J Korean Hip Soc.
2010 Jun;22(2):116-121. 10.5371/jkhs.2010.22.2.116.
Treatment for the Acetabular Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea. weonkim@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1461132
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/jkhs.2010.22.2.116
Abstract
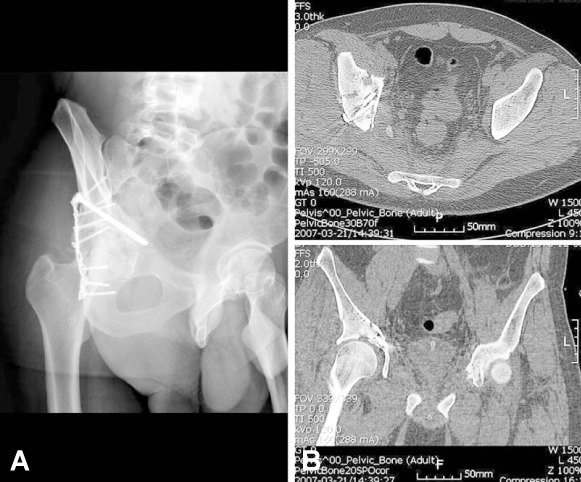
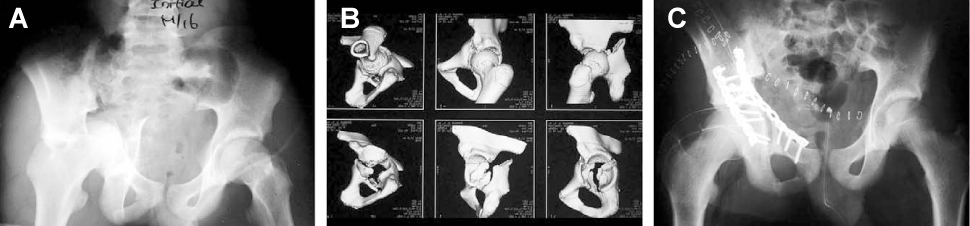
- The acetabulum is the socket of the hip joint and incongruence of the joint surface caused by fracture causes hip pain and posttraumatic arthritis. The usual choice of treatment for displaced acetabular fracture is operative treatment, which entails a challenging, stiff learning curve. The principle of treatment is restoring the stable and congruent hip joint for early mobilization to prevent local and systemic complications.
Keyword
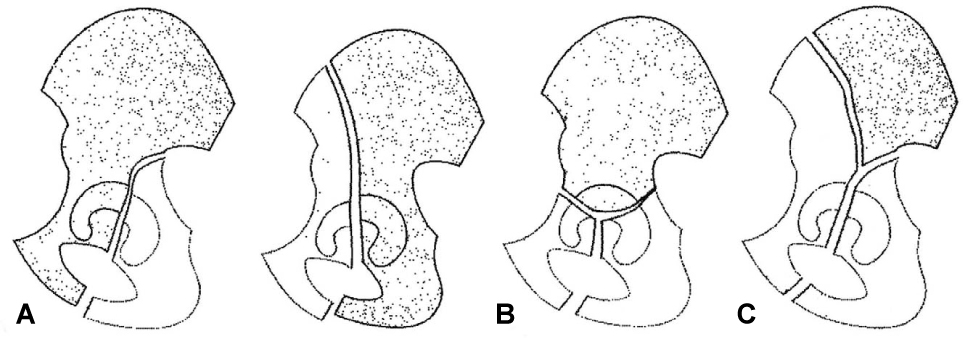
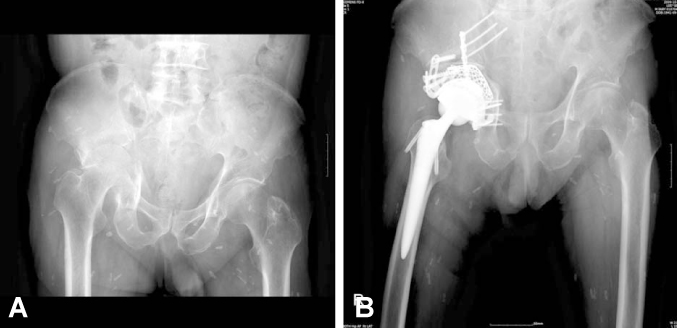
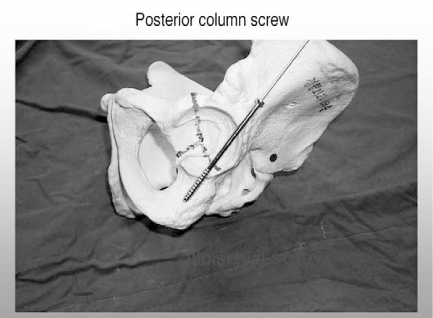
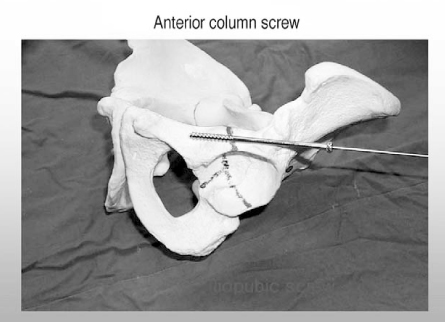
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Analysis of Predictors of Results after Surgical Treatment of Acetabular Fractures
Jong Ki Shin, Sung Jin An, Tae Sik Go, Jung Sub Lee
Hip Pelvis. 2015;27(2):104-109. doi: 10.5371/hp.2015.27.2.104.Surgical Results of the Cephalomedullary Nail for the Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture: Comparison between Non-experienced Surgeons and Experienced Surgeon
Jae-Seong Seo, Hak-Jin Min, Dong Min Kim, Seung-Min Oh, Sang-Min Kim
Hip Pelvis. 2016;28(4):225-231. doi: 10.5371/hp.2016.28.4.225.
Reference
-
1. Letournel E, Judet R. Fracture of the acetabulum. 1993. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.2. Rüedi TP, Murphy WM. AO principles of fracture management. 2000. New York: Thieme.3. Tile M, Helfet D, Kellam J. Fracture of the pelvis and acetabulum. 2003. 3rd ed. Philadelpia: Lippincott Willams & Wilkins.4. Smith WR, Ziran BH, Morgan SJ. Factures of the pelvis and acetabulm. 2007. New York: Informa healthcare.5. Young JW, Burgess AR, Brumback RJ, Poka A. Pelvic fractures:value of plain radiography in early assessement and management. Radiogoly. 1986. 160:445–451.
Article6. Mears DC, Velyvis JH. Acute total hip arthroplasty for selected displaced acetabular fractures: two to twelve-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84:1–9.
Article7. Mears DC, Velyvis JH. Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture. Instr Course Lect. 2001. 50:335–354.
Article8. Boraiah S, Ragsdale M, Achor T, Zelicof S, Asprinio DE. Open reduction internal fixation and primary total hip arthroplasty of selected acetabular fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2009. 23:243–248.
Article9. Starr AJ, Jones AL, Reinert CM, Borer DS. Preliminary results and complications following limited open reduction and percutaneous screw fixation of displaced fractures of the acetabulum. Injury. 2001. 32:Suppl. 45–50.
Article10. Kim WY, Sung JH, Han CH, Cheon JS, Hwang HJ. Combined anterior and posterior approach in operating on complex acetabular fractures. J Korean Ortho Assoc. 2001. 36:287–292.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arthroscopic Management of Intraarticular Screw Perforation after Surgical Treatment of an Acetabular Posterior Wall Fracture: A Case Report
- Combined Femoral and Sciatic Nerve Palsy Associated with Acetabular Fracture and Dislocation: A Case Report
- Significance of Anatomic Reduction in Acetabular Fracture
- A Case of Periprosthetic Fracture of Acetabulum Associated with Osteolysis
- Arthroscopic Reduction and Transportal Screw Fixation of Acetabular Posterior Wall Fracture: Technical Note