation with double parallel plates. According to the AO classification, there were 2 A3, 2 C1, 7 C2, and 6 C3 type fractures. Outcome assessment was performed by using the Mayo Elbow Performance index (MEPI).
RESULTS
At a mean follow up of 18 (range, 12 to 32) months, 4 patients were rated as excellent, 8 as good, and 5 as fair in terms of MEPI. The average arc of elbow flexion after primary operation was 116 (range, 90~140) degrees with a mean flexion contracture of 13 (range, 0 to 30) degrees. One patient required reoperation due to fixation failure and six patients underwent capsulolysis and three patients underwent ulnar nerve neurolysis. The time to begin elbow motion exercise had negative correlation with total elbow range of motion and multiple trauma patients had significantly lower MEPI functional score compared to those without combined injury.
CONCLUSION
Double parallel plating allowed adequate fixation for distal humerus fractures regardless of patient age and fracture pattern. Partial ankylosis and unlar nerve compression symptoms were the main causes of reoperation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ackerman G, Jupiter JB. Non-union of fractures of the distal end of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988. 70:75–83.
Article2. Ahn HS, Cho YH, Byun YS, Kwon DY, Nam SO, Kim DY. Elbow function and complications after internal fixation for fractures of the distal humerus. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006. 19:56–61.
Article3. Aitken GK, Rorabeck CH. Distal humeral fractures in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. (207):191–197.
Article4. Ali A, Douglas H, Stanley D. Revision surgery for non-union after early failure of fixation of fractures of the distal humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:1107–1110.
Article5. Arnander MW, Reeves A, MacLeod IA, Pinto TM, Khaleel A. A biomechanical comparison of plate configuration in distal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 22:332–336.
Article6. Cho JH, Kim JY, Lee SL, Han KJ. Surgical treatment of intercondylar fractures of the humerus with posterior plates. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2008. 13:212–216.7. Holdsworth BJ, Mossad MM. Fractures of the adult distal humerus. Elbow function after internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:362–365.
Article8. Jacobson SR, Glisson RR, Urbaniak JR. Comparison of distal humerus fracture fixation: a biomechanical study. J South Orthop Assoc. 1997. 6:241–249.9. John H, Rosso R, Neff U, Bodoky A, Regazzoni P, Harder F. Operative treatment of distal humeral fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994. 76:793–796.
Article10. Jupiter JB. Complex fractures of the distal part of the humerus and associated complications. Instr Course Lect. 1995. 44:187–198.
Article11. Jupiter JB. The management of nonunion and malunion of the distal humerus--a 30-year experience. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 22:742–750.
Article12. Jupiter JB, Mehne DK. Fractures of the distal humerus. Orthopedics. 1992. 15:825–833.
Article13. Kundel K, Braun W, Wieberneit J, Rüter A. Intraarticular distal humerus fractures. Factors affecting functional outcome. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. (332):200–208.14. Moon ES, Rowe SM, Seon JK, Kim MS, Cho SB. Treatment in distal humerus fracture with anatomical Y plate. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004. 17:76–82.
Article15. O'Driscoll SW. Optimizing stability in distal humeral fracture fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005. 14:186S–194S.16. Oh JR, Yoon YS, Lee DK, Her MS. Comminuted intercondylar fracture of the distal humerus in adults. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006. 19:208–214.
Article17. Pajarinen J, Björkenheim JM. Operative treatment of type C intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus: results after a mean follow-up of 2 years in a series of 18 patients. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002. 11:48–52.
Article18. Ring D, Jupiter JB. Complex fractures of the distal humerus and their complications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999. 8:85–97.
Article19. Ring D, Jupiter JB. Fractures of the distal humerus. Orthop Clin North Am. 2000. 31:103–113.
Article20. Ring D, Jupiter JB, Gulotta L. Articular fractures of the distal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85-A:232–238.
Article21. Rueger JM, Rucker A, Briem D. Distal fracture of the humerus. Chirurg. 2007. 78:959–971.22. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Torchia ME, O'Driscoll SW. Complex distal humeral fractures: internal fixation with a principle-based parallel-plate technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. 89:961–969.23. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Torchia ME, O'Driscoll SW. Complex distal humeral fractures: internal fixation with a principle-based parallel-plate technique. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. 90:Suppl 2 Pt 1. 31–46.
Article24. Schemitsch EH, Tencer AF, Henley MB. Biomechanical evaluation of methods of internal fixation of the distal humerus. J Orthop Trauma. 1994. 8:468–475.
Article25. Schwartz A, Oka R, Odell T, Mahar A. Biomechanical comparison of two different periarticular plating systems for stabilization of complex distal humerus fractures. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006. 21:950–955.
Article26. Self J, Viegas SF, Buford WL Jr, Patterson RM. A comparison of double-plate fixation methods for complex distal humerus fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1995. 4:10–16.
Article27. Shin R, Ring D. The ulnar nerve in elbow trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. 89:1108–1116.
Article28. Song KW, Lee SY, Shin SI, et al. Treatment of intercondylar fracture of distal humerus in adult. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006. 19:62–66.
Article29. Soon JL, Chan BK, Low CO. Surgical fixation of intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus in adults. Injury. 2004. 35:44–54.
Article30. Stoffel K, Cunneen S, Morgan R, Nicholls R, Stachowiak G. Comparative stability of perpendicular versus parallel double-locking plating systems in osteoporotic comminuted distal humerus fractures. J Orthop Res. 2008. 26:778–784.
Article31. Viola RW, Hanel DP. Early "simple" release of post-traumatic elbow contracture associated with heterotopic ossification. J Hand Surg Am. 1999. 24:370–380.
Article32. Wang KC, Shih HN, Hsu KY, Shih CH. Intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus: routine anterior subcutaneous transposition of the ulnar nerve in a posterior operative approach. J Trauma. 1994. 36:770–773.33. Wong AS, Baratz ME. Elbow fractures: distal humerus. J Hand Surg Am. 2009. 34:176–190.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Orthogonal versus Parallel Plating for Distal Humeral Fractures
- Surgical Treatment Strategy for Distal Humerus Intra-articular Fractures
- Treatment for Comminuted fractures of Distal End of Humerus by Newly Developed Anatomical Plate: Three case report
- Posterior-Posterior Dual Plates Fixation for the Distal Humerus Fractures
- External Fixation for Distal Radius Fractures